In the past 15 years, turbochargers have become more common on all types of vehicles from 1.4L to 7.0L. These are the top TSBs to help diagnose the most common problems.
Subaru: Inspect Oil Supply Before Replacing a Turbo
Models: All turbocharged Subarus
TSB Number: 02-106-08R
This TSB serves as a warning to technicians that before installing a replacement turbocharger, the integrity of the oil supply that lubricates the shaft bearings must be inspected. The TSB instructs technicians to remove the mesh filter in the oil supply line. If the filter is obstructed, it could be a sign of engine sludge and poor maintenance.
The filter is located in the banjo bolt that attaches the line to the engine. Subaru advises that, if the filter is clogged, to also look for additional debris in the pan. Also, the copper washers on the banjo fitting are a one-time-use item.
 Chevrolet Cruze: Check the ECM Calibration
Chevrolet Cruze: Check the ECM Calibration
Models: All Cruze models with the turbocharged 1.4L engine.
TSB Number: PI0851A
This TSB advises technicians to check the ECM to make sure it’s running the latest calibration. The latest calibration contains a function that allows the cooling fans to run for a short period of time when the vehicle is off (after the vehicle has been driven under certain conditions).
This latest calibration also allows the turbocharger to cool in less time, reducing the likelihood of the oil coking in the oil feed pipe. Good vehicle maintenance practices will also help to reduce the chances of the oil coking in the oil feed pipe. To avoid the customer coming back with a concern, you should inform them of the calibration change that allows the fans to run after the vehicle is shut off.
Chevrolet: DTCs P0234 or P0238 Set and No Performance
Models: Cruze
TSB Number: PI0466
This TSB points technicians in the direction of the vacuum hose connected to the waste gate regulator solenoid valve. An obstruction in the vacuum hose can cause codes P0234 or P0238 along with a no-power complaint from the customer.
Ford: 6.0 Diesel Turbo Coking
Models:
2003-‘05 Excursion
2003-‘07 F-Super Duty
2004-‘09 E-Series
2004-‘07 F-650, F-750 with the 6.0L diesel
TSB Number: 09-16-05
Some Ford F-Series trucks equipped with a 6.0L turbo diesel engine may exhibit any one, or a combination of the following concerns: lack of power, white/black smoke or a surge.
On the 2003-‘07 F-Super Duty, 2003-‘05 Excursion and 2004-‘09 Econoline, the lack of power and smoke may or may not be accompanied by any one, or a combination, of the following DTCs: P0238, P0299, P0404, P0478, P2262 and/or P2263. These concerns and/or DTCs could be a result of coking deposits inside the turbocharger.
Coking deposits inside the turbocharger turbine housing can impede vane response causing high or low instances of exhaust pressure. Unexpected exhaust pressure results can cause over-boost, under-boost, insufficient or excessive exhaust gas recirculation, or unexpected EGR valve position, which would result in these symptoms.
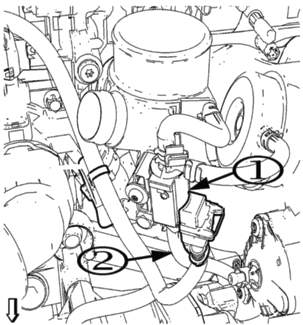 Chrysler: Diagnosing Dust
Chrysler: Diagnosing Dust
Models: Cummings Diesel from 2003-‘12
TSB Number: 09-004-11
This TSB looks at the dust in the intake and turbo system and what can happen to the turbo system if the filter fails or non-approved intakes are used. This nine-page TSB is a must read during some down time. It will make some drivers think twice about skipping maintenance service.
Mazda: Dimples Are Not Damage
Models:
2007-‘10 Mazdaspeed3
2006-‘07 Mazdaspeed6
2007-‘10 CX-7 2.3L
TSB Number: 01 033/10
This TSB concerns a small dimple found on the surface of a turbocharger blade of the 2.3L Mazda engine. The dimple is machined by design and is not due to damage or poor manufacturing quality. The machined dimple is important to ensure rotational balance of the turbine and compressor wheels at high rpm.