Some owners of 2004-2005 Dodge Durango vehicles may complain of brake shudder or vibration. The following technical service bulletin involves installing brake pads, resurfacing the rotors and checking rotor runout.
Symptom/Condition:
The vehicle may exhibit pulsation or vibration in the brake pedal and/or steering wheel when the brakes are applied. The condition is most noticeable at speeds over 50 mph, but can occur at lower speeds.
Diagnosis:
If the customers indicate that the condition is present, perform the repair procedure.
Repair Procedure:
1. Inspect the front brakes for any signs of abnormal wear or damage. Repair as necessary.
2. Resurface the front brake rotors with a DaimlerChrysler approved on-car brake lathe. If an on-car lathe is not available, the rotor resurfacing must be sublet to a facility with an approved on-car lathe.
3. Remove the calipers.
4. Clean the caliper adapter.
5. Replace the front pads and anti-rattle springs with p/n 05139733AA (brake pads).
6. Mark one wheel stud on each side with a dab of paint or suitable marker.
NOTE: Wheel stud torque is critical to the success of the repair. The following procedure is intended to identify excessive rotor distortion, which could be caused by improper wheel stud torque.
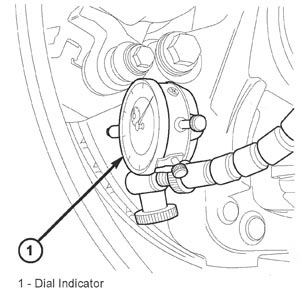 7. Install the wheel and assembly to the hub. Pre-tighten the lug nuts in a cross pattern to 100 Nm (75 ft.lbs.) then final tighten the lug nuts in a cross pattern to 200 Nm (145 ft.lbs) for steel wheels or 175 Nm (130 ft.lbs) for aluminum wheels. Mark the wheel at the same location as the marked wheel stud.
7. Install the wheel and assembly to the hub. Pre-tighten the lug nuts in a cross pattern to 100 Nm (75 ft.lbs.) then final tighten the lug nuts in a cross pattern to 200 Nm (145 ft.lbs) for steel wheels or 175 Nm (130 ft.lbs) for aluminum wheels. Mark the wheel at the same location as the marked wheel stud.
8. Set up a dial indicator to measure mounted rotor runout. Place the dial indicator plunger against the inner machined rotor face, visible between the brake caliper and the front splash shield (Figure 1). Rotate the wheel and tire assembly two turns and take runout measurement. If the measurement is less than .025 mm (.001 in.), no further action is required. If the measurement is greater than .025 mm (.001 in.) remove the lug nuts and relocate the wheel one stud clockwise, tighten the lugs nuts and described in step 7 and check the runout again. Do not remove any brake parts. Repeat step 8 for each wheel location until you achieve the lowest mounted runout. Minimum mounted rotor runout will be achieved by moving the wheel, not the rotor.
Technical service bulletin courtesy of Mitchell 1.
For more information on Mitchell 1 products and services, automotive professionals can log onto the company’s website at www.mitchell1.com.