Some owners of the models listed below may comment on a creaking noise occurring when applying the brakes. It is usually heard only during slow-speed brake maneuvers. If this condition exists, you should be able to duplicate the noise when the vehicle is not moving by depressing the brake pedal and listening for the noise from the wheel-well/caliper area.
Models:
1999-2003 Chevrolet Malibu
2004 Chevrolet Malibu Classic
1999-2004 Oldsmobile Alero
1999-2004 Pontiac Grand Am
This condition may be caused by a caliper piston-to-seal interface issue when applying the brakes. If the caliper is removed and the piston is pushed back, the noise may be eliminated. This is usually only a temporary fix.
NOTE: DO NOT replace the caliper.
To repair this condition, lubricate the entire circumference of the seal at the caliper piston interface using Kluber Fluid (GM Part Number: 89022161) or equivalent and the following procedure:
Service Procedure
(Review safety procedures in ALLDATA Repair before beginning.)
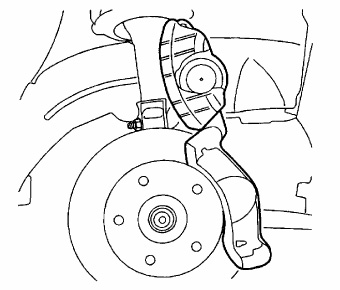 1. Remove the wheel and reinstall two lug nuts. This will hold the rotor to the bearing surface so debris does not fall between the surfaces and cause lateral run out (LRO).
1. Remove the wheel and reinstall two lug nuts. This will hold the rotor to the bearing surface so debris does not fall between the surfaces and cause lateral run out (LRO).
2. Remove the bottom bolt from the caliper assembly without disturbing the hydraulic system.
3. Swing the caliper assembly up so the caliper assembly is facing upward.
4. Thoroughly clean the piston boot with GM approved Brake Clean or equivalent. Pay particular attention to the area where the boot interfaces with the piston.
5. Using compressed air, dry the piston/boot area.
6. Remove the cap from the tip of the bottle and carefully insert the tip between the boot and piston, inward of the piston boot groove.
7. From the top side of the piston, inject the lubricant. With the caliper in the tilted position, the lubricant will flow down and work its way around the entire circumference of the seal. Let the caliper body assembly remain in this position for a minimum of two minutes to allow for the fluid to completely work its way around the seal.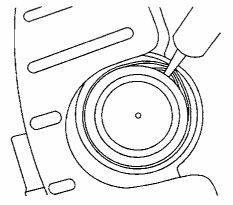 8. Push the piston into the seal to ensure the lubricant is on both the piston and seal surface.
8. Push the piston into the seal to ensure the lubricant is on both the piston and seal surface.
IMPORTANT: Excessive fluid could appear as a failure and lead to a comeback. To prevent unnecessary future repairs, it is important to only use one bottle per side and make sure excess fluid is wiped away.
9. Wipe away any excessive fluid.
10. Reassemble the caliper to the vehicle. Tighten the caliper bolts to 31 Nm (23 lb-ft).
11. Repeat Steps 1 – 9 on the opposite side of the vehicle, if necessary.
CAUTION: Pump the brake pedal to push the caliper piston back into place.
12. Reinstall the wheel and test drive the vehicle to verify repair.
Written by ALLDATA Senior Automotive Editor, Rich Diegle. Rich is an Advanced Engine Performance Certified, ASE Master Technician with an AA Degree in automotive technology and 23 years of dealership and independent shop experience.
For additional information, visit www.alldata.com.