What is a medium-duty truck? The industry defines it as a vehicle with a Gross Vehicle Weight of 14,000 to 26,000 lbs. At 14,000 lbs., most heavy-duty one-ton trucks qualify as a medium duty vehicle. In light- and medium-duty trucks, the automatic transmission is ever increasing in popularity and numbers. So why am I talking about a clutch for a manual transmission in a shrinking market? Most of these trucks with the manual transmissions tend to be in the ownership of individuals and small fleets that do not have their own maintenance facility. This makes them a customer for a shop that has a lift and equipment to service medium-duty chassis and suspension to expand their service opportunities.
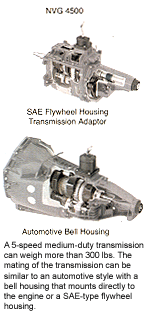
 When it comes to tools, you will need a heavy-duty transmission jack. The transmission with bell housing or flywheel housing adapter can weigh more than the technician, because it is probably connected to a diesel engine. Medium-duty diesel engines are available from Cummins, Detroit Diesel, Ford, GM, Isuzu, Navistar, and other manufacturers. A Cummins ISC engine weighs 1,500-plus lbs. The transmissions are from Dana, Eaton, Getrag, New Venture Gear, and other manufacturers. A Dana Fuller 5-speed can weigh more than 300 lbs. The mating of the transmission can be similar to an automotive style with a bell housing that mounts directly to the engine or a SAE-type flywheel housing.
When it comes to tools, you will need a heavy-duty transmission jack. The transmission with bell housing or flywheel housing adapter can weigh more than the technician, because it is probably connected to a diesel engine. Medium-duty diesel engines are available from Cummins, Detroit Diesel, Ford, GM, Isuzu, Navistar, and other manufacturers. A Cummins ISC engine weighs 1,500-plus lbs. The transmissions are from Dana, Eaton, Getrag, New Venture Gear, and other manufacturers. A Dana Fuller 5-speed can weigh more than 300 lbs. The mating of the transmission can be similar to an automotive style with a bell housing that mounts directly to the engine or a SAE-type flywheel housing.
As for specialized training, all shops need is a good tech who knows how to use a dial indicator and has changed an automotive clutch assembly. It is just a larger than normal nut and bolt job. Details to follow.
 A medium-duty clutch disc can range form 11-1/2 to 14 inches in diameter and be spring dampened or a solid disc. The lining material can be an asbestos-free organic or a sintered metallic. The pressure plate can have a diaphragm-type spring or coil springs. The coil spring clutch is sometimes referred to as a Borg & Beck-type clutch.
A medium-duty clutch disc can range form 11-1/2 to 14 inches in diameter and be spring dampened or a solid disc. The lining material can be an asbestos-free organic or a sintered metallic. The pressure plate can have a diaphragm-type spring or coil springs. The coil spring clutch is sometimes referred to as a Borg & Beck-type clutch.
The clutch release bearing, or as some call it a throw out bearing, is a thrust-type bearing located around the input shaft and is actuated mechanically or hydraulically. The mechanical system uses a lever and pivot to engage the release bearing. A hydraulic master and slave cylinder actuates the lever of the mechanical system. In the hydraulic system, the slave cylinder directly actuates the release bearing.
New Clutch Installation
Resurfacing of the friction surface on the flywheel should be considered a standard part of a new clutch installation. All of the mounting surfaces should be clean and free of any surface distortion. No nicks or gouges on the edges, as well as on the mounting surface itself. The input shaft pilot bearing should also be replaced with the new disc and pressure plate. It is a good practice to go back with the same configuration as designed for the vehicle.
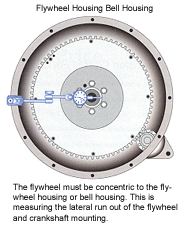
 Flywheel Mounting and Alignment
Flywheel Mounting and Alignment
A dial indicator is used to check the alignment of the flywheel and housings. A magnetic base dial indicator can be attached to the flywheel housing or engine block. If the flywheel housing or engine block is aluminum, the dial indicator will have to be clamped or a bolt hole fixture can be made by welding a small stud to a piece of plate.
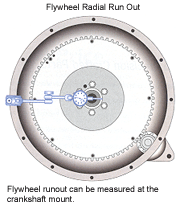
The flywheel concentricity is measured by attaching the dial indicator to the flywheel housing or engine block and the contact point is set to ride against the flywheel and crankshaft at an angle.
The flywheel must be concentric to the flywheel housing or bell housing. This is measuring the lateral run out of the flywheel and crankshaft mounting. A magnetic base is attached to the flywheel and the contact point aligns with the center of the flywheel.
 The lateral run out of the flywheel surface is measured by attaching the dial indicator to the flywheel housing or engine and the contact point is set to ride in the center of the friction surface.
The lateral run out of the flywheel surface is measured by attaching the dial indicator to the flywheel housing or engine and the contact point is set to ride in the center of the friction surface.
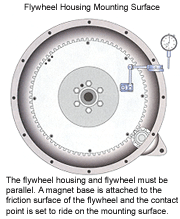
The flywheel housing and flywheel must be parallel. A magnetic base is attached to the friction surface of the flywheel and the contact point is set to ride on the mounting surface.
All manufacturers’ specifications for torque, run out and clearances should be followed. If no specifications are provided for the dial indicator, a