Applies to 1994-’97 Integras (see Affected Vehicles below)
SYMPTOM:
A buzz from the exhaust system between 3,500 and 3,600 rpm.
PROBABLE CAUSE:
The flexible joint connections in the exhaust system have insufficient spring tension.
AFFECTED VEHICLES:
• 3-door (All except GS-R): Through VIN JH4DC4…VS015663.
• 4-door (All except GS-R): Through VIN JH4DB7…VS005274.
CORRECTIVE ACTION:
Replace the nuts, bolts, springs and gaskets at the “A” pipe outlet and the muffler inlet.
PARTS INFORMATION:
Flange gasket kit: P/N 18010-ST7-305.
REPAIR PROCEDURE:
1. Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature.
2. Make sure the exhaust system heat shields are not cracked or dented, and do not have any rocks in them. Perform any necessary repairs before continuing with this procedure.
3. Run the engine between 3,500 and 3,600 rpm, and listen for a buzzing noise from the exhaust system. If you hear it, continue to the next step.
4. Raise the vehicle and let the exhaust system cool for at least 30 minutes.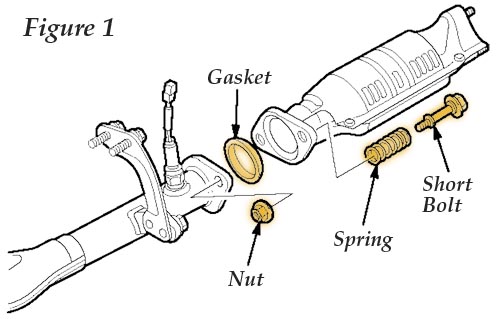 5. Remove and discard the nuts, bolts, springs and gasket at the connection of exhaust pipe “A” and the catalytic converter. See Fig. 1.
5. Remove and discard the nuts, bolts, springs and gasket at the connection of exhaust pipe “A” and the catalytic converter. See Fig. 1.
6. Find the two shorter bolts in the flange gasket kit and install them, along with the new nuts, springs and gasket at the connection of exhaust pipe “A” and the catalytic converter. Torque the bolts to 22 Nm (16 lb.-ft.).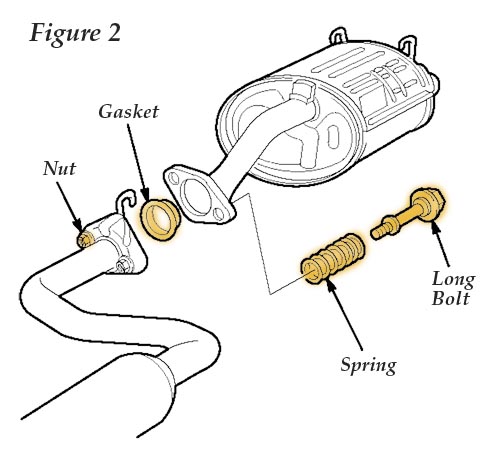 7. Remove and discard the nuts, bolts, springs and gasket at the connection of exhaust pipe “B” and the muffler. See Fig. 2.
7. Remove and discard the nuts, bolts, springs and gasket at the connection of exhaust pipe “B” and the muffler. See Fig. 2.
8. Install the two longer bolts from the flange gasket kit with the new nuts, springs and gasket at the connection of exhaust pipe “B” and the muffler. Torque the bolts to 22 Nm (16 lb.-ft.).
9. Lower the vehicle.
10. Run the engine to make sure the noise is gone.
Technical service bulletin courtesy Acura Parts Express.