Automakers are always trying to remove items from the accessory drive belt. This improves the efficiency of the engine and can extend the life of the belt. But where do you put the water pump? Some manufacturers like Ford and Mazda have driven the pumps with a pulley on the exhaust camshaft. Other manufacturers have decided that the chain on the front of the engine may be a better solution.
In the early 1990s, a serpentine belt on the front of the motor typically drove the water pump. That same belt also drove the alternator, power steering pump and the A/C compressor. The belt had to be long, with high tension, in order to keep the belt on the pulleys.
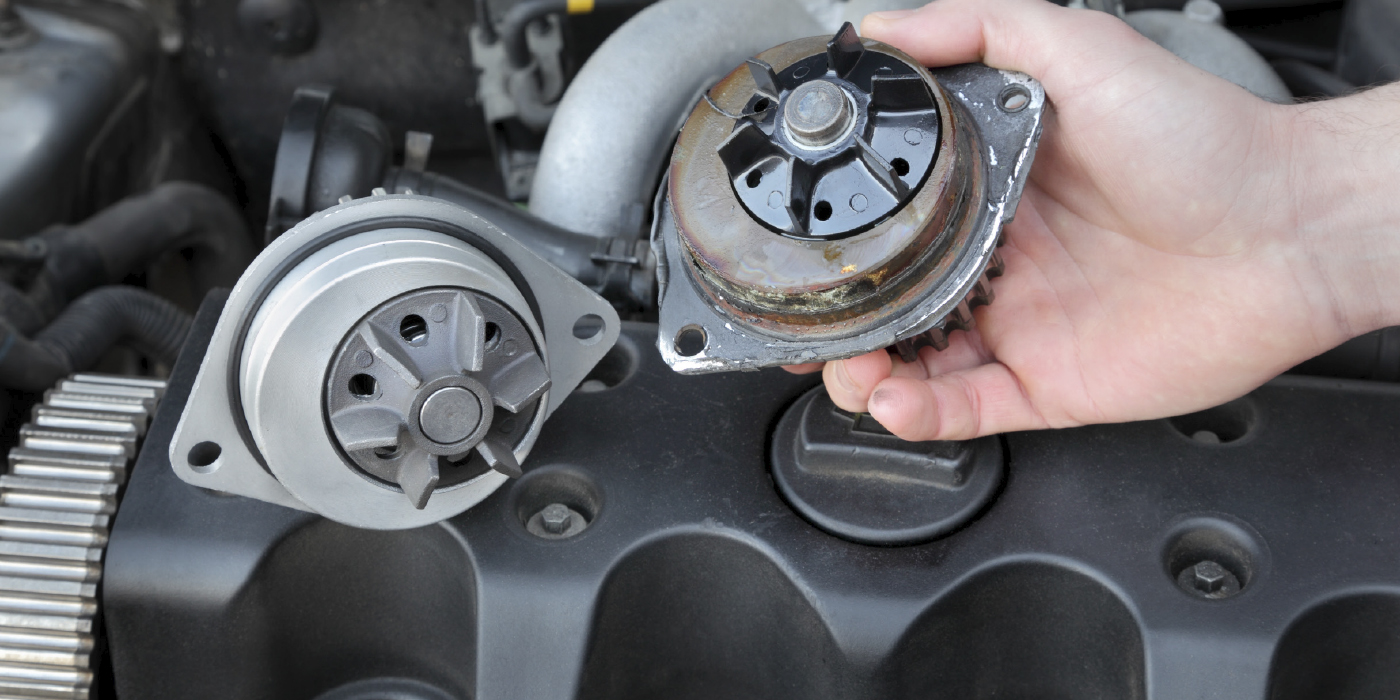
But this setup was noisy and put undue pressure on the water pump shaft. This pressure would cause the bearings and seals inside the water pump to fail. The solution for some manufacturers was to drive the water pump with the timing chain.
Pump Inspection
Before passing judgment on one of these water pumps after seeing a little bit of coolant around the weep hole, perform a pressure check. Some minor coolant seepage at the coolant drain hole is a normal condition and replacement of the water pump is not required.
All water pump shafts are sealed with a mechanical-type seal between the pump and the outer housing. This mechanical seal is lubricated by engine coolant and, because of its construction, some coolant will seep out. Therefore, a coolant drain hole is provided.
Why Did It Fail?
Before you replace any water pump, you have to diagnose why it failed. Stock water pumps will often last more than 100,000 miles. If one fails sooner and is replaced without an investigation, the new water pump is likely condemned to an even shorter life.
Harmful contamination is common in systems that are not properly maintained. The abrasiveness of the particles found in a contaminated system will prematurely wear the water pump seal. Also, a system that is not properly pressurized will allow air to enter and promote the build up of rust.
Thoroughly flush a contaminated system before replacing a timing chain-driven water pump. Also, double-check your work by pressurizing the system and checking for leaks.
