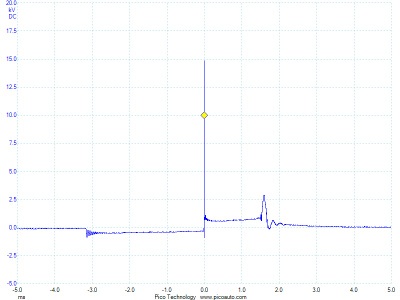
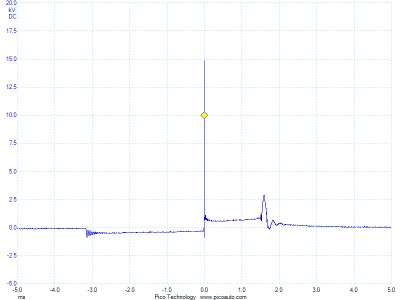


What if there are no codes and a misfire is intermittent? This is where it gets complicated.
What is a misfire? Is a misfire when the cylinder does not fire? Is it when the cylinder fires too soon or too late? The answer is “yes” to both questions. Some misfire complaints are a flashing check engine light, and a P0300 to P0312 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring. This is the easiest misfire to diagnose. But, what if there are no codes and a misfire is intermittent? This is where it gets complicated.
Engineers have devised two strategies that can be called the “immune system” for the electrical system.
The measurement of voltage is like the speed of the traffic.

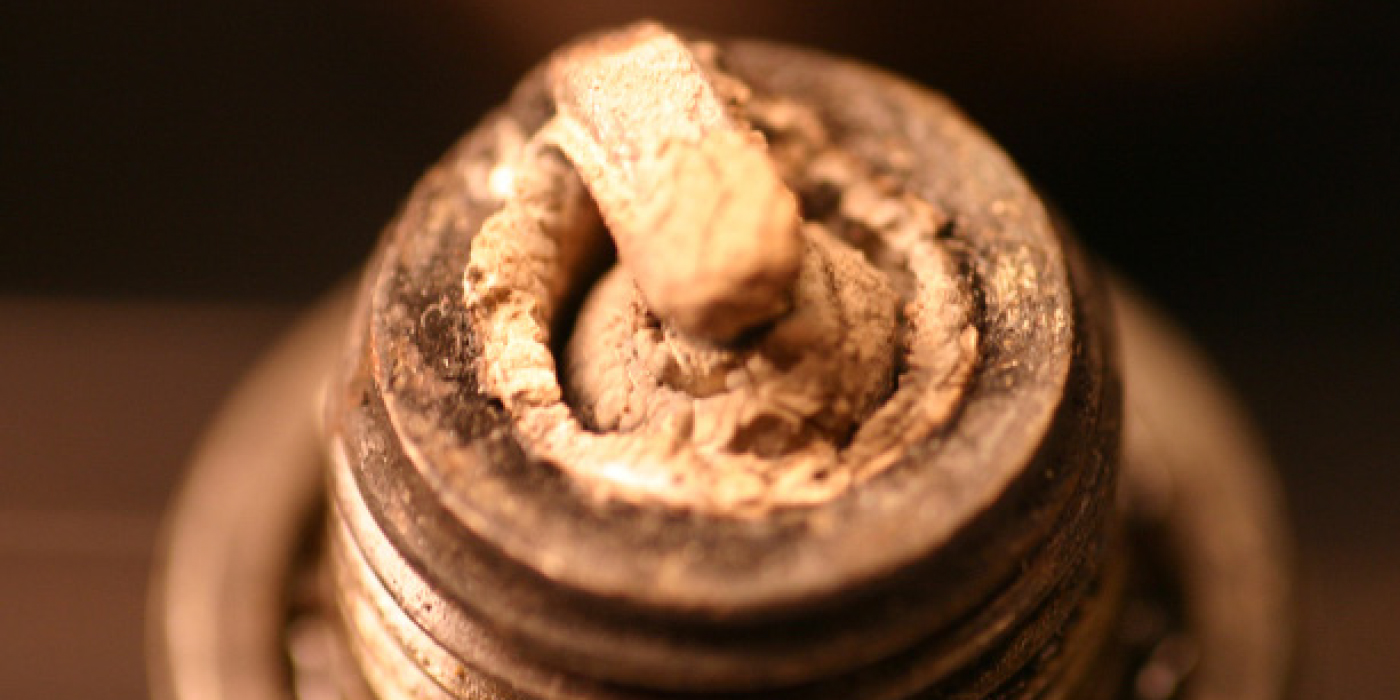
Understanding why spark plugs get dirty.

