Some Mazda B-2500 drivers may complain of a high idle in vehicles with a manual transmission. This may be caused by a poor electrical connection at the wire harness to the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS). A service kit (P/N 1F00-18-145) is available to resolve this concern. Correct the condition by following the steps in this Tech Tip.
Applicable Models:
All 1998-2000 Mazda B-2500 trucks with manual transmission.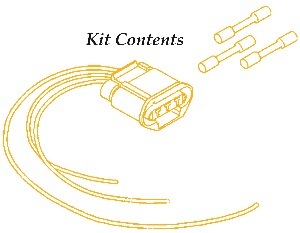
Repair Procedure:
1. Verify the customer’s concern.
2. Install the service kit (Fig. 1) per the instructions.
TPS Connector Installation Instructions:
1. Unhook the TPS connector (see Fig. 2).
2. Cut the TPS connector off at the connector and remove the plastic sheathing.
3. Install the sheathing on the new TPS connector pigtail.
4. Locate the brown/white wire at location A.
• Cut and splice in a butt connector (provided in the kit) approximately 45 mm from the TPS connector.
• Crimp butt splice connector and shrink tubing with a heat gun of an acceptable heat source.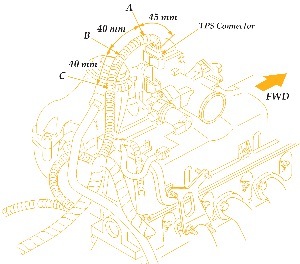
5. Locate the gray/white wire at location B.
• Cut and splice in a butt connector (provided in the kit) approximately 85 mm from the TPS connector using the above procedure.
6. Locate the gray/red wire at location C.
• Cut and splice in a butt connector (provided in the kit) approximately 125 mm from the TPS connector using the above procedure.
7. Reinstall the plastic sheathing.
8. Tape over all the wiring and sheathing with electrical tape or equivalent.
9. Install the TPS connector to the TPS sensor.
10. Road-test the vehicle to verify the repair.
Written by Ed Dorowski, ALLDATA editor, and Jeff Webster, ALLDATA technical writer.