Models:
2006-2015 Sonata equipped with 2.0T or 2.4L engines
2010-2014 Santa Fe equipped with 2.0T or 2.4L engine
2010-2014 Tucson equipped with 2.4L engine
This bulletin provides information regarding the proper indexing of the timing marks of the Oil Pump Module during in-vehicle installation on vehicles equipped with Theta four-cylinder engines. If the Oil Pump Module timing marks are improperly indexed, abnormal engine vibration may result. Follow the service information outlined in this bulletin whenever a new or existing Oil Pump/Balance Shaft Module (BSM) is being installed.
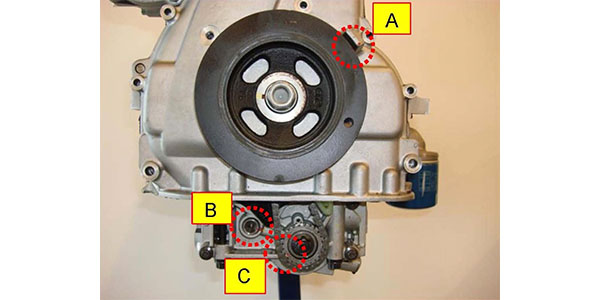
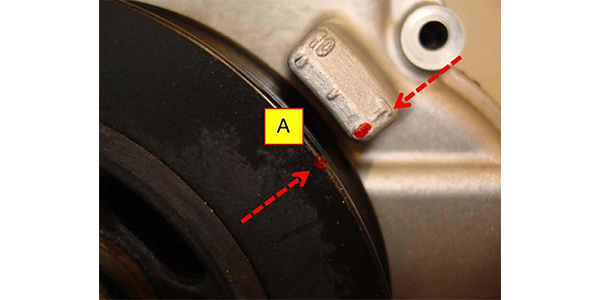
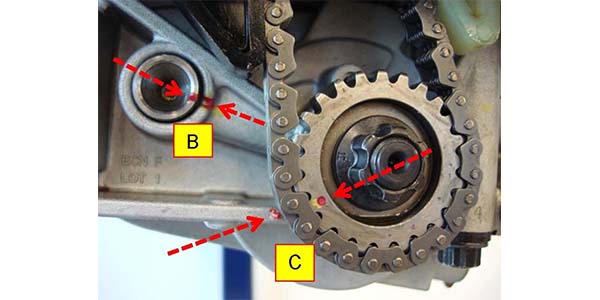
1. Prior to installing the lower oil pan, confirm the proper indexing of the Oil Pump Module timing marks. Locate the timing marks for: (A) crankshaft pulley and timing chain cover; (B) counterbalance driven shaft and housing; and (C) oil pump driven sprocket and housing.
2. Rotate the (A) crankshaft pulley until the notched mark on the pulley lines up with the 0° TDC sight mark “T” on the timing chain cover.
3. Confirm that the (B) counterbalance driven shaft and housing marks are lined up when the (C) oil pump driven sprocket and housing marks are lined up. If the (C) oil pump driven sprocket and housing marks are not lined up, then repeat Step 2 above by rotating the crankshaft pulley one complete turn clockwise. Step 2 may need to be repeated up to three times until the marks for both (B) and (C) line up.
• The counterbalance driven shaft (B) turns twice the crankshaft speed.
• The oil pump driven sprocket (C) returns to the same indexed position after four complete clockwise rotations of the crankshaft pulley (A).
• Reinstall the oil pump chain to the driven sprocket if all marks are not aligning correctly.
Courtesy of Mitchell 1.