The problem may not have been caused by a complicated reason, something simple may have caused the system not to work.

The area of contact between the lifters and cam lobes is the highest loaded surface inside an engine.

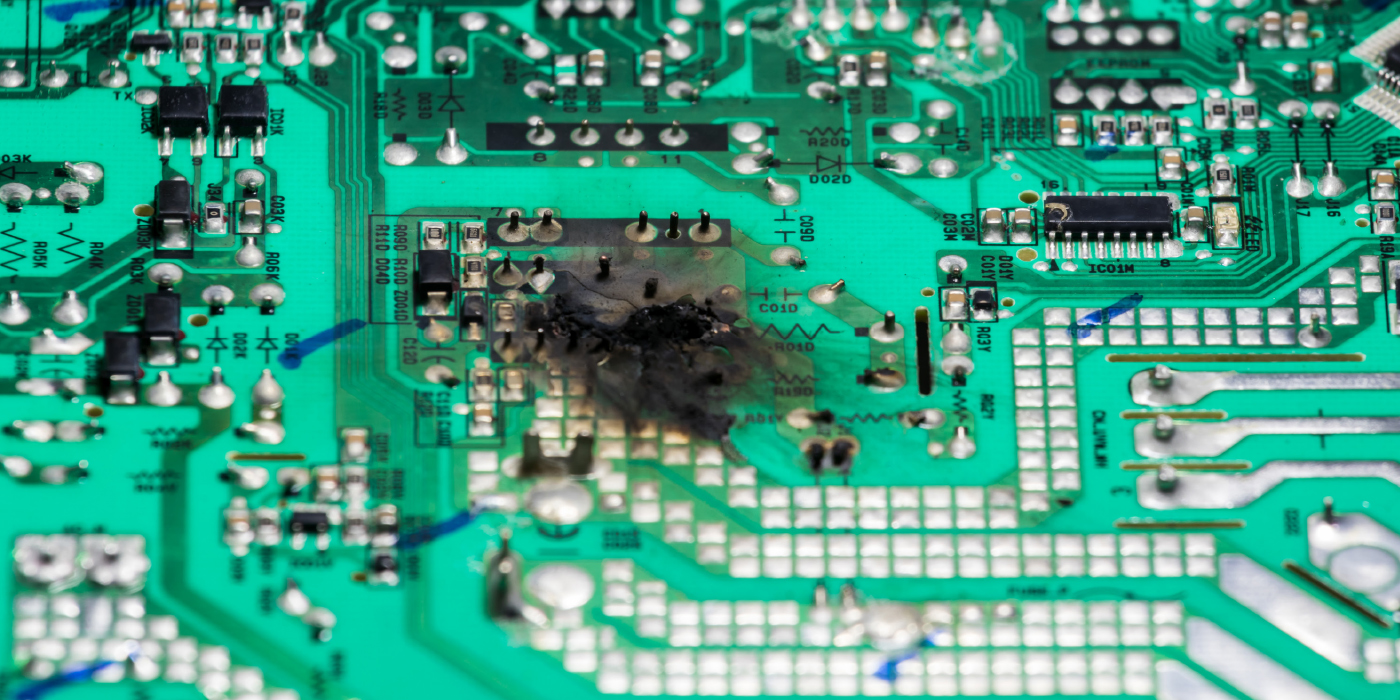
Many alternator problems turn out to be nothing more than a bad connection at the alternator or a bad wiring harness.

This video will focus on how a product like CAT COMPLETE can improve the chances of completing the monitors faster. This video is sponsored by Rislone.

All-season coolant used inorganic acid technology and worked great for almost 30 years.
