Model(s) affected: All 1998–2006 1.8L Turbo vehicles.
Condition:
DTCs P1297 (17705) or P1557 (17965) are stored in DTC memory. This may be caused by intake hoses leaking (during boost conditions), due to incorrect torque on clamps or improper placement, or worn or torn intake hoses, etc.
Service Procedures:
Perform an intake system pressure test to detect leaks in the intake system as follows:
1. Separate the intake hose from the mass air flow sensor (MAF) assembly.
2. Remove the crankcase ventilation hose from the PCV valve and close off the crankcase side of the valve with the plug (orange arrow, Fig. 1), hose and clamps (supplied with the turbocharger tester, P/N VAG 1687). 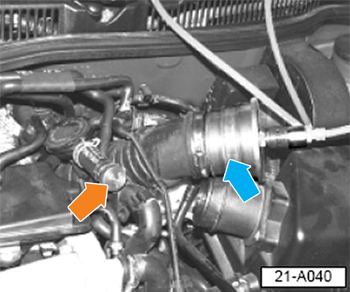
Tip: This will disconnect the engine crankcase from the intake system.
3. Insert the air pressure adaptor, P/N VAG 1687/1 (blue arrow, Fig. 1) into the intake hose between the MAF sensor and the intake system (clamp using the existing hose clamp).
Tip: The hose at the throttle assembly will stay connected during the test.
Pressure Test:
1. Attach the outlet hose of the turbocharger tester to the fitting on the air pressure adaptor (blue arrow, Fig. 2).
2. Close the outlet valve after the gauge.
3. Back off the pressure regulator knob of the turbocharger tester fully to protect the gauge when shop air supply pressure is applied to the assembly. 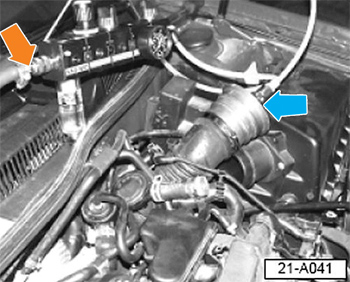
4. Attach an air line to the inlet fitting on the turbocharger tester.
5. Open the valve between the regulator valve and gauge.
6. Adjust the test pressure up to 0.5 bar by turning the regulator valve.
Note: Do not pressurize the system above the 0.5 bar! Doing so will force oil into the intake through the throttle body assembly, causing damage to the engine.
7. Slowly open the outlet valve (after the gauge) to test the hose connections.
8. Observe the pressure gauge for a drop in pressure.
Tip: Some pressure will be lost past the throttle plate.
9. Apply soapy water or leak-check liquid to all intake system connections to check for leaks.
Tip: An ultrasonic tester may also be used to locate leaks.
10. Repair any leaks that are found.
11. Remove the plug from the crankcase ventilation hose.
12. Remove the air pressure adaptor and reinstall the hoses.
Courtesy of Mitchell 1.