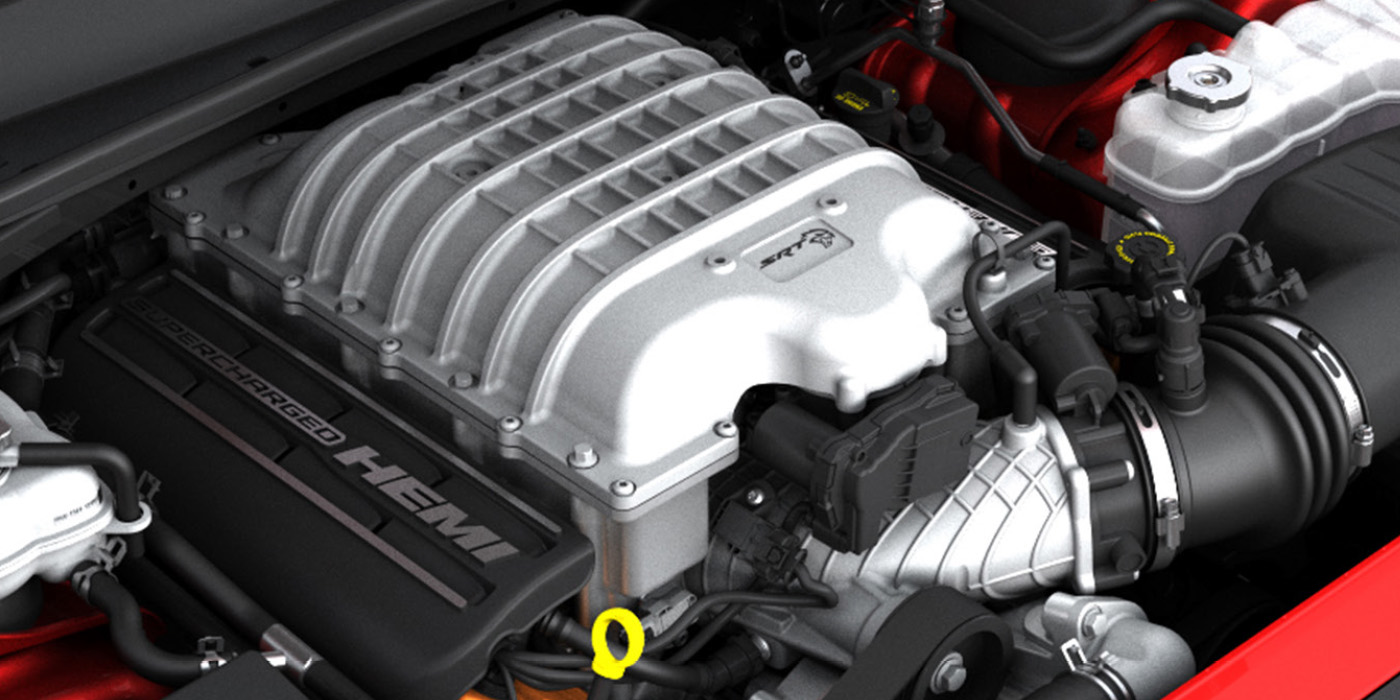
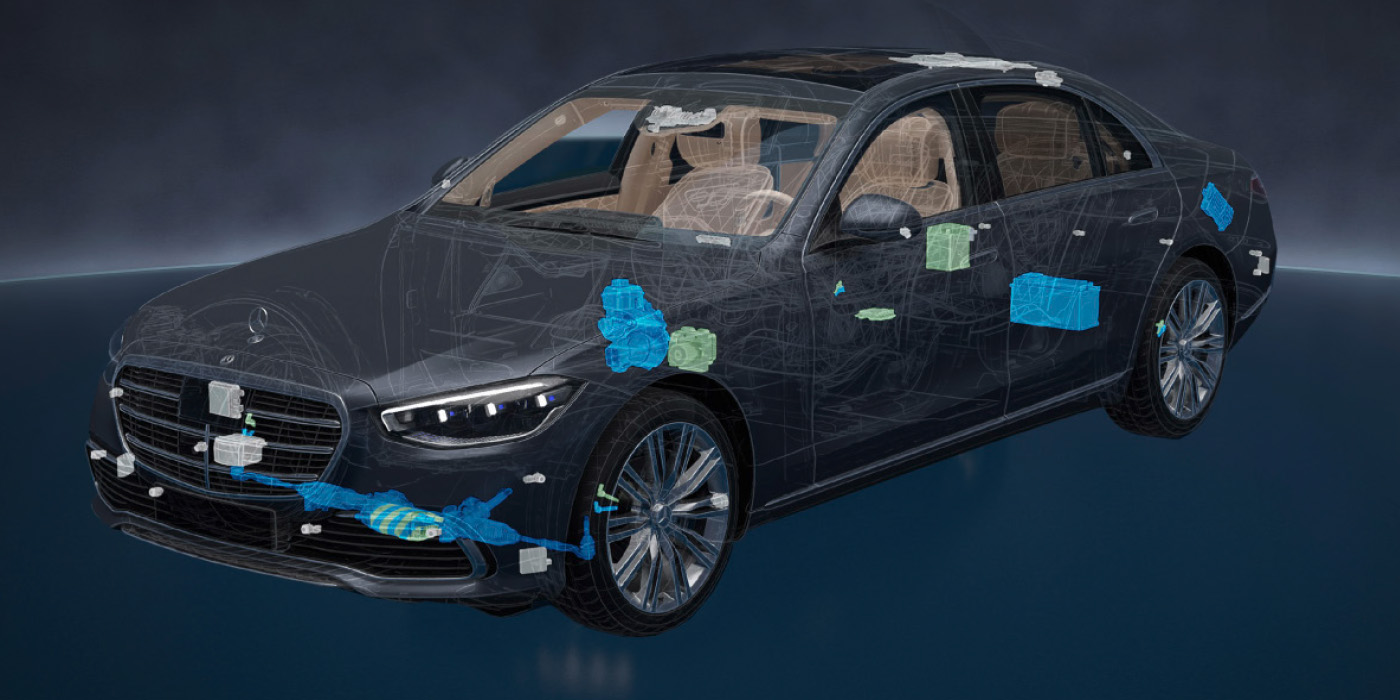
Technicians, shop owners and service advisors are not Shakespeare. If something can be summed up in two words, we will do it. Unfortunately, this can lead to a loss of detail when it comes to an ignition complaint or symptom.
Take the phrase, “no spark.” It typically means the engine is not starting because a spark can’t be “seen” or “felt” between the electrodes. But, “no spark” is not a diagnostic or repair path.
