Complaints about poor heater performance may become more prevalent as more Americans begin driving again and cooler fall and winter temperatures return. Following up on complaints about cold air blowing from the vents even with the heater set to high might lead you to the conclusion that a faulty thermostat or heater core may be the cause.
Unfortunately, replacement of those components may not be the solution.
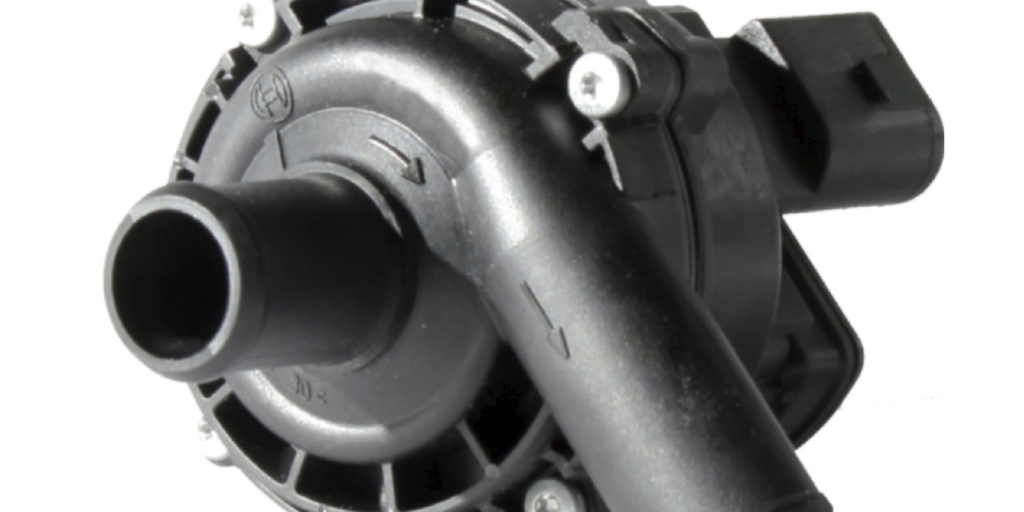
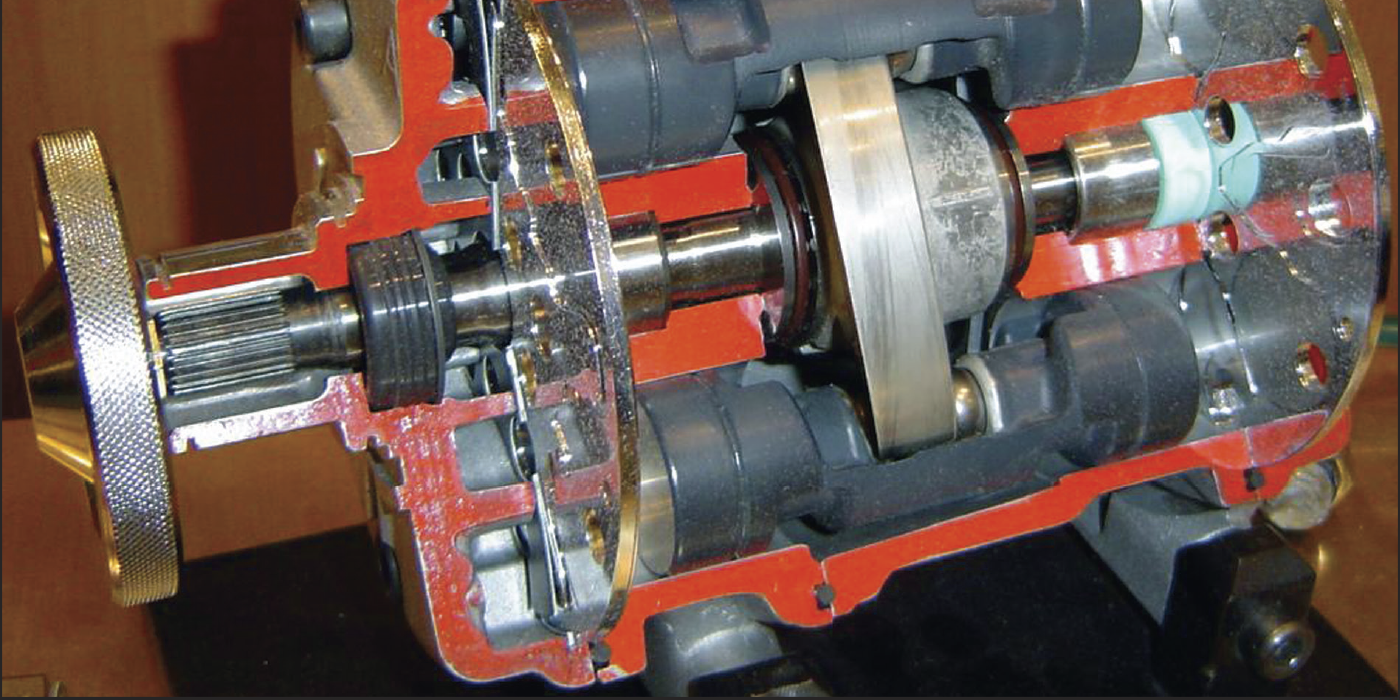
The auxiliary water pump is designed to circulate warm coolant to the heater core and, if too little coolant is circulated, the blower fan will pull enough heat out of the coolant and cause the heater core to get cold.
