Codes P0300 to P0319 are known as misfires codes. These codes are some of the most misunderstood codes because of how a misfire is detected.
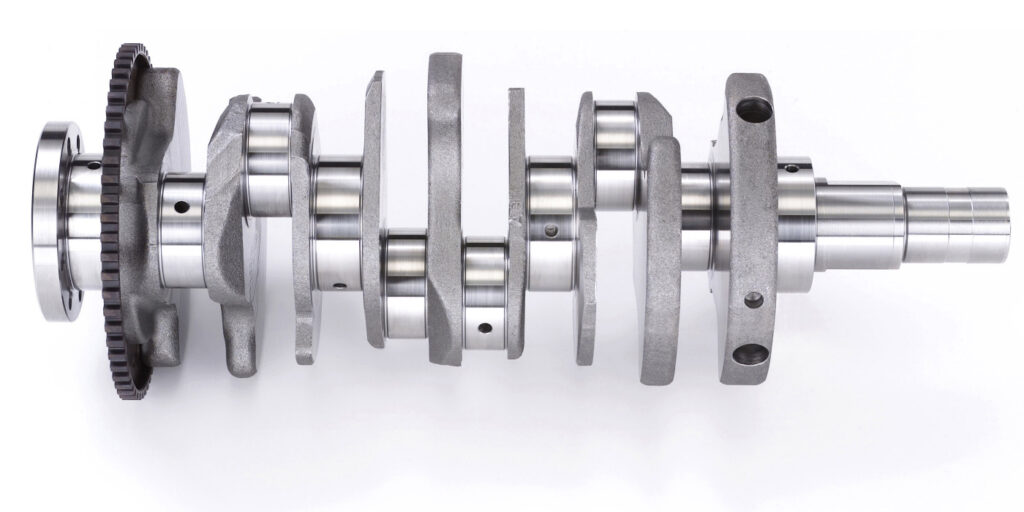
A misfire could be caused by an ignition, fuel or mechanical issue. There is no such thing as a misfire sensor. Instead, the ECM detects a misfire using the crankshaft position sensor or, in some cases, the knock sensor. The ECM calculates the time between the edges of the crankshaft reluctor wheel teeth by receiving a signal from the crankshaft position sensor. The ECM knows the firing order and the crankshaft’s position, so changes to the rotational velocity are detected. The ECM classifies abnormal changes as misfires.
This brings us to the criteria for setting a misfire code. The reality is, even new vehicles misfire.
If the check engine light turned on every time there was a misfire, it would constantly flash, even on new vehicles. To prevent this from annoying the customer, all OBDII vehicles have a misfire. A misfire monitor will count the number of misfires for the engine and specific cylinders.
Depending on the vehicle and misfire detection criteria, it could be 200 revolutions or a thousand revolutions. If the number of misfires exceeds the limit for the number of revolutions, it will set a single cylinder misfire code. If multiple cylinders are misfiring, a P0300 for random misfires could also be set. Codes P0301 to P0312 are cylinder-specific misfire codes for cylinders 1 to 12. These cover four cylinders, V6s, V8s, V10s and even V12s.
Code P0313 is like a P0300 but will only be set if the fuel tank level is low.
P0314 indicates a single misfiring cylinder that is powerful enough to damage the catalytic converter. When code P0314 is active, the check engine light will flash.
Misfire code P0315 indicates the system can no longer run misfire monitors because the input from the crankshaft position sensor is not present or learned. The most common cause of a P0315 is that the crankshaft position is not learned after an ECM replacement or ECM reflash. On most vehicles, clearing a P0315 is impossible with a scan tool or disconnecting the battery.
The only way to clear the code is to use a crankshaft position relearn with a scan tool. This procedure typically involves holding the engine RPMs at a specific level for a given time. Most scan tools will walk you through the procedure.
P0316 indicates misfires during the first 1,000 revolutions of the crankshaft after starting. The code will stay around for a few key cycles if the conditions do not occur again. P0316 is designed to detect high cold start emissions before the oxygen sensors are at operating temperature.
A P0316 code can occur as the seasons change and gas stations switch from summer to winter fuel blends. If a P0316 code persists, other items on the engine need to be evaluated, like carbon build-up or the condition of the spark plugs.
Misfire monitors can be suspended under certain conditions. Rough roads can be one reason. Engineers will program the vehicle to turn off the misfire monitor when the A/C clutch is engaged, the torque converter locks up or a rough road is detected.
P0317, P0318 and P0319 indicate that misfire monitor is disabled due to a malfunctioning rough road sensor. Some vehicles will have two accelerometers connected to the vehicle’s body to detect potholes and other road surface imperfects that might mimic a misfire. P0317 indicates that the input from the sensor is missing. P0318 means a malfunction of circuit A, P0319 indicates a malfunction of circuit B.
Most late-model vehicles do not have a rough road sensor. Instead, the sensing of a bumpy road is the job of the ABS sensor cluster.
The most crucial diagnostic strategy to remember is misfire codes hardly even occur on their own or are rarely related to the ignition coils or spark plugs. Most of all, to replicate a misfire problem, it will require a test drive with a scan tool.