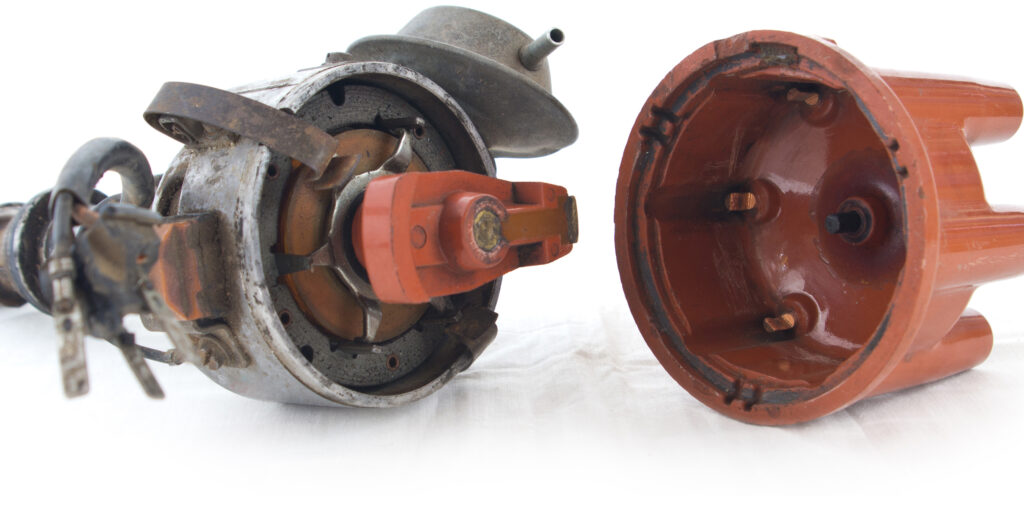
In the past, a “no spark” problem was easy to solve with the parts shotgun. A technician could install plug, wires and points without flinching or additional authorized funds. A replacement distributor might raise some eyebrows. But, “no spark” diagnostics changed in the early 1970s as magnetic pick-ups replaced points and fuel injection synchronized with the ignition system to reduce emissions.
