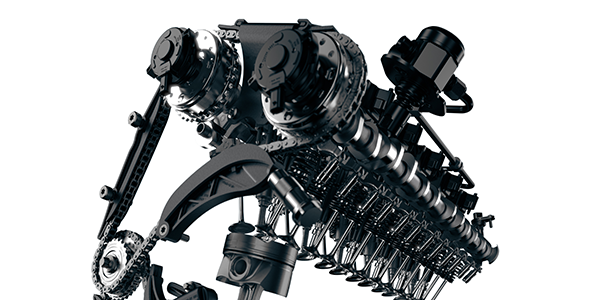
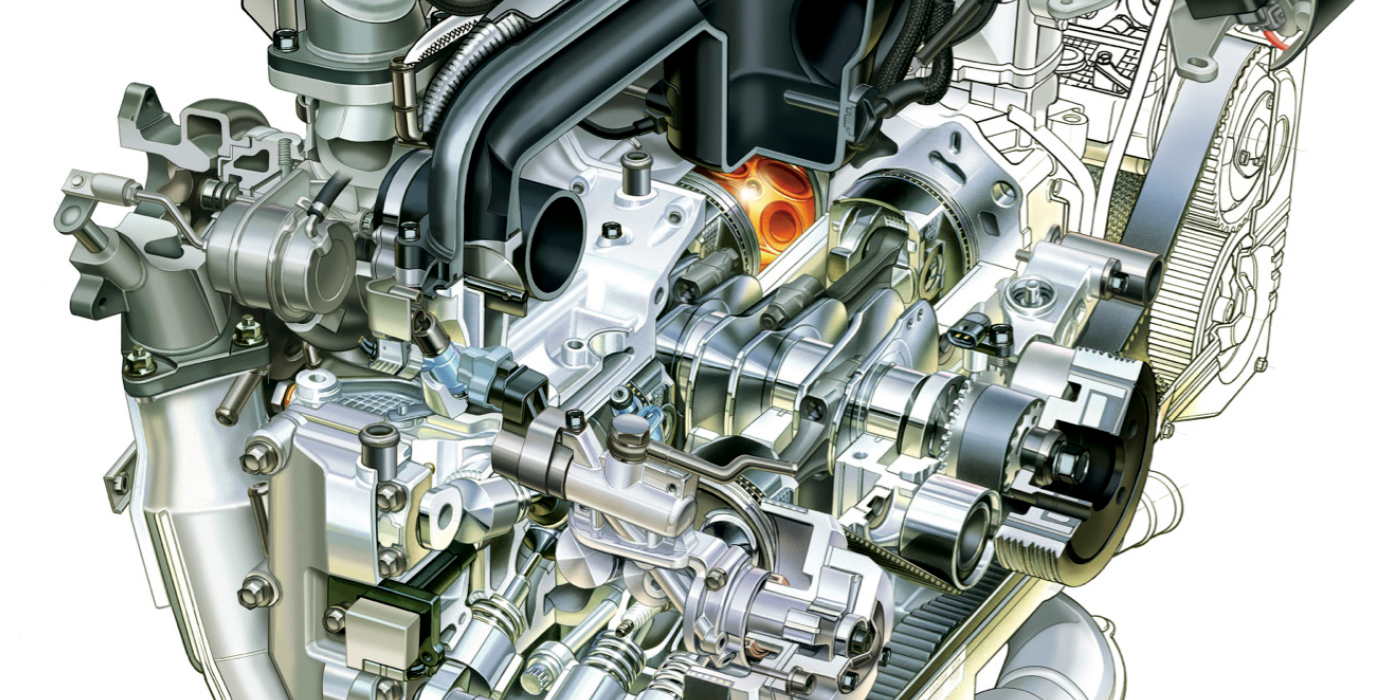
Here are the top five things you should be checking to resolve a timing chain problem before it breaks.
1. Check the Oil Level First
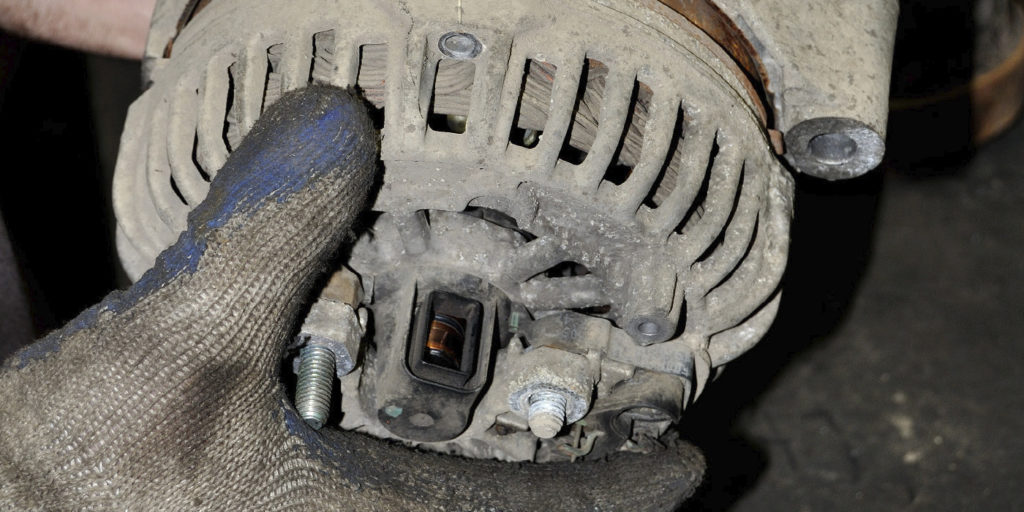
 If the oil pump is ingesting air due to a low oil level, the timing chain adjuster can’t properly tension the timing chain. If possible, remove the oil filler cap to inspect for engine oil sludge under the camshaft cover. If the engine is heavily sludged, it’s going to be nearly impossible to clean. In most cases, a complete engine replacement is the recommended repair.
If the oil pump is ingesting air due to a low oil level, the timing chain adjuster can’t properly tension the timing chain. If possible, remove the oil filler cap to inspect for engine oil sludge under the camshaft cover. If the engine is heavily sludged, it’s going to be nearly impossible to clean. In most cases, a complete engine replacement is the recommended repair.
2. Listen to the Noise

Timing chains can accumulate enough wear in the chain’s links and guides to allow the chain to rattle against the timing case. A particularly “tinny” sound might indicate a broken timing chain guide.
3. Connect Your Scan Tool

Crankshaft/camshaft correlation errors on DOHC engines can be difficult to diagnose if only one of the four camshafts on a V6 engine is out of time. In most cases, a P00XX diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will be stored in the engine control module (ECM) diagnostic memory indicating which camshaft is out of time. Hyundai also includes P00XX and P03XX codes indicating if the solenoid control systems and camshaft position sensors are working.
4. Manual or Automatic?

Manual transmission vehicles are particularly susceptible to jumping a tooth on a timing chain because many drivers develop a habit of depressing the clutch, turning the engine off and using first gear as a parking brake. In some cases, the vehicle is rolling backward when the clutch is released, which, in turn, causes the crankshaft to rotate backward and causes one or more timing gears to jump time.
5. Go to the Internet!
Use online vehicle reliability information to predict timing chain failures for the types of vehicles you service. Timing chain and guide failures are relatively common on some vehicles, even at the 100,000-mile mark. In other cases, the timing chain system might be trouble-free if engine oil specifications and change intervals are followed. Whichever way your market might go, pay attention to how the workflow through your service bays is changing because the only constant in today’s automotive service market is change itself.