It may be hard to believe, but antifreeze has been around since the mid-19th century and was used initially in dynamite before finding its way into the automobile. Early engine designers tried other means of cooling before antifreeze gained a foothold. It came to prominence during World War I when it was used in tanks and vehicles to prevent them from freezing in the battlefield.
Cooling systems and chemistry have changed a great deal since then, and the need for coolant has also been on the rise in today’s modern engines.

Antifreeze lowers the freezing point of a water-based liquid and increases its boiling point. An antifreeze/water mix is used to achieve freezing-point depression for cold environments and also produces boiling-point elevation for higher coolant temperatures. Antifreeze freezing and boiling points depend on the concentration of the dissolved substance. Water gives the antifreeze more surface area to transfer heat to the radiator.
Different types of coolants cover a range of applications from diesel to domestic, Asian and European vehicles. Each one is formulated to a specific manufacturer’s specifications to keep their engines at an optimal temperature. But, changes to the old one-size-fits-all formula has led to confusion for consumers and even some technicians.
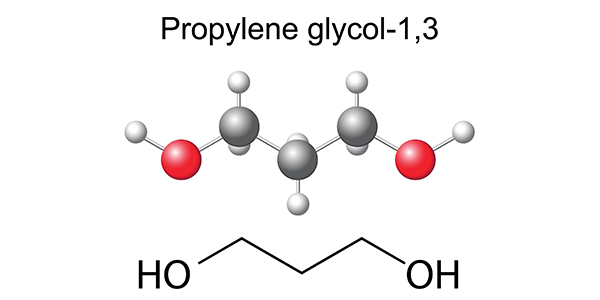
The most common variety of antifreeze is an Inorganic Additive Technology (IAT) formula. This traditional-style green coolant, which has been in use forever, provides corrosion protection as well as lubrication to the water pump. IAT coolants contain either ethylene glycol or propylene glycol with silicate or phosphate additives to increase its compatibility with metal cooling system components. The generally recommended replacement interval is once a year. Most consumers will not replace their coolant that often, so new, long-life formulations were introduced.
Since water is a natural coolant, when mixed with 50% antifreeze, it improves the heat transfer above what it would be alone. The ratio of coolant can vary, depending on the application or situation, to as much as 70% coolant. A 70/30 mix will lower the freezing point to -67° F and raise the boiling temperature to 235° F. But, a 70/30 mixture of antifreeze and water is not as efficient as a 50/50 mixture because the thermal capacity of antifreeze is not as high as water.

All antifreeze types require high-quality water to be used if it’s not in a pre-50/50 mix from the manufacturer. City or well water can contain a certain amount of dissolved minerals and is not recommended to be mixed with coolant. De-ionized water uses a process that removes these minerals and particulate, making it ideal for use in coolants. If corrosion sets in, it can attack radiators, heater cores, water pumps, thermostats, head gaskets and hoses, and will eventually cause a leak.
Antifreeze with a long service life is based on Organic Acid Technology (OAT), and each manufacturer has its own blend of additives. However, the majority of the products are typically ethylene glycol-based without any silicates, phosphates, borates, nitrites and amines. It protects metals in the coolant system against rust and corrosion and also provides high-temperature aluminum protection. It is fully compatible with other OAT coolants and is recommended for use in newer-model vehicles. Most Extended Life Coolant (ELC) offers up to a 5-year or 150,000-mile service life protection when properly diluted and added as an initial fill.

For best results, ELC should never be mixed with IAT (conventional) coolants that contain high pH, phosphate, borate or silicate. ELC has an orange color to help differentiate it from traditional “green” coolant (although it is not always green). Mixing conventional coolants with an ELC can reduce the anticipated lifetime of the combined fluids, but it will not be detrimental to the engine.
If your customers are using IAT coolants, you should recommend a cooling system flush and replacement every one to two years. While ELC can last up to 5 years, it is best to test whether the antifreeze your customers are currently using is still active with an antifreeze tester. Antifreeze can break down over time, especially IAT and some hybrid OAT solutions where the additives drop out and, therefore, don’t provide enough corrosion protection. Contaminated coolant may also boil over or freeze sooner.

Use the same type of coolant according to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations. It won’t hurt to have a different brand or type, but the effectiveness of each coolant type’s additive package may be compromised (depending on their specifications). In general, if you are mixing coolants, the recommended coolant change interval will be for the shorter-life coolant.
Maintaining proper mixture and fluid levels ensures corrosion inhibitors are able to protect the engine. Most OEMs create cooling systems to operate with the optimal level of antifreeze. A system that is always low on coolant creates a corrosive environment.
The water-to-antifreeze ratio is critical, which is why so many brands offer pre-mixed products. All pre-mixed coolants are produced with distilled water, so there are no concerns with mineral deposits. If concentrate is used when refilling or topping off any cooling system, it should be mixed with distilled water, not tap or filtered water.
Because a third of the energy an engine produces becomes heat, the fluid used to transfer it out of the block is as important as what is put in the gas tank.