The “no spark” phrase is even vaguer these days when you encounter vehicles that have multiple modules that power, control and secure the ignition system. A no- spark condition could be the result of communication errors or missing data from a dead module.
‘Know Spark’ not ‘No Spark’
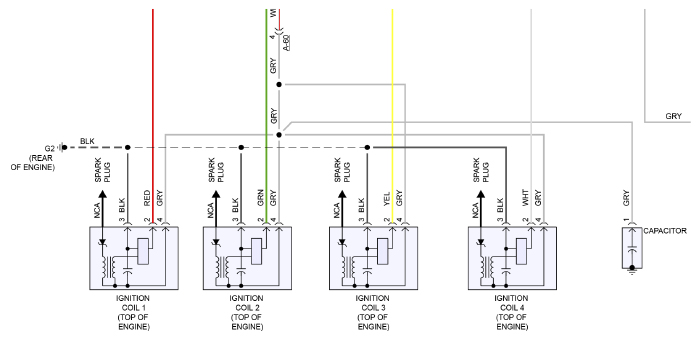
The reason why so many techs never confirm a “no spark” diagnosis before ordering parts is because of a lack of information and understanding of the ignition system. The first thing a technician needs to grasp is a coil’s control and output.
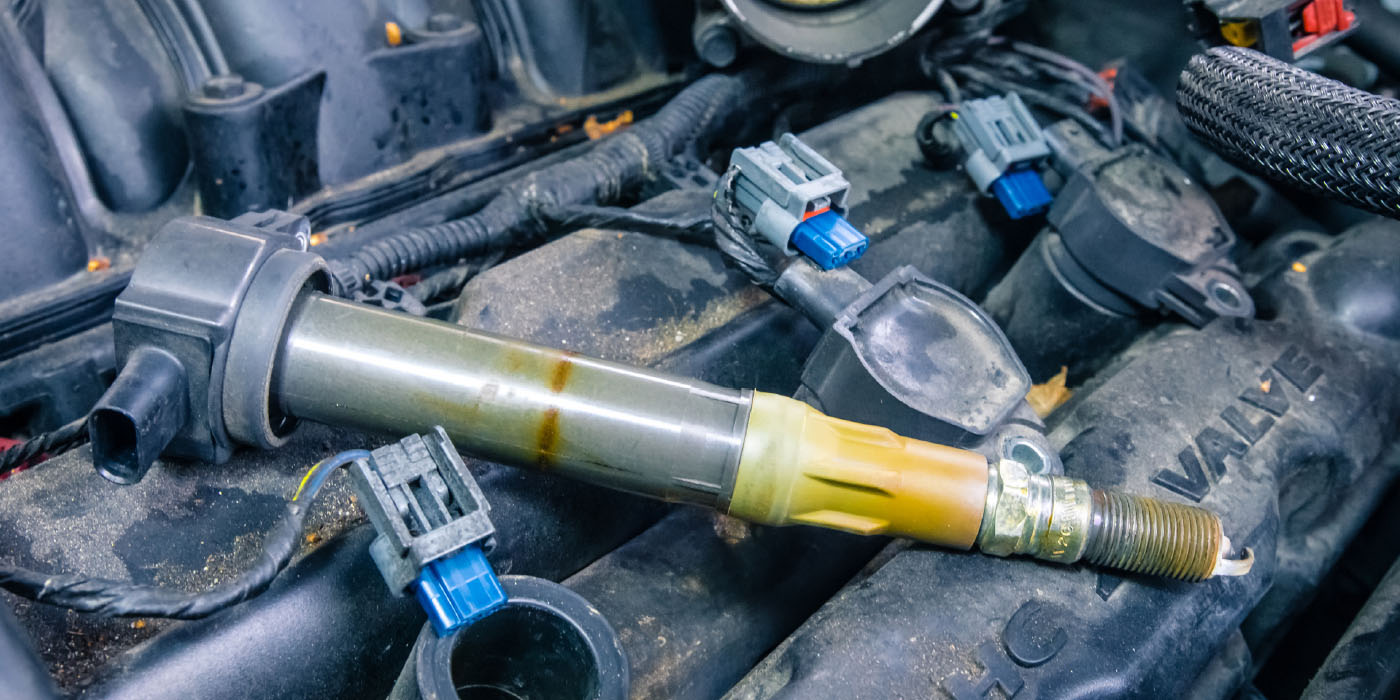
Since the 1900s, a coil uses low-voltage/high-current electricity to saturate the primary windings, where it is transformed into high-voltage/low-current power to jump the electrodes of the spark plug.
