Although diesel power normally is associated with medium- and heavy-duty trucks, since the mid-1970s, diesel power has moved into the light truck and even the passenger car categories. In Europe, the diesel-powered passenger car shares 50% of the market. 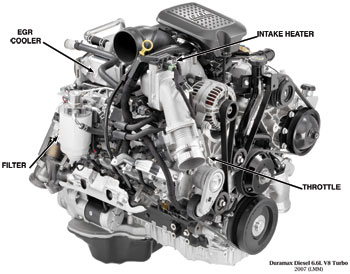
Is there a diesel in your service bay? Maybe not now, but there definitely will be in your future. You’re going to see trucks as well as SUVs and passenger cars. Mercedes-Benz produced a 3.0L V6 diesel-powered SUV for the 2008 model year and Volkswagen has a Twinturbo 5.0L V10 diesel engine in its Touareg. As the automakers focus on better fuel economy, you might say the diesels are coming again.
The primary advantage of diesel power is fuel economy. A