 Models: All
Models: All
The Problem
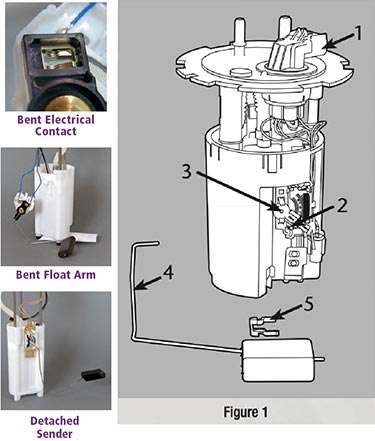
In some cases, float arm assemblies have been damaged after the fuel pump has been tested. Shipping, mishandling and pump insertion/removal from packaging are causes for potential damage.
The Solution
The float arm is shipped loose to avoid unnecessary damage and disruption during installation. The undamaged float arm assembly should be properly mounted to the fuel level sender before installing the pump module into the fuel tank.
Float Arm Installation
NOTICE: Handle the fuel pump module, fuel level sender and float arm assembly carefully. Any damage, bending or distortion will adversely affect the accuracy of the fuel level readings.
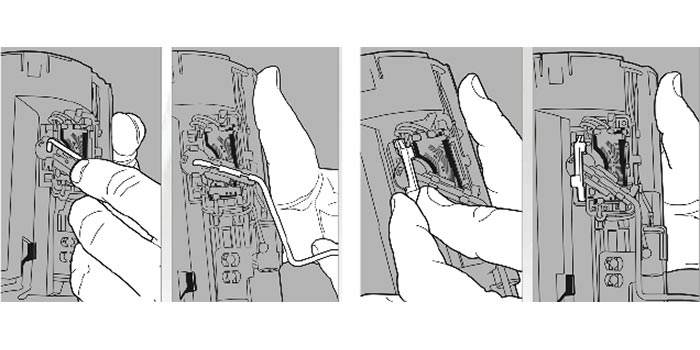
Identify Components
The following components will be referenced during the assembly process (Figure 1):
1. Fuel pump module
2. Fuel level sender
3. Pivot hole
4. Float arm assembly
5. Float arm retaining clip
Assemble Float Arm
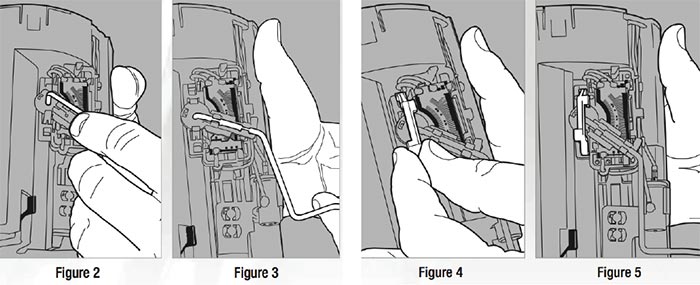
1. Insert the float arm into the pivot hole of the fuel level sender (Figure 2).
2. Carefully push on the float arm until it snaps into the fuel level sender.
The float arm will now be in place (Figure 3).
Install Float Arm Retaining Clip
Position the float arm retaining clip over the float arm as shown (Figure 4) and push it into the fuel level sender housing until it snaps into place (Figure 5).
Courtesy of Airtex