Another reason why chain-driven water pumps fail is a worn or defective tensioner and guides. Most engines use oil pressure to actuate a tensioner that puts pressure on a guide. If the tensioner fails (typically due to a lack of oil changes), the chain will move around due to centrifugal force acting on the chain. When a chain is moving in ways not intended by the engineers, it could cause stress on the shaft of the pump and uneven wear on the sprocket.
GM Ecotec 2.0-2.4
The water pump for the Ecotec four-cylinder engine is driven by the chain that turns the engine balance shaft.
Remove the Exhaust Manifold or Turbocharger
This will increase access to the pump and thermostat housing on the back of the engine. The studs and bolts that hold the manifold are of a decent quality and there haven’t been too many complaints of broken fasteners.
In order to prevent exhaust leaks, always use a new exhaust manifold gasket. Make sure the surfaces are clean on the head, and use the correct torque settings and sequence.
Keep it Clean
Removing the access plate and water pump creates a big hole that debris can fall into and reach the oil sump. Make sure no bolts or gasket fragments fall in.
Also, make sure the surfaces that hold the pump to the block are clean. An oil leak will form if debris is stuck between the two surfaces.
Thermostat Housing Problems
When you replace the water pump, the thermostat should be replaced.
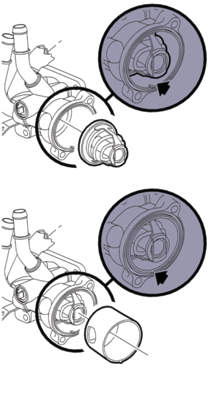
The nose of the thermostat should go into the thermostat housing, followed by the plastic inner sleeve as in Fig. 1. If the plastic liner and thermostat are not aligned, the temperature gauge will read 235° F or higher while driving at highway speeds but return to 210° F or less after an extended idle.
Use the Right Tools
Most service information on water pump replacement will assume you are doing a complete engine rebuild or at least have the chain cover off — but there is a better way. Water pump holding tool J-43651 will hold the water pump sprocket in place while the water pump is being replaced. The tool attaches to the bolts in the access cover and on two bolt holes of the sprocket. If you don’t use this tool, you will damage the chain tensioner.
When you remove the pump without fixing the water pump sprocket, the tensioner could ratchet out and cause the tension to increase to the point where the chain makes noise and the water pump fails prematurely.
 Nissan VQ Water Pumps
Nissan VQ Water Pumps
The Nissan VQ-series V6 engines come with one of the toughest water pump jobs, regardless of how the engine is mounted. The VQ35-series of engines can be found in 2001-current Nissans and Infinitis. The pump is nestled in the engine block and is turned by the timing chain. Book time on this job can range from two to three hours depending on the model and layout. There are no shortcuts.
Signs of Failure
The first signs of trouble are usually the engine overheating, coolant loss or coolant leaking from the front of the engine. The engine in these cars is mounted sideways, so if the pump is leaking, you may find a puddle of coolant on the ground under the passenger side of the engine just behind the front-right wheel.
Of course, a coolant leak doesn’t always mean the water pump shaft seal has reached the end of the road. The leak might be a bad hose or a cracked coolant reservoir. Use a mechanic’s stethoscope to isolate the sound because it might be due to worn bearings in one of the engine’s accessories or pulleys. If the sound seems to be coming from the area of the water pump, and the vehicle has a lot of miles on it, chances are the pump is failing.
On rare occasions, a water pump will fail internally. The pump may not be leaking, but the engine is overheating because the pump is not pushing coolant through the motor. Some late-model water pumps have plastic impellers that are designed to reduce drag and noise. Over time, the fins on the plastic impeller can erode away and reduce the pump’s ability to circulate coolant through the engine. The water pump used in these Nissan 3.5L engines has a stamped steel impeller, so this may not be an issue, but a metal impeller can sometimes come loose and slip on its shaft, preventing it from spinning or pumping coolant.
O-Ring Attention
When replacing the pump, pay close attention to the O-rings. These need to be lubricated with either oil or coolant. The rings need to be able to seal and shift slightly as the block heats and cools. Do not use silicone or another sealant because they can block the weep hole in the block.
Timing is Everything
Before starting the job, set the engine to top-dead-center. This can prevent the cams and engine from wanting to flop over when you release the slack on the chain. If you exceed 20º with the tensioner slacked, the chain could jump.
When the new pump is installed, you will need to reinstall the tensioner. Turn the crankshaft pulley approximately 20° counterclockwise so that the timing chain on the timing chain tensioner side is loose, and then install the tensioner. Don’t forget to remove the pin holding in the tensioner, and check the timing before you install the covers.
 Subaru
Subaru
Since the 2000 model year, just about every flat-six boxer engine has timing chains. The water pump is attached to an idler sprocket of the left bank of the timing chain. To replace the water pump, both chains need to be removed.
This pump has been known to go 200,000 miles or more. If the engine has had timing belt tensioner and guide issues, the sprocket can become worn.