 This bulletin provides information relating to an engine hesitation or the illumination of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) for P0123 (Throttle Position Sensor/ Switch “A” Circuit High Input).
This bulletin provides information relating to an engine hesitation or the illumination of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) for P0123 (Throttle Position Sensor/ Switch “A” Circuit High Input).
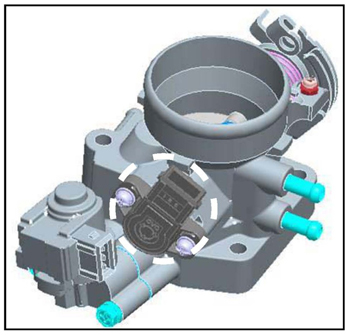
See Figure 1.
Some 2001-’06 Optima (MS) models produced between Oct. 7, 2000 and Aug. 31, 2005, equipped with the 2.5L or 2.7L (V6) Delta engine and some Sportage (KM) models produced between Oct. 28, 2004 and May 18, 2007, equipped with the 2.7L (V6) Delta engine are applicable for this bulletin.

Improper throttle position sensor (TPS) values may cause the engine to hesitate under loads or cause the illumination of the MIL. To correct this condition, the TPS has been improved.
Part Number
Previous New
35170 37100 35170 37100FFF
Repair Procedure
1. Turn the ignition key to the Off position. Open the hood and remove the engine cover.

Disconnect the VIS (Variable Induction System) connector and the injector connector if equipped.
See Figure 2.
2. Disconnect the idle speed control actuator (ISCA) connector and remove the two retaining bolts. Remove the ISCA and gasket.
See Figure 3.

3. Disconnect the throttle position sensor (TPS) connector and remove the two mounting screws.
See Figure 4.
4. Install the new TPS sensor onto the throttle body and torque the two screws (1.5-2.5 Nm/13.2-21.6 in.-lbs.) reconnect the TPS connector.

See Figure 5.
5. Install a new ISCA gasket and re-install the ISCA actuator. Torque the ISCA bolts (6-8 Nm/52.8-69.6 in.-lbs.) and reconnect the ISCA connector. Reconnect the VIS connector and the injector connector it equipped.
See Figure 6.

6. Reinstall the engine cover.
Courtesy of ALLDATA.