These pumps were first used on luxury and diesel vehicles in the 1990s. Most diesel engines typically do not generate a lot of heat when running or idling. Coupled with the lower engine speeds, the coolant in the heater core would lose most of its heat before it passed through to the outlet. This would frequently cause drivers to complain about insufficient heating if they drove in stop-and-go traffic or cruised at speeds with lower RPM. So, adding an auxiliary coolant pump would provide enough volume of coolant to keep the heater core warm.
Engineers then started to use these pumps on gasoline-powered vehicles for the same purpose. This allowed vehicle designers to use larger heater cores to provide better passenger comfort.
The control of the pump as part of the automatic temperature control system keeps the cabin heated even after the driver has turned off the ignition. The system can keep the interior warm for short periods of time while the driver goes shopping or grabs a bite to eat.
These pumps will continue to be used on more and more vehicles as engines become more efficient and generate less excess heat. Also, new technologies like hybrid drives and stop/start systems need auxiliary pumps to not only improve driver comfort, but also to keep the batteries at a constant temperature.
MODES OF OPERATION
Note that the auxiliary pump does not operate continuously. It is controlled and regulated using the BCM or controlling module using a variety of inputs including:
• Vehicle speed;
• Engine RPM;
• Coolant temperature;
• The temperature selected on the control head;
• Blend door position;
• Fan speed; and
• Exterior and interior temperatures.
If the vehicle has key-off control, there are additional parameters that must be met to activate the pump. These include:
• Battery voltage;
• Supply voltage to blower motor;
• Recirculation flap position;
• Security module input; and
• Keyless entry fob location.
