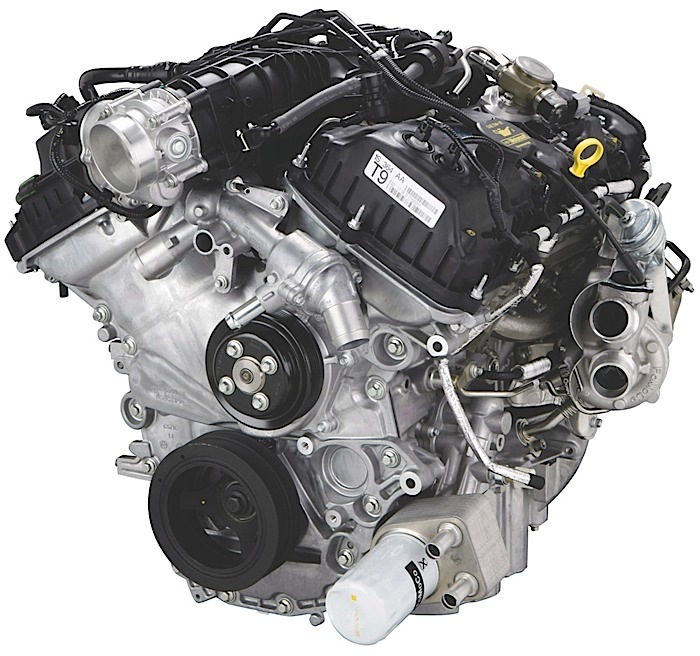
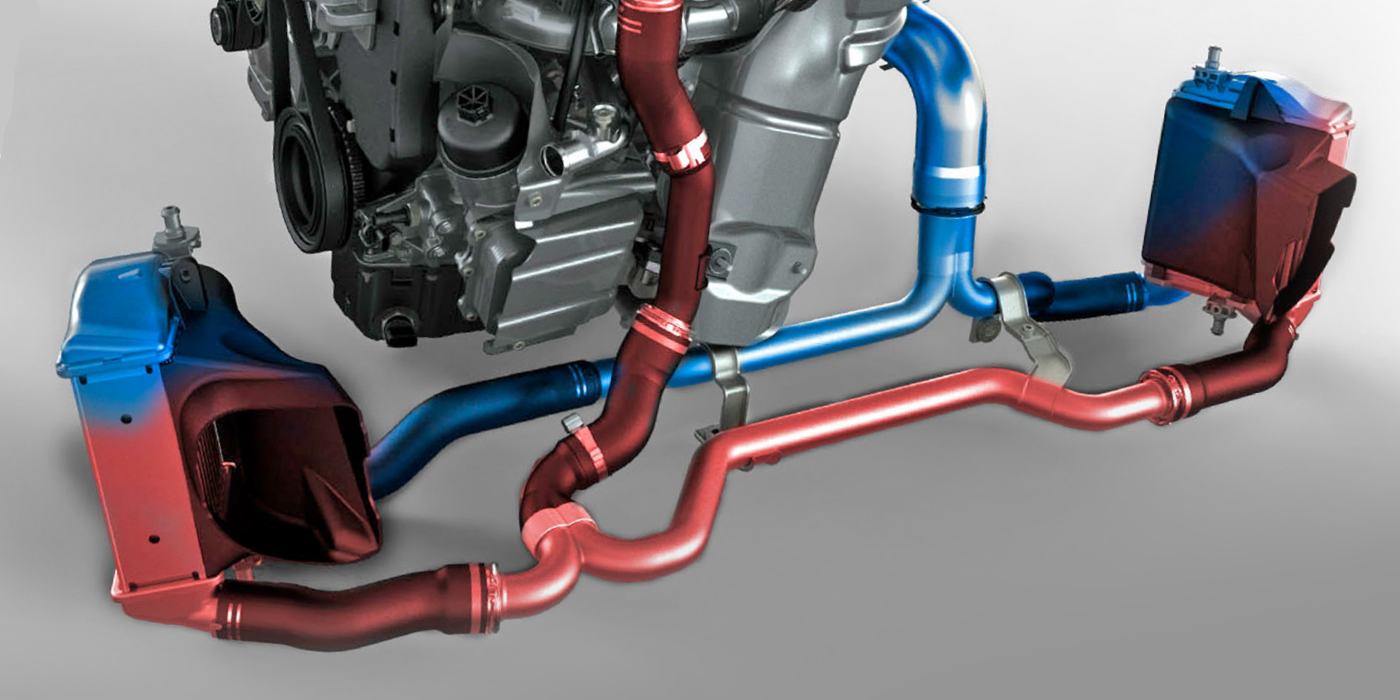
With almost 400,000 3.5L EcoBoost engines on the road today, these engines have proven to be a solid power unit. Many of these engines are out of warranty and heading to your shop. Here are the top failures and what to look for.
