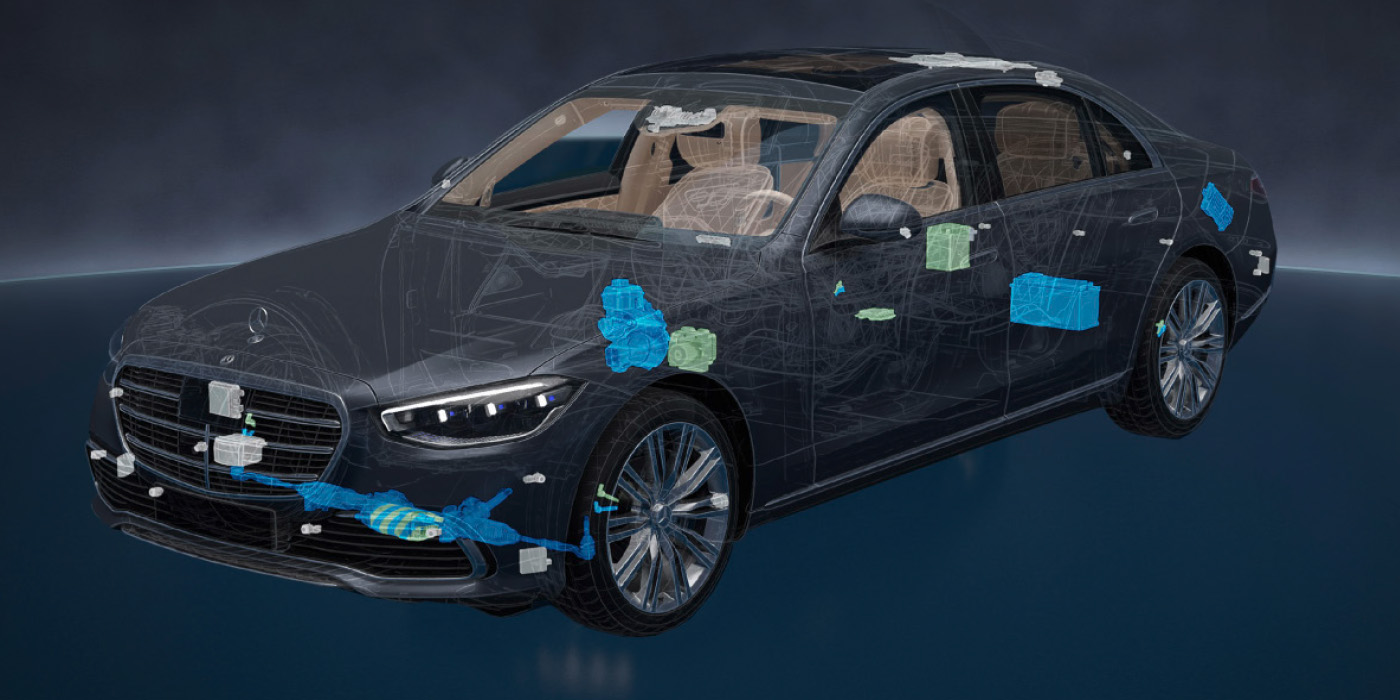
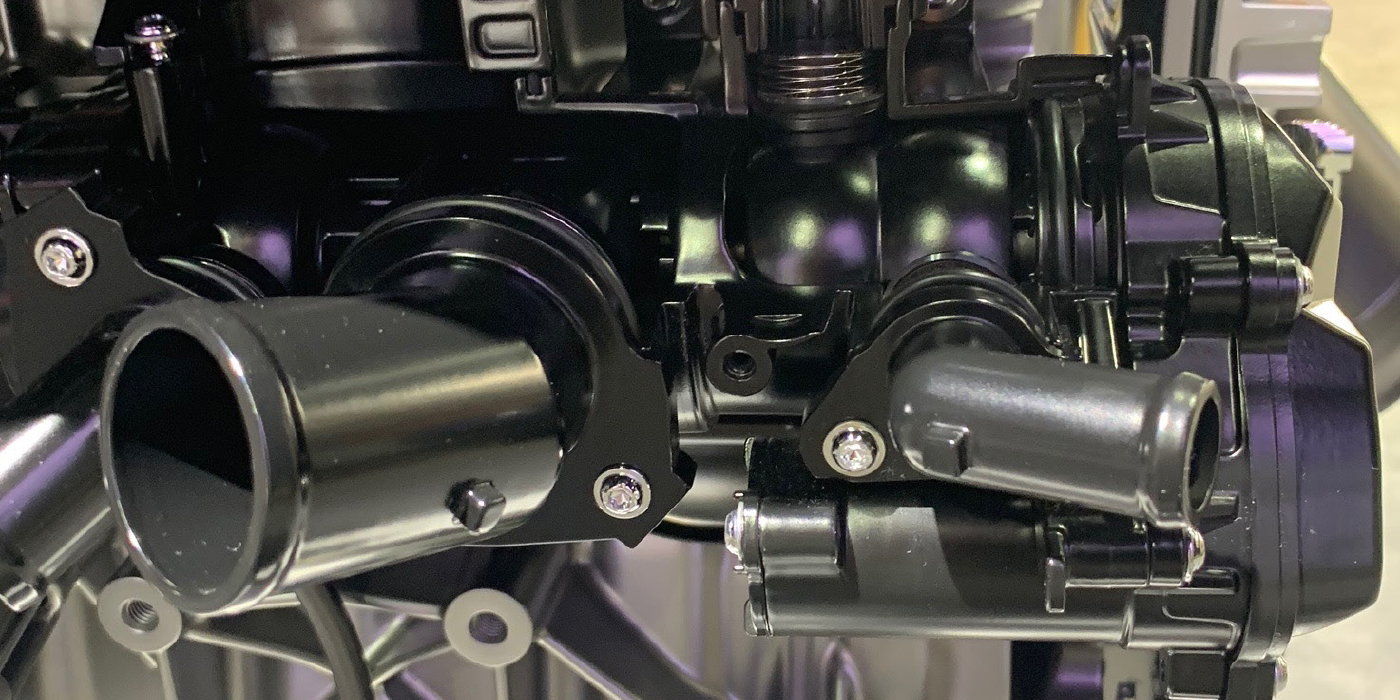
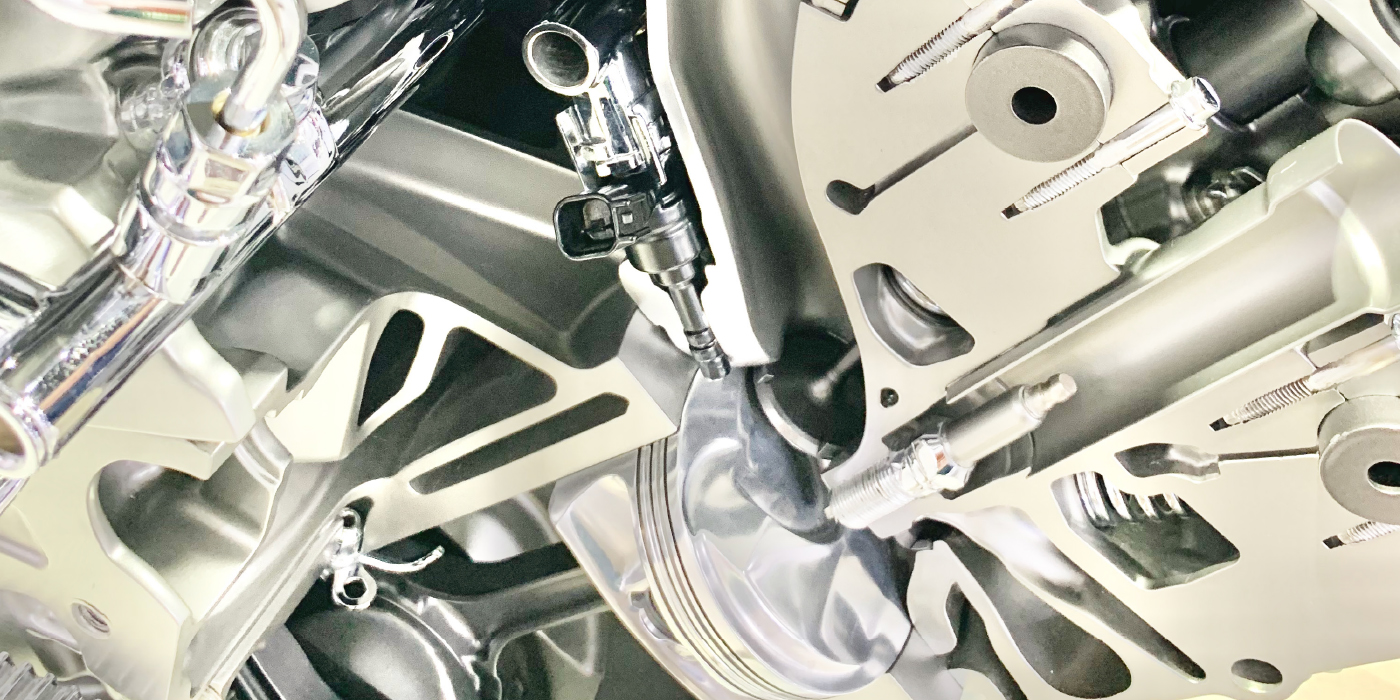
The electric fuel injector has been around for more than 50 years. The principles of operation are simple. An electromagnetic coil moves a pintle in a chamber that has pressurized fuel on one side and a nozzle on the other.
