By Roy Berndt

I have a couple of tidbits on the Cadillac 4.6L DOHC engine. The first is one of those that you may never see unless you painstakingly look for it or it bites you on a warranty. However, it becomes obvious almost immediately if you need to resurface the block deck.
The problem is cracking of the aluminum block casting around the cast iron liner (Figure 1). Knowing that this possibility exists, I strongly suggest that you take the time to make a close examination of the deck prior to doing any machining at all – and before you then spend numerous hours installing cylinder head bolt repairs.
The second tip involves cylinder head c/n 3533989 and 12554607, which would be the left head (or front, in the transverse mount engine) that has an alternator bracket bolted onto it in some applications. This head will always have 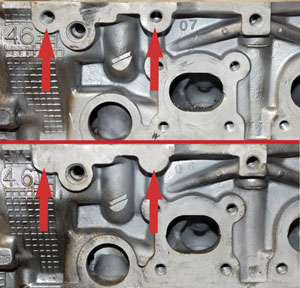 the bosses for this mounting bracket but both of them may or may not be drilled (see Figure 2).
If you want to avoid problems I recommend that you drill all of them, thereby eliminating the possibility of having a warranty problem upon installation and also reducing head proliferation.
the bosses for this mounting bracket but both of them may or may not be drilled (see Figure 2).
If you want to avoid problems I recommend that you drill all of them, thereby eliminating the possibility of having a warranty problem upon installation and also reducing head proliferation.
I hope these tips help keep you out of the firestorm that sometimes surrounds us in the engine-building world.
Roy Berndt has been in the engine rebuilding and remanufacturing industry for over 30 years. He is an ASE Master Machinist and co-author of SAE documents and standards. He is Program Manager for LKQ Remanufacturing, a PER in Springfield, MO.













