By the time an engine needs a new oil pump it has had considerable wear. The cylinder walls, rings, cam and lifters all wear.
By the time an engine needs a new oil pump it has had considerable wear. The cylinder walls, rings, cam and lifters all wear.
The material worn off all goes to the oil pan where some is washed out during the oil changing process, but a portion goes through the oil pump and to the filter. Pushing grit through the oil pump puts an additional load on the oil pump intermediate shaft.
The photos in Figures 1-2 show the two most common types of intermediate shafts, the tongue and groove and hex. In both photos the respective shafts on the left are used. The shafts on the right are new. The used shafts are representative of ones from an engine ready for its first rebuild.
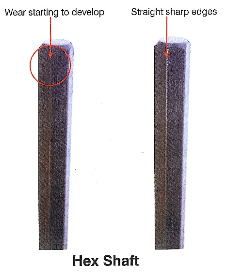 Both used shafts show wear and deformation when compared to the sharp, crisp lines of the new shafts. In time, the deformation can become severe enough to cause slippage and engine failure. Replacement is inexpensive insurance.
Both used shafts show wear and deformation when compared to the sharp, crisp lines of the new shafts. In time, the deformation can become severe enough to cause slippage and engine failure. Replacement is inexpensive insurance.
Source: Melling Engine Parts