Ford Motor Company has released information on a cylinder head gasket caution for 2003-’07 Ford 6.0L VIN P diesel engines.
According to Ford’s TSB 06-24-4, some 2003-’07 vehicles equipped with a 6.0L engine may require the cylinder head to be replaced, while design changes can affect interchangeability between model years and service of 2003-’07 6.0L engines.
According to the bulletin, the manufacturer for this engine used two separate facilities. And, while both locations built engines with the same design data, three cylinder head variations have been used. There are engine serial number change dates to help in determining which cylinder heads were used.
The cylinder head gasket and locating dowels also changed in the 2006 model year to accommodate the increase in the dowel size from 18 mm to 20 mm. Using the wrong head gasket for the application will lead to engine damage.
The revised dowel hole was made to accommodate the larger head bolts to be used in the new 6.4L diesel engine and was commonized for manufacturing purposes. The injector clamp design and associated cylinder head casting support area also were modified on the changeover date in early 2006.
The cylinder head and block dowel hole sizes must be measured to determine the correct cylinder head gasket kit to be used. If there is a difference in dowel hole size between the head and block, a special “stepped dowel” (P/N 6C3Z-6B041-B) is available to accommodate proper assembly.
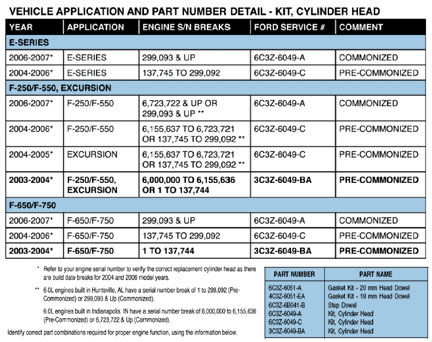
Ford notes that the cylinder head gasket and injector clamp versions are not interchangeable; they must be used with the corresponding cylinder head versions. Refer to the chart to determine the correct application.
Courtesy of Ford Motor Co. and Ford Truck Enthusiasts (www.ford-trucks.com)













