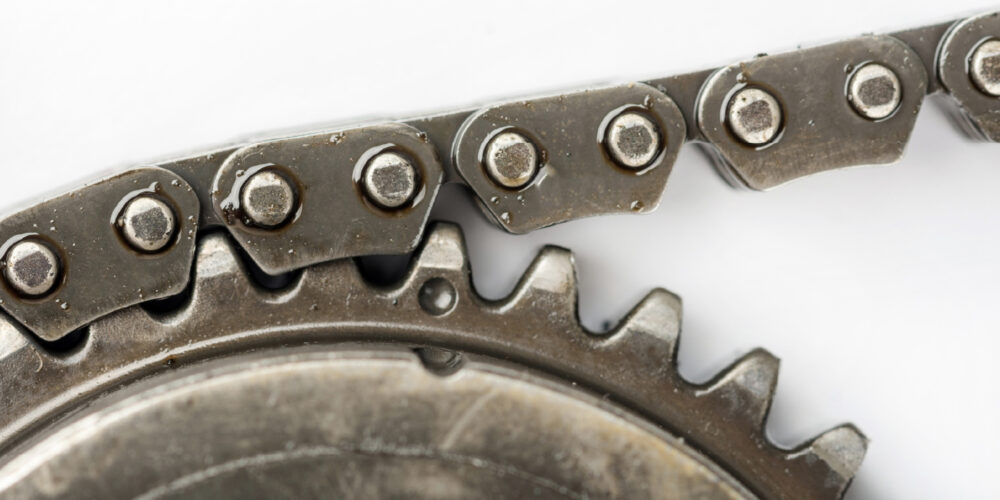
Timing chain stretch is not the stretching of the timing chain’s links, it is an elongation of the timing chain caused by wear to the chain’s components. The most common cause of timing chain stretch is lack of regular oil changes.
Worn-out oil can no longer lubricate the chain and will cause the rollers and links to wear against each other. As the chain runs around the camshaft and crankshaft gears, the movement between the rollers and links causes wear and elongation.
As the timing chain wears, it can change the timing of the camshaft and crankshaft. The change in timing is sensed by the camshaft and crankshaft position sensors. This can cause codes that indicate the correlation or synchronization problem with the engine position sensors.
If the driver ignores the check engine light, eventually the timing chain will elongate to the point that the engine may have a significant loss of power due to a lack of compression. In some cases, a worn timing chain may cause the engine to jump time a few teeth. If this happens on a multi-cam engine, it may appear to be a dead miss on multiple cylinders. The bad oil can also damage the tensioner which makes the possibility of the engine skipping time or a catastrophic failure even greater.
Some of the most notorious engines for timing chain stretch include the GM High-Feature V6, Ford Modular V8 and Nissan VQ V6. All of these OEMs have stated that the lack of oil changes and use of the wrong oil causes timing chain stretch conditions.
If you are replacing a timing chain or chains, it is also critical to inspect and, in some cases, replace components that tension the chain and variable valve timing actuators. The actuators are powered by the same oil that damaged the timing chain. Inside a variable valve timing actuator are finely machined surfaces and seals that can are easily damaged by worn out or the wrong type of oil. In some cases, it is cheap insurance to replace the actuators while you are replacing the timing chain to ensure that the customer gets the full value of the labor time.
If you are trying to diagnose timing chain stretch, it might be impossible to access the timing mark without major disassembly. The easiest way to check timing is to use a scope to capture the crankshaft and camshaft position sensor waveforms.
The Oil
One of the criteria for oil certifications like API and ILSAC is timing chain stretch. During tests, the laboratories will run several test engines for many hours. When the tests are complete, they will tear down the engine and measure components like the timing chain for wear. They will also inspect the engine carbon deposits and varnish.
Every new oil specification means new engines for the tests. For GF-6 oil, ILSAC choose three engines for the tests. Among the engines, they choose the GM 3.6L LY7, otherwise known as the High-Feature V6. This V6 has direct fuel injection, three timing chains and four variable valve timing actuators. The test sequence can take 197 hours to run. To pass the test, the timing chain can have only minimal wear.
The other reason they choose the High-Feature V6 is direct fuel injection. The amount of soot generated by the combustion process is greater than with port-injected engines. This is due to how fuel droplets burn inside the combustion chamber. These soot particles can find their way into the engine oil. While one soot particle will not cause wear, clumps of soot particles will cause abrasive wear. Additives in oil can keep the soot particles in suspension, so they can’t clump together and damage the timing chain.