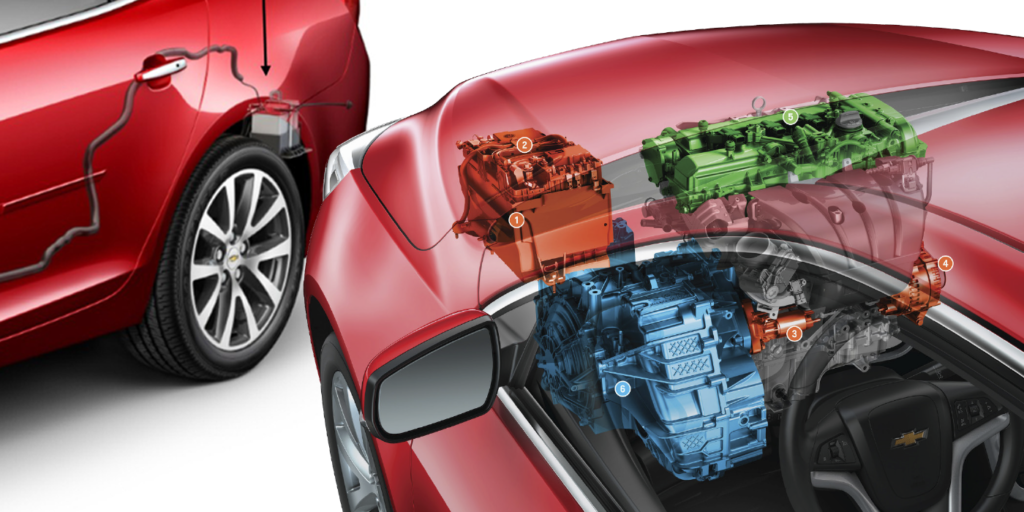
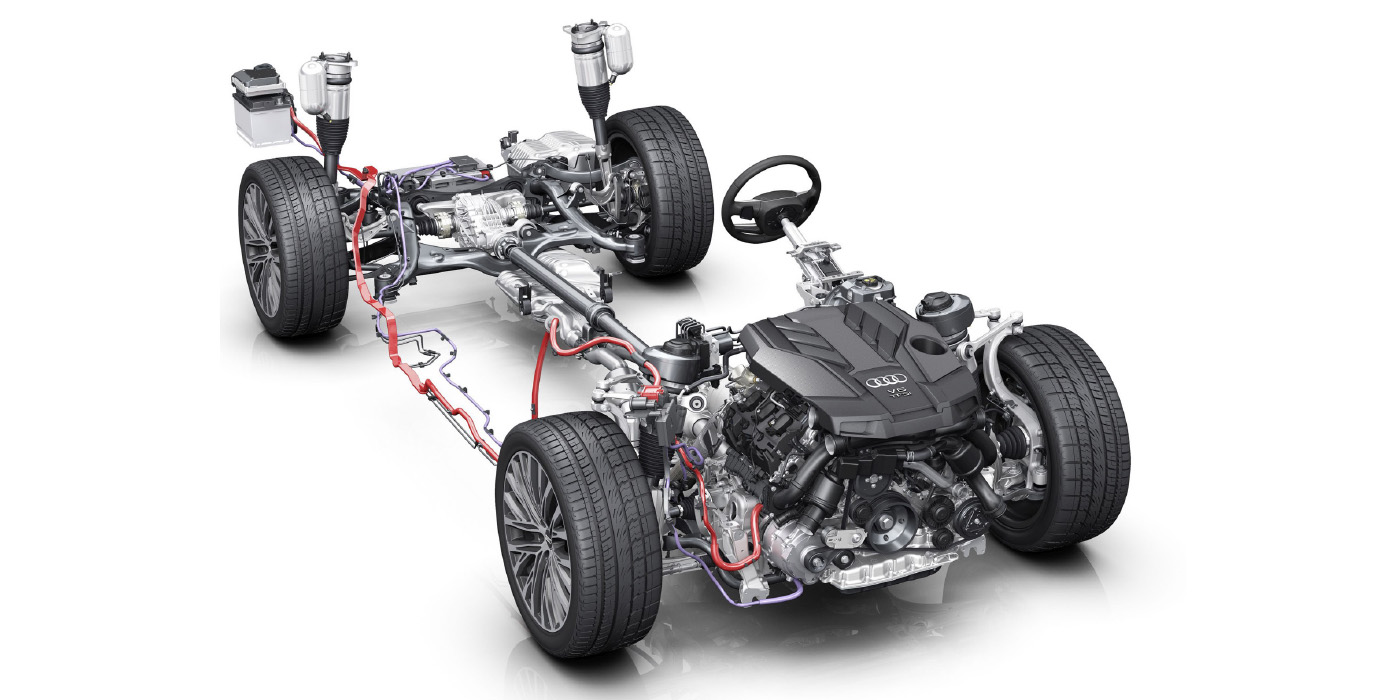
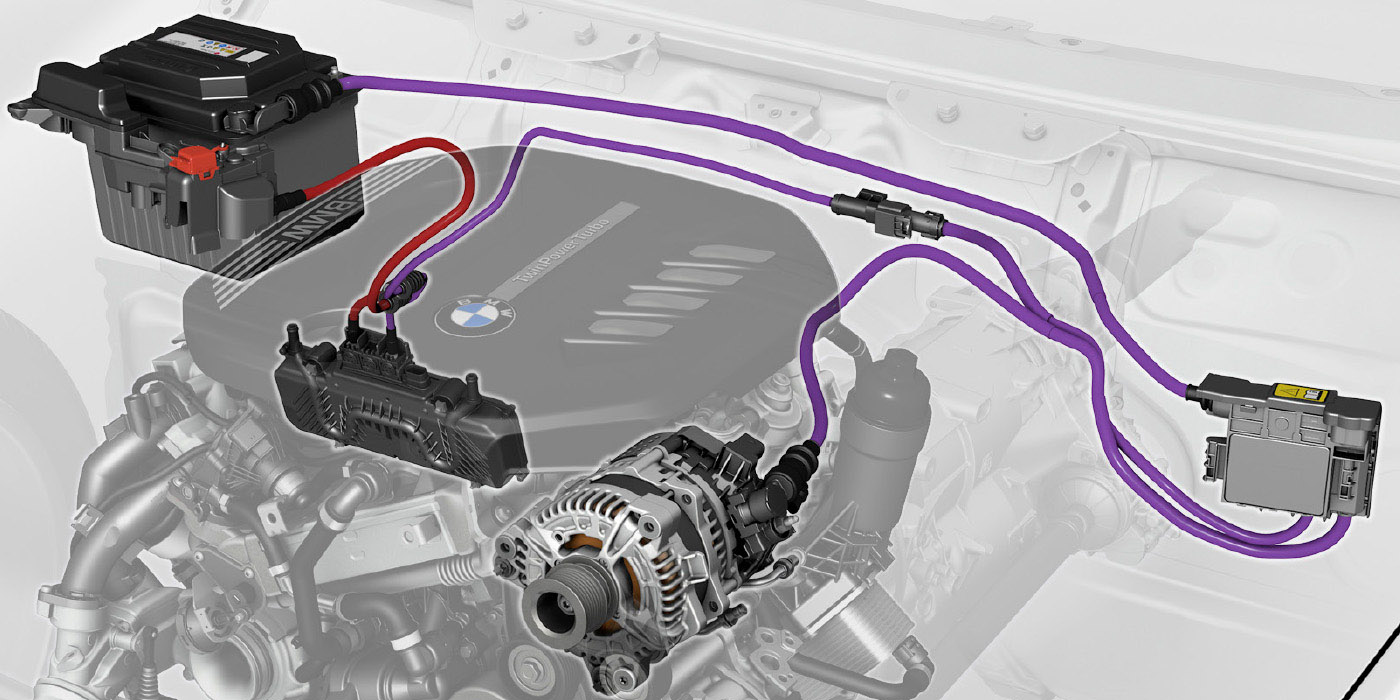
Since 2013, GM has offered stop/start technology on a growing number of engines and platforms. These systems can improve fuel economy by 3-5% depending on the driving habits of the customer. For your shop, it is essential to understand what is different on these vehicles and how it might change your diagnostic approach.
