Models
All 1994-2016 (except Routan)
Technical Background
Coolants G11, G12, G12+ and G12++ have been replaced by an improved version. G13 coolant is introduced on all engines.
Service
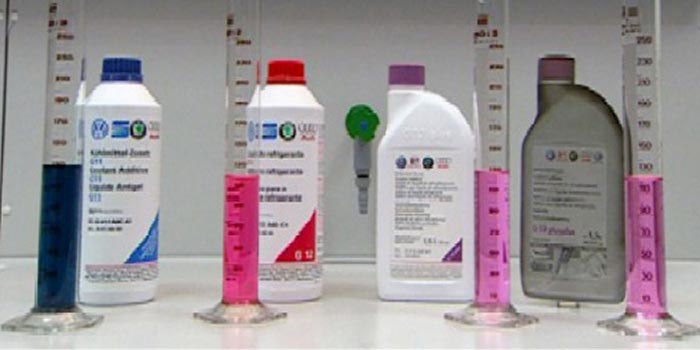
Identify which coolant the vehicle was filled with from the factory. The photo below shows the color of each type of engine coolant.
Note: The photo above is for color identification only. Your packaging may vary.
The table identifies which coolant can be added to the factory coolant.
Note: G12+, G12++ and G13 coolants are lifetime coolants when used exclusively in the coolant system (not mixed with other coolants).
Coolants can be mixed, as described in the chart, but it is always a best practice to change the coolant due to reduced corrosion protection when coolants are mixed.
Additionally, coolants can be mixed, as described in the chart, when adding/topping off fluid levels. When the coolant is changed due to a cooling system issue, the cooling system should be drained and filled.
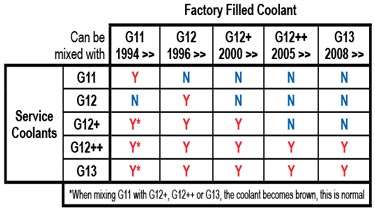 The table is read by identifying the factory filled coolant at the top and comparing it to the available service coolants to the left. (Example: If the car was factory filled with G12++, the coolant allowed is G12++ or G13.)
The table is read by identifying the factory filled coolant at the top and comparing it to the available service coolants to the left. (Example: If the car was factory filled with G12++, the coolant allowed is G12++ or G13.)
Tip: If a vehicle is found to have the incorrect coolant, the cooling system should be drained and then filled with the correct coolant.
Note: Cooling system drain and fill due to coolant mixing or incorrect coolant is not covered by warranty.