With almost 400,000 3.5L EcoBoost engines on the road today, these engines have proven to be a solid power unit. Many of these engines are out of warranty and heading to your shop. Here are the top failures and what to look for.
1. REFLASH: There have been at least seven updates to change calibrations and operation software for the 2011 models to address problems with the vacuum, ignition and transmission shifting. If you get a customer in your shop complaining of a loss of power or stalling, check the PCM to make sure it has the latest calibration. TSB 13-8-10 covers 2011-2013 models with the 3.5L V6 and discusses how new software calibrations can resolve a buck/jerk at steady cruise conditions with the transmission in sixth gear and lugging up grades at 1500-2000 RPM.
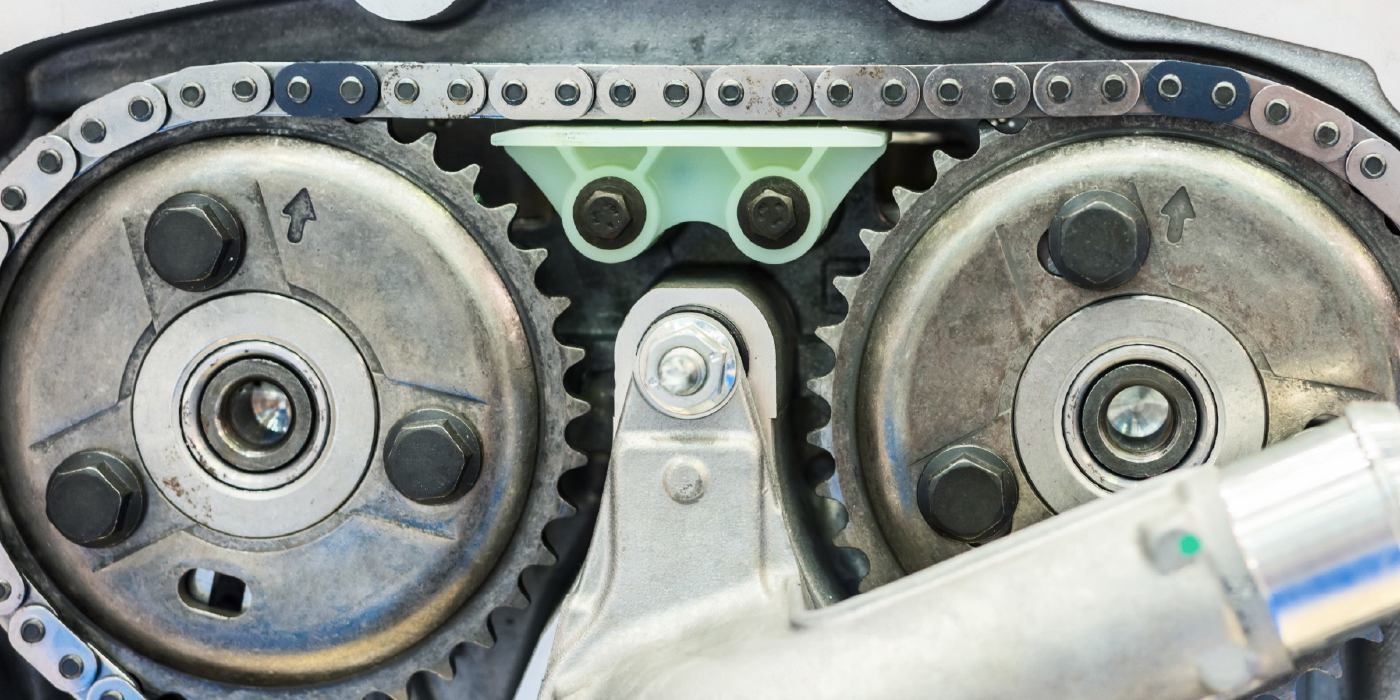
 2. Timing Chain Wear: Since the 3.5L EcoBoost is turbocharged, the oil is under extreme stress. If the driver pushes it past the recommended oil change interval, the first item to show the abuse is usually the timing chain. Worn-out oil can damage the chain, guides and tensioner. When the chain is worn and stretched, the PCM detects the changes in camshaft position and sets code P0016 for crankshaft/camshaft correlation. Check out TSB 14-0194 for more information.
