Affected Vehicles: 2007-’10 Nissan Sentra
If you confirm the fuel gauge is erratic, inaccurate or inoperative and/or the MIL is on with DTC P0461, P0462 or P0463 stored in self-diagnosis, replace the fuel lever sensor unit (P/N 25060-ZJ60A).
Note: Do not replace the entire fuel pump module assembly for this incident, if it should occur.
Service Procedure:
Fuel Lever Sensor Removal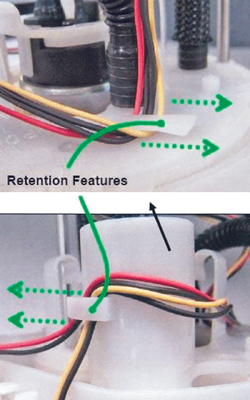
1. Remove the fuel pump module assembly.
Note: Perform repairs in a clean work environment.
2. Remove the three wire terminals with red, white and double-wire black wires from under the top of the module. 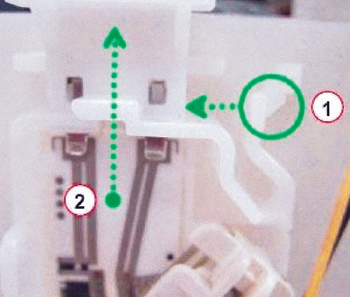
Note: The white wire may appear yellowish in color.
– Press the tab in and then gently pull the wire off its terminal.
3. Remove all wires from under both retention features on the module. See Fig. 1.
4. Remove the fuel tank temperature sensor from its retention feature.
5. Remove the fuel level sensor from the module. See Fig. 2.
– While pushing the tab inward (1), push the level sensor up (2), and the pull the level sensor away from the module.
Fuel Level Sensor Installation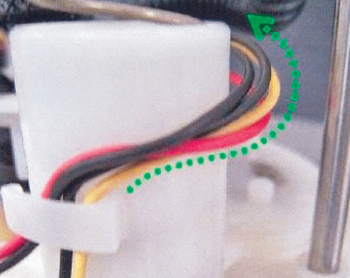
1. Install the new level sensor onto the module.
– Perform Step 5 in reverse, making sure its tab locks into place.
2. Install the temp sensor into its retention feature.
3. Install the four wires into the first retention feature. 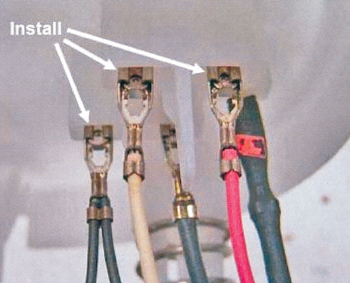
4. Route the same wiring as shown in Fig. 3.
5. Install the wiring into the second retention feature.
6. Install the wires to the correct terminals as shown in Fig. 4.
– Route the wiring on the outside of the fuel line.
– Make sure the tabs are securely locked.
7. Re-install the fuel pump module assembly with new packing (O-ring seal).
Courtesy of Mitchell 1.