1. Larger or Multiple Batteries
When the engine stops so does the alternator. The battery must run the HVAC, infotainment and other systems with little or no disruption. Most stop/start systems use a deep cycle aggregated glass mat battery (AGM). In some GM applications, there is a second or accessory battery. This battery is typically mounted in the trunk. The battery management system has current sensing devices on the positive battery terminals and requires the use of a scan tool for testing.
2. Transmission
When the engine stops, the transmission pump behind the torque converter stops turning and line pressures drop. Most GM stop/start vehicles use an electric pump and maybe an accumulator to keep the transmission fluid under pressure. If the pump fails or valves fail, the transmission will slam into gear when the engine is started and the person pulls away from a light.
3. HVAC
Managing the temperature inside the cabin is critical. Roasting a driver for better fuel economy is not be a good idea. When the engine shuts down, the HVAC system will monitor outside and cabin temperatures to determine if the engine needs to be started to power the A/C compressor or if the auxiliary coolant pump needs to be turned on to pump hot coolant to the heater core.
4. Brake Pedal Sensor
Don’t think of the brake pedal position sensor as just a switch. Stop/start vehicles measure brake pedal travel and force, so by the time the driver has moved their foot from the brake pedal to the gas pedal, the engine has started. For most GM vehicles with stop/start systems, the sensor needs to be calibrated if replaced.
5. Oil
GM Dexos Gen 2 approved engine oils protects components like the camshaft, crankshaft and the bearings during stop/start operation. Dexos tests measure how the oil sticks to the surfaces. For Ecotec turbocharged engines that have a stop/start system, a coolant pump circulates coolant to prevent it from coking up in the housing and lines.
6. Electrical System
Imagine if a stop/start car shut down and when the driver lifted their foot from the brake pedal the engine did not start. To prevent this from happening, stop/start systems have three ways or more to measure the condition of the battery. The first measurement is voltage coming from the battery. Second, the system is measuring current and loads at the battery with coil winding like a current clamp on the positive battery cable. Third, most systems measure the temperature of the battery directly or through data PIDs for underhood temperatures.
With this information, the ECM can predict if a stop/start cycle is possible. It is also a very good indicator of the health of the battery. Many systems will turn on a battery life indicator if it detects a low battery. On GM vehicles, a warning message will be displayed to have the battery charged or serviced.
7. Starter
High-end stop/start systems use a large generator/motor combo between the engine and transmission to turn the engine and generate power. But, the majority of systems use a starter that looks a lot like a conventional starter.
It’s not only appearance; these starters operate the same way but with some critical internal differences. The first thing you will notice is that the gear on the starter is larger and the gear reduction system is lower. This allows the starter to turn slower, this reduces wear on the brushes and bearings. Also, the armature and bushes are upgraded to improve the longevity of the starter.
8. The Engine
With improved engine position sensors and gasoline direct injection, the ECM is able to do a neat trick. Since the system knows the position of the piston and valves, it can use the fuel injector and spark plug in the cylinder to “nudge” the engine over to make life easier for the starter. The system will look for cylinders that are on a downward stroke. When the engine needs to start, a small amount of fuel will be injected and ignited to get the engine moving.
9. Cooling System
Some stop/start vehicles are using an auxiliary water pump to move the coolant in the block, head and heater core so the engine will not be heat soaked from the coolant not moving. If ambient temperatures are too hot, the stop/start system will not be active.
10. Smarter Vehicles with More Sensors and Shared Information
A GM stop/start system is not a module. It is a shared strategy among many modules using information like cabin humidity to crankshaft position to determine what happens at the next stoplight. For the technician, it means that serial data communication bus and electrical diagnostics will be much more important in the future.