How power is turned off and on to the primary side of the coil is often where the problem can be for a “no- spark” scenario. In the days of points, the switch for the primary coils were lobes on the distributor’s shaft. The mechanical nature of this switch requires adjustment as the parts wear.
As magnetic pick-up sensors replaced points, it is a transistorized or solid-state switch that rapidly turns power on or off to energize the primary side of the coil. While the need to adjust for worn parts was no longer part of the problem, electronic parts are susceptible to environmental conditions and system problems like high resistance in a connector.
Your Ignition ‘Inner Child’
As you progress in your diagnostic career, you can lose your curious inner child when it comes to solving ignition problems. Sometimes, your curiosity has lead you in the wrong direction and cost you time, or it has led to a comeback. But, hopefully, your curious inner child is still growing, fueled by new knowledge and experience.
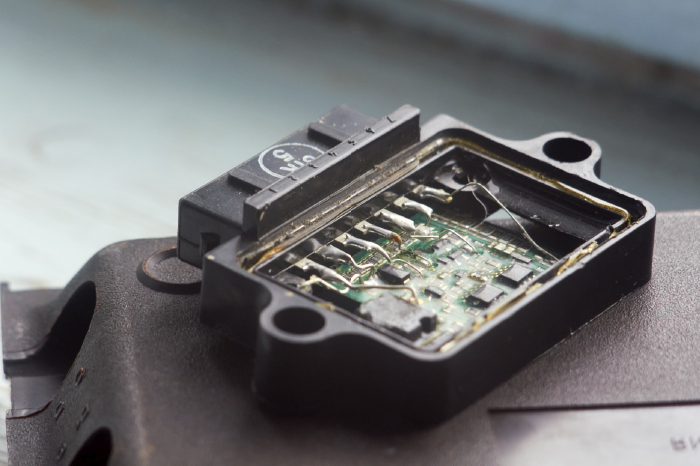
The most important thing to feed your inner child is information to ask questions that form a proper diagnostic procedure. One of the most critical question you can ask is, “What drives the primary side of the coil?” In some systems, it is the engine control module or ignition control module. On some vehicles, it could be a small circuit board on the coil that triggers the primary and secondary. This is why the first task in your diagnosis should be to retrieve a wiring diagram.
No matter where the driver is located, as mentioned earlier it is a transistorized or solid-state switch that rapidly turns power on or off to energize the primary side of the coil. This is a great starting point to see if an ignition circuit has power and control. This information is far better than swapping a coil to track a misfire or no-spark condition. Why? That small transistor that switches power in the primary can be damaged by shorts and bad grounds. You could be injuring another driver in an expensive module if you have a grounded coil. If the transistor is on the coil, you could end up damaging multiple coils by swapping.
You have to let your ignition inner child roam further if there is no control or power at the connector; it can require some hand-holding. Deciding when or if the coil is fired is typically governed by several pieces of data. On the engine management side, the coil may need inputs from engine position, oil pressure and knock sensors. On the body side, the ignition system might need inputs from security and body modules.
These can be difficult for the ignition inner child to envision. This is why we have scan tools. By talking to the modules, you can see if inputs are missing and if codes are set.
An ignition inner child is only as good as your ability and patience to navigate service information. Service information can contain critical test, resistance values and service procedures to help isolate the fault.