The coil is typically energized by a driver pulling the circuit to ground. As the coil is saturated by energy, the pintle moves upwards against a spring. This allows fuel to be injected into the engine.
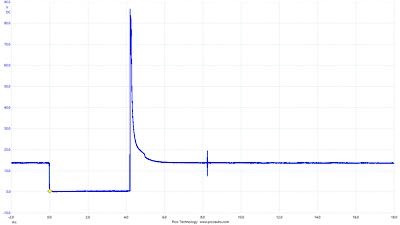
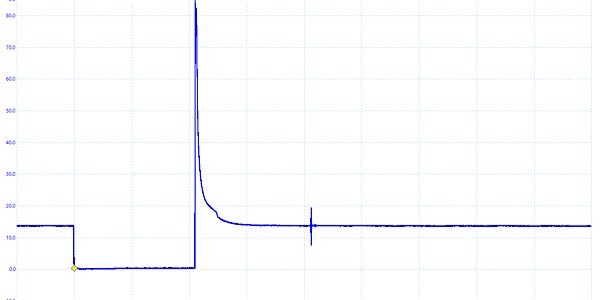
Voltage
Most injectors use 12 volts to energize the coil, and the driver energizes the circuit by pulling it to ground. When the injector is energized, the voltage drops to almost zero. If it does not, it could mean an open or weak connection in the wiring harness or open coils inside the injector.
When the voltage is turned off, the needle starts to close. When it closes, it generates a voltage spike known as the inductive kick. This is a generated magnetic field collapsing in the coils. This spike can range from 50 to 100 volts. Some circuits use a diode to cap the voltages seen at the driver to prevent damage. These diodes will dump the voltage to ground if they reach a specific range. This may cause the peak to be cut off on the waveform.
On the backside of the inductive kick, you may see a small positive hump or bump. This is the pintle hitting the seat of the injector and closing. This is a very powerful diagnostic insight.
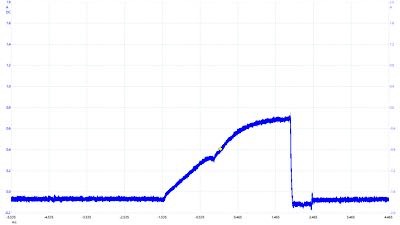
Current
The current waveform of a fuel injector is a ramp that shows the coil becoming saturated with current. The current ramp starts to go up as soon as the voltage is applied by the driver. The ramp can be split into two parts.
The first part is where the injector is closed while the coil has yet to build up enough electromotive force needed to counteract the spring on the back of the pintle.
When there is enough current in the coil, the needle moves. This event can be seen as a small rise in the slope. Where it appears in the slope is debatable. Many variables like injector specifications, fuel pressure and other factors can change the position of the event on the waveform. However, some scopes might not be fast enough to catch it.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a saturated switch fuel injection circuit with a scope can help you to confirm the health of the drivers and injectors. You can compare the waveforms to other injectors on the vehicle or to a known-good waveform found online or in the service information. On their own, the current and voltage waveforms can confirm that the internals of the injector are moving. This can be very helpful when trying to track down a misfire problem due to an open, leaking or stuck injector.