>
Note: To access the mount, remove the battery box.
11. Lift the engine again using the jack until the No. 4 engine mount is lifted slightly from the vehicle body. Note: Do not raise engine too much or A/C pipe damage may occur.
12. With the top plate of the No. 4 engine mount removed, move the engine mount bottom plate or the engine until all four installation studs on the vehicle align with the engine mount holes.
See Figure 2.
13. Place the top plate back on and tighten the No. 4 engine mount bracket nuts and bolts to the torque indicated in Figure 3.
Tightening torque:
a: 32.5-45.0 ft.-lbf. (44.0-61.0 Nm)
b: 61.1-86.7 in.-lbf. (6.9-9.8 Nm)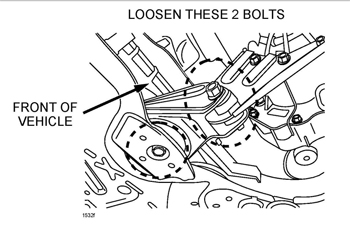
14. Lift the engine again using the jack and loosen the two bolts on the No. 1 engine mount rubber until they are slightly loose on the No. 1 engine mount rubber.
See Figure 4.
15. Shake/rock the engine back and forth.
16. Tighten the bolts in order below.
a: Crossmember-side No.1 engine mount rubber. Tightening Torque: 68.7-86.1 ft.-lbf. (93.1-116.6 Nm)
b: Engine-side No. 1 engine mount rubber. Tightening Torque: 68.7-86.1 ft.- lbf. (93.1-116.6 Nm)
A/C Pipe Adjustment
Note: The A/C pipes and bracket are located on the right rear of the engine compartment, bolted to the frame rail.
1. Loosen the A/C pipe bracket bolt and/or nut.
2. Position the A/C pipe bracket so the A/C pipes are as close to the center in the bushings as
possible.
Note: On Mazda5, center both A/C pipes and on Mazda3, center only the rear pipe as the front pipe cannot be centered due to bushing thickness.
3. Tighten the bolt and nut. Tightening torque: 61.0-86.8 in.-lb. (6.89-9.80 Nm)
Courtesy of Mitchell 1.