A scan tool can test the pump function in most vehicles, but it is also possible to test the system by pressing an HVAC control head button sequence listed in the service information.
CAUSES OF FAILURE
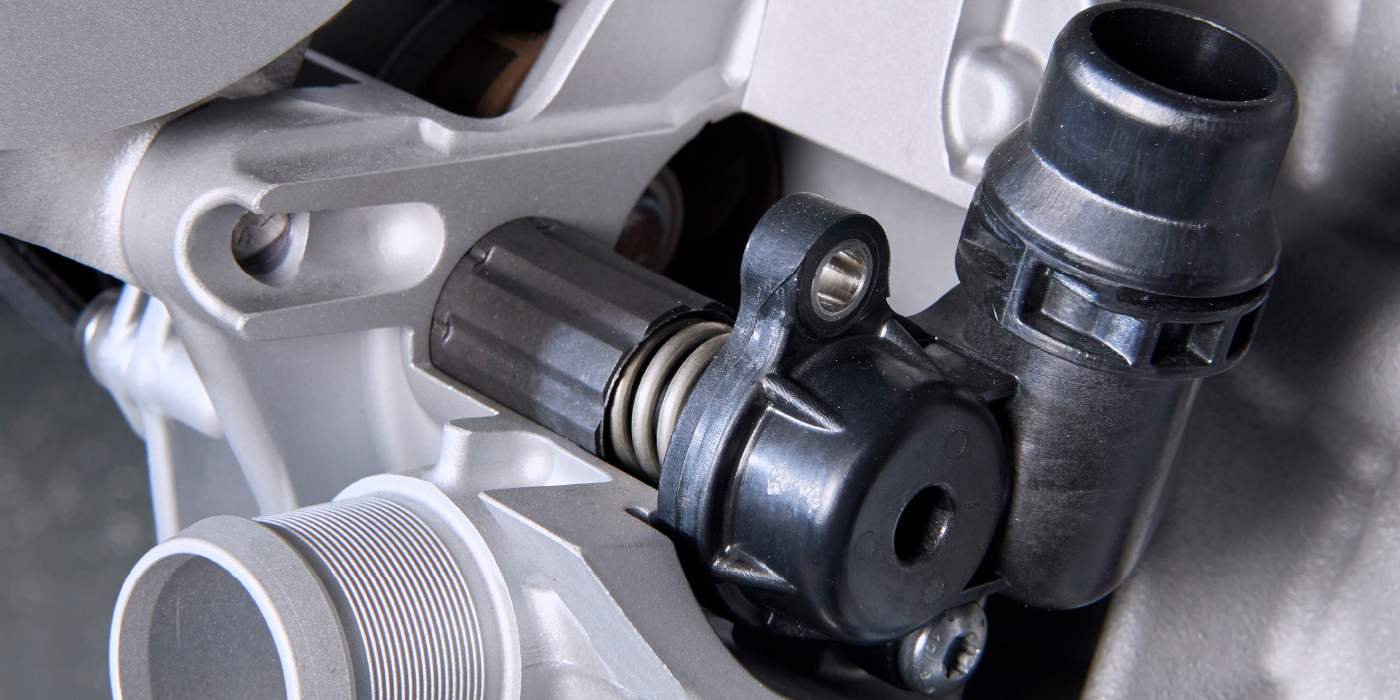
These pumps usually fail due to age and wear of the electric motor. Like all rotating electrical devices, brushes wear and windings short. Overheating can hasten the electric pump’s failure because increased cooling system pressures can force coolant past the shaft seals. Low coolant can also cause a pump to fail because of its position, which is typically high in the system, either on the firewall or strut tower.
FAILURE MODES
A failed pump will almost never cause the vehicle to overheat. If the auxiliary coolant pump is inoperative, the customer might notice reduced heater performance at low speeds and at idle.
Your first instinct might be to replace the thermostat, the water pump or the heater core, but if the vehicle is equipped with an auxiliary coolant pump, you will need to dig a little bit deeper with your diagnostic process.
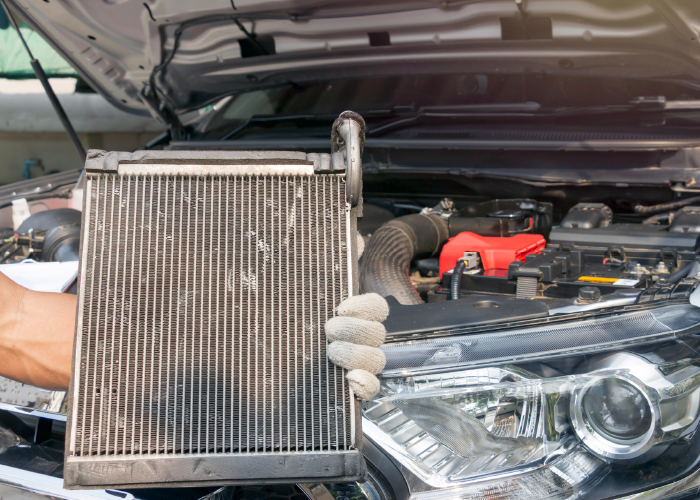

DIAGNOSIS
The first step in the diagnostic process is to check for codes with a scan tool. Unrelated codes for collision detection, door module operation and loss of communications incidents can cause the deactivation of the pump. This is where service information can make the difference between a quick diagnostic process and parts swapping.
Newer vehicles may vary the voltage to control pump speed. Like all electrical devices on a vehicle, the operation is a balancing act between driver comfort and minimizing electrical loads on the alternator.
The cooling circuit on some vehicles with electric pumps may be called an auxiliary cooling circuit in the service information. The coolant may travel through the transmission cooler and windshield washer fluid bottle as part of the circuit on some Mercedes models.