 Vehicles affected:
Vehicles affected:
Ford: 2005-’07 Five-Hundred, Freestyle; 2006 Fusion; 2006-’07 Escape
Lincoln: 2006 Zephyr
Mercury: 2005-’07 Montego; 2006 Milan; 2006-’07 Mariner
Some of the affected vehicles built Jan. 17, 2006 and later equipped with the 3.0L 4V Duratec engine with exhaust camshaft-driven water pumps may exhibit a ticking noise from the left bank cylinder head with the engine at normal operating temperature.
Service Procedure
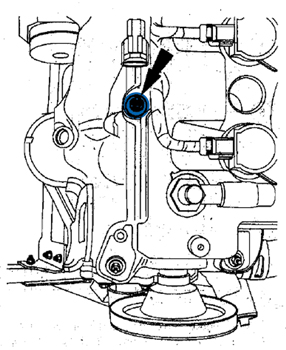
To diagnose, with the engine running and warm (normal operation temperature), using a mechanic’s stethoscope determine if the ticking noise is coming from the left-hand exhaust camshaft at cylinder number 6, see Figure 1.
If the ticking noise can be verified, continue with the Service Procedure.
 1. Remove the left-hand camshaft cover.
1. Remove the left-hand camshaft cover.
2. Rotate the engine clockwise until the cylinder number 6 exhaust cam lobes are pointing up and the valves are fully closed.
3. Remove all left-hand exhaust cam caps individually and reinstall them finger-tight.
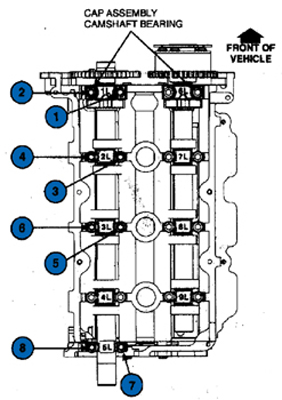
4. Torque bolts in the sequence shown in Figure 2 to 72 lb.-in. (8 Nm) excluding cam cap number 4L.
See Figure 2
5. Using a screwdriver positioned on each side of the top of cam cap number 4L, apply hand pressure and shift cam cap number 4L toward the exhaust side of the cylinder head.
See Figure 3
6. While holding cam cap number 4L in the shifted position, torque the fasteners number 9 (inboard) first, to 72 lb.-in. (8 Nm) then torque fastener number 10 (Figure 3).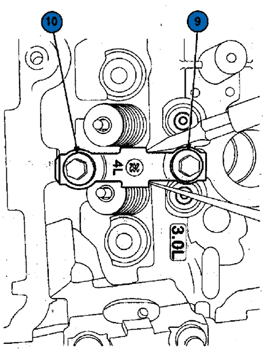
7. Install the left-hand camshaft cover.
8. Fully warm the engine to verify the repair.
Courtesy of Identifix.