Applies to: All 2002-’04 Honda CR-V
The MIL comes on with one or more of these evaporative DTCs stored: P0451 (FTP sensor circuit range/performance problem); P0452 (FTP sensor circuit low voltage); P0453 (FTP sensor circuit high voltage); P1454 (FTP sensor circuit range/performance problem).
Diagnosis:
The FTP (fuel tank pressure) sensor has an internal malfunction. Replace the fuel tank pressure sensor.
1. Connect the HDS to the DLC (data link connector).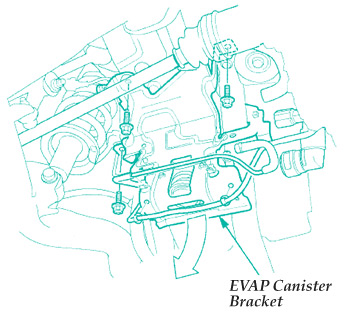
2. Remove the fuel fill cap.
3. Turn the ignition switch to the On (II) position.
4. Select the PGM-FI data list, and observe the fuel tank pressure sensor voltage.
• If the FTP sensor voltage is between 2.46V and 2.56V, run the evaporative function test and follow normal troubleshooting. This service bulletin does not apply:
• If the FTP sensor voltage is not between 2.46V and 2.56V, go to Repair Procedure.
Repair Procedure:
1. Remove the EVAP canister.
• Refer to page 11-217 of the 2002-’04 CR-V service manual, or
• Online, enter keyword EVAP, then select EVAP Canister Replacement from the list.
2. Remove the three EVAP canister bracket bolts and lower the EVAP canister bracket. See Fig. 1.
3. Remove the EVAP two-way valve and the fuel tank pressure sensor vacuum hoses. Then remove only the EVAP two-way valve.
4. Install the EVAP two-way valve onto the new canister bracket. See Fig. 2.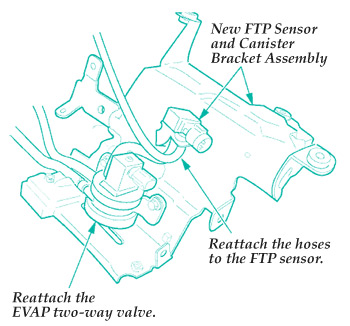
5. Install the remaining parts in the reverse order of removal.
Courtesy of IDENTIFIX.