2. Timing Chain Wear: Since the 3.5L EcoBoost is turbocharged, the oil is under extreme stress. If the driver pushes it past the recommended oil change interval, the first item to show the abuse is usually the timing chain. Worn-out oil can damage the chain, guides and tensioner. When the chain is worn and stretched, the PCM detects the changes in camshaft position and sets code P0016 for crankshaft/camshaft correlation. Check out TSB 14-0194 for more information.
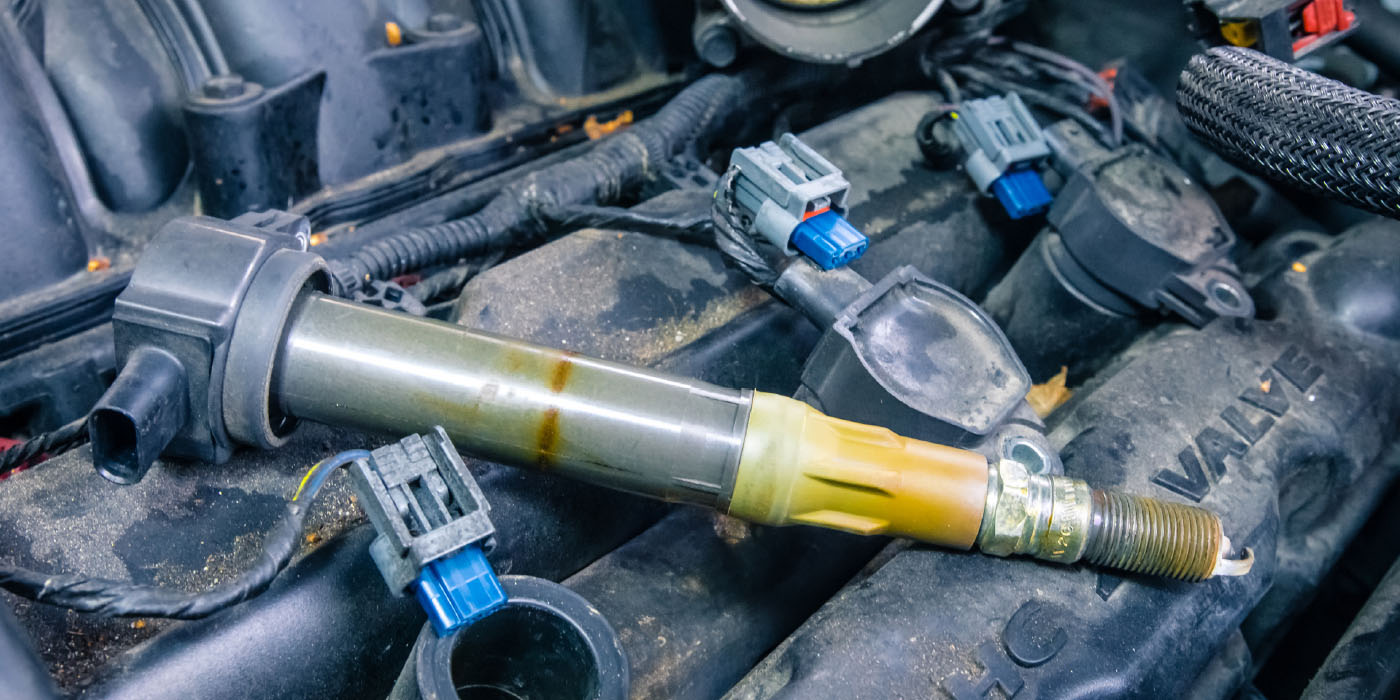
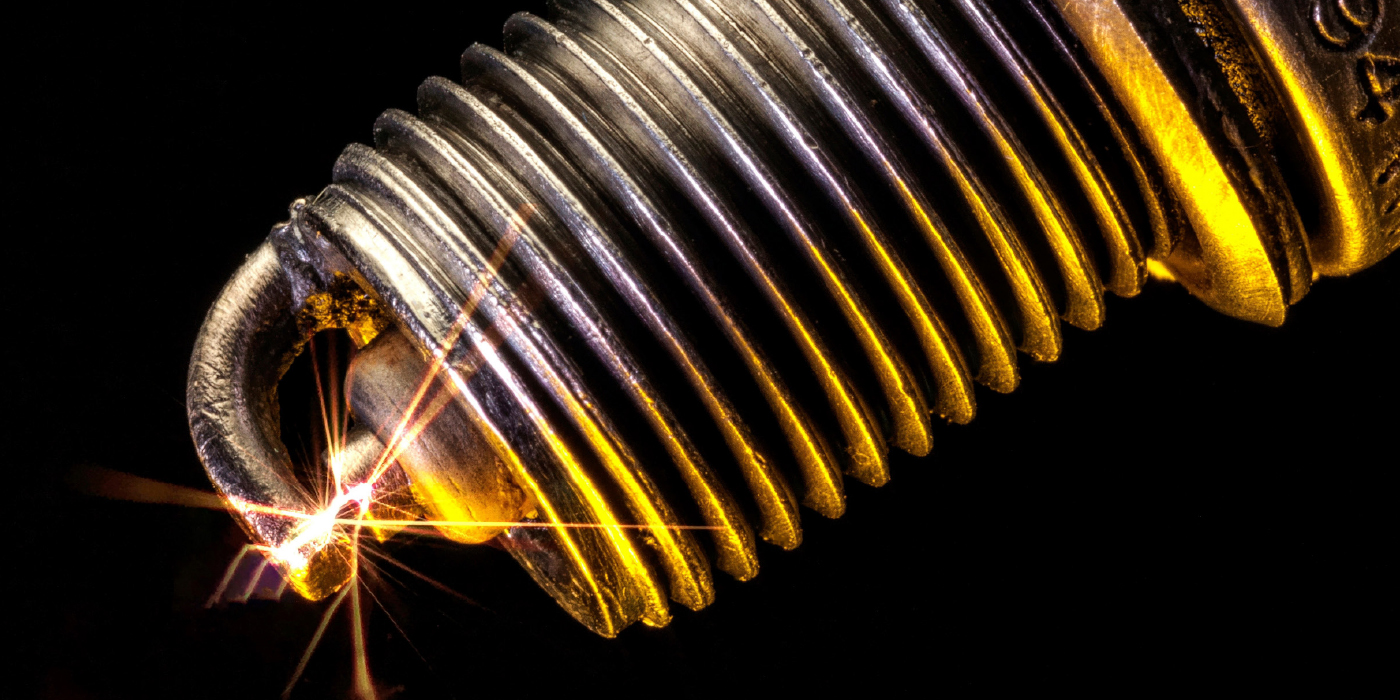
 3. Ignition Issues: If you get a 3.5L EcoBoost in your shop with misfire code(s) P0300-0306, pull the plugs and coil boots and look for carbon tracks on the insulator of the plugs. If any tracking is present, replace all the plugs and boots. See TSB 14-0180 for more information.
