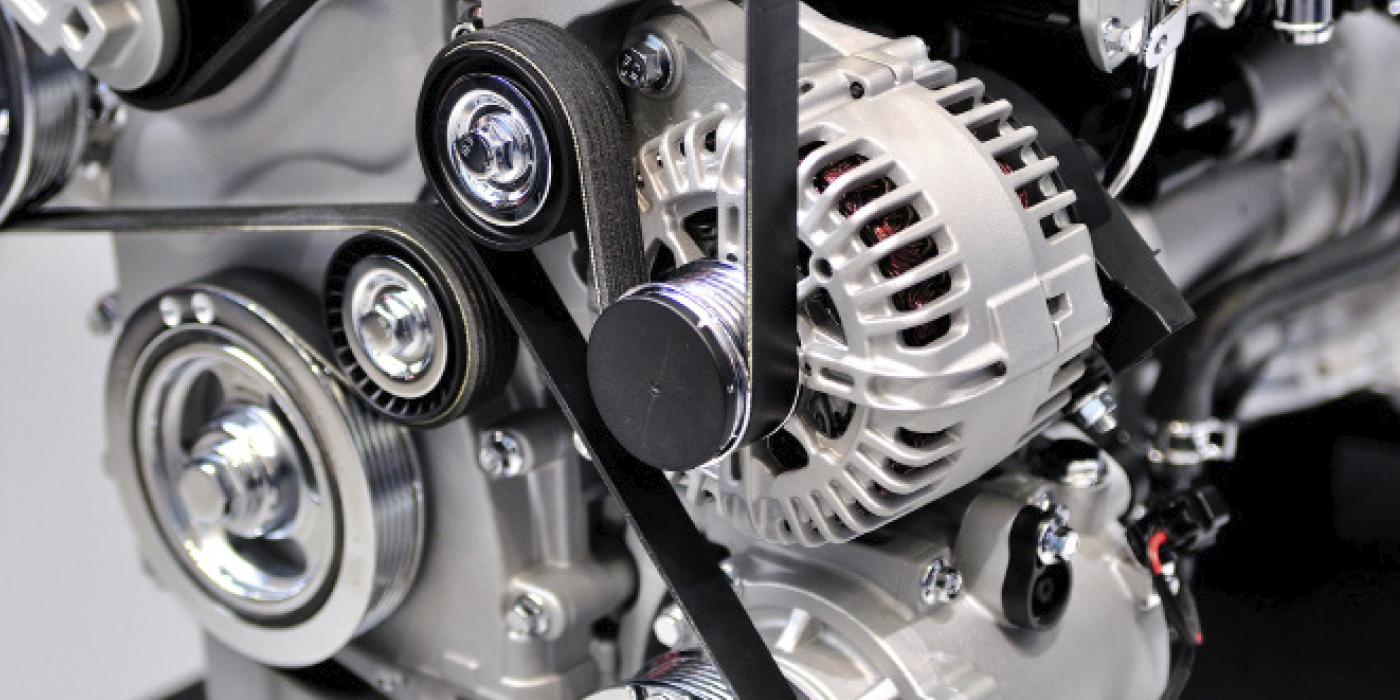
Drive Belt Alignment Alignment is key to the health of an engine belt. The belt drive system is designed to create friction between the grooves on the belt and pulley to transfer power from the crankshaft to the alternator, water pump or power steering pump. If the grooves on the belt do not align with the pulleys, the friction won’t be evenly applied and can result in wear and noise.
A misalignment of the plane of the belt can occur when a pulley is not parallel to the other pulleys on the belt drive system. This can cause wear to the shoulders of the belt and add stress to the belt’s structure. This type of misalignment often occurs when components on the belt drive system are replaced. If the power steering pump is replaced and the pulley needs to be transferred, the pulley must be installed at the right depth. If it is not aligned, the belt might make a squeaking noise and eventually incur abnormal wear.
For alternators, the case dimensions or pulley might not match the original alternator, resulting in an alignment problem. Other rare causes for misalignment could be the result of a separation of the crankshaft dampener or if the crankshaft develops endplay. If the crankshaft has excessive endplay, it could indicate there are other problems with the engine. The other type of misalignment stems from the angular alignment of the pulleys. This causes the pulley to rotate on an axis that is not perpendicular to its rotational plane.
The most common cause of this alignment is worn bearings, which could either be in idler pulleys or components driven by the belt. The worn bearings can cause the pulley to be cocked to one side. The second most common cause is a worn tensioner. The wear occurs between the arm and the shaft, with the most common sign being an uneven gap between the base and arm.
Inspection
The first point of inspection is the belt. With your ear, listen for the most common noise: a chirping noise. The first visual clue would be wear or damage to the shoulders of the belt. Second, look at the tensioner and the alignment of the tensioner’s arm. Third, remove the belt to inspect the entire length and to rotate the pulleys and idlers to detect roughness and play. With the belt off, you can check the alignment with specialty tools. The most basic tool is a machinist’s straight edge. There are other specialty belt alignment tools that use rods or even lasers to check pulley alignment. Specs from the OEMs on belt alignment are not typically published – the issue being that varying degrees of misalignment can affect the given length of the belt run.