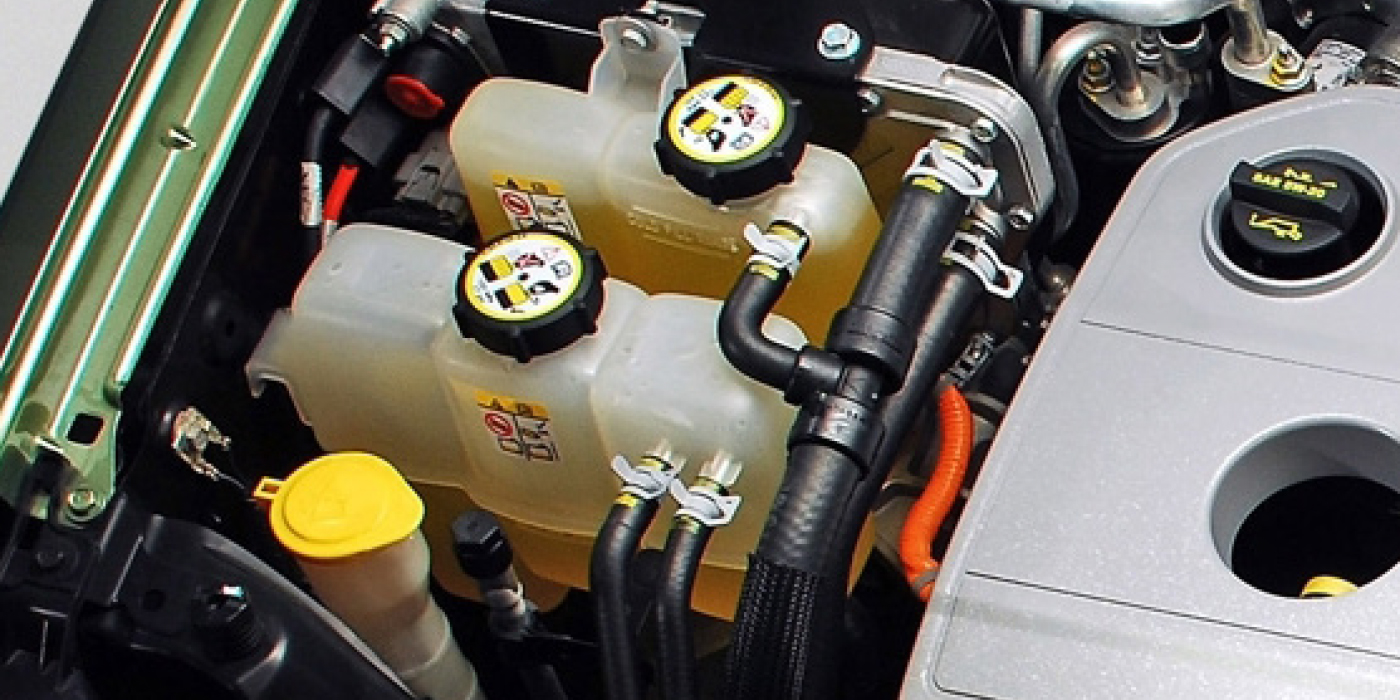
On modern vehicles, overheating is a rare occurrence thanks to high-quality hoses, thermostats and better engine management. Unfortunately, the weak point is still the coolant. Whether it’s a 100,000-mile or 150,000-mile coolant, eventually it will break down and lose the ability to protect the components with which it comes into contact.
Coolant at 100,000 miles may look the same as coolant with zero miles, as the real difference between good and bad coolant can’t be seen with the naked eye; it is in the chemistry and based on mileage.
Coolant contains additives called buffers that keep it at a neutral pH but these buffers are meant to last forever. When these chemicals become depleted, the pH can’t be controlled. It rises dramatically in a short period of time the moment the buffers are fully depleted. This is why replacing the coolant at the recommended interval is critical.
Coolant has two specifications that can be used to justify replacement — the condition of the additive package and the freezing point.
The additive package is the secret sauce for a coolant. Its main function is to control corrosion. Other components of the additive help with heat transfer and cavitation reduction. Some additive packages use seal conditioners to extend the life of the gaskets and plastic carriers.
The freezing point is measured by the overall specific gravity of the coolant, which has a direct relationship to the coolant/water mixture. This test can help spot coolant that has been compromised by the owner topping off with water. This measurement works well on systems that do not have pressurized reservoirs.
The strength or freezing point of coolant can be measured with a simple hydrometer. This device uses a calibrated float or plastic balls (not as accurate) to show the specific gravity of the coolant. This, in turn, shows how much freezing/boiling protection the coolant offers. You must remember to compensate for temperature because the specific gravity (density) of the coolant is lower when the coolant is hot.
The more professional tool for this purpose is an optical refractometer because it is very accurate and automatically compensates for temperature. Be aware: these are not simple, inexpensive tools. A refractometer can cost up to $300 or more because of the precision optics in its lens. Ethylene glycol (EG) and polyethylene glycol (PG) antifreeze have slightly different densities, so you have to use a hydrometer or refractometer with the appropriate scale (or one with a dual scale) for accurate test results.
Color-coded chemical test strips that are dipped into the coolant can be used to quickly and easily reveal the condition of the coolant. These strips of coated capillary paper react to the presence of certain dissolved minerals in the coolant and change color to give a good, marginal or bad indication of the coolant’s pH condition. Some test strips also show the concentration of antifreeze in the coolant.
The added benefit of test strips is that the results can be shared with the owner by attaching the used strip to the inspection form.
But, mileage is the gold standard for any coolant replacement recommendation. Engineers and chemists spend a lot of time formulating the coolant to match the engine and interval.
If you are performing a water pump, heater core or hose repair, recommend a full coolant flush. Just topping off the coolant can lead to a mixed bag when measuring the pH and freezing point. Also, check the specific gravity before a repair. Many customers know how to top off their coolant with water that could dilute the coolant concentration.
Selling any fluid maintenance service is difficult these days. But, if you document and educate customers on the importance of coolant, it becomes more than just an “add on” service.