3. Ignition Issues: If you get a 3.5L EcoBoost in your shop with misfire code(s) P0300-0306, pull the plugs and coil boots and look for carbon tracks on the insulator of the plugs. If any tracking is present, replace all the plugs and boots. See TSB 14-0180 for more information.
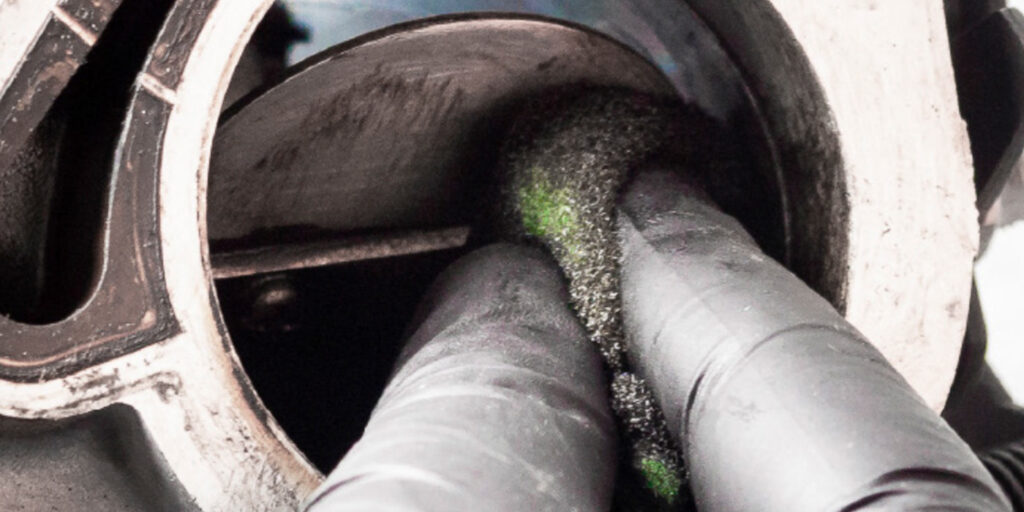
4. Induction Cleaning Mistakes: The 3.5L has not had many issues with carbon build-up on the intake valves. But, some DIY owners will use induction cleaners that are injected into the intake. These types of cleaners can damage the turbochargers’ bearings, seals and turbines. The best advice is to use high-quality fuel. Also, Ford has released new PCV parts and PCM calibrations to reduce the amount crankcase vapor ingested into the intake. See TSB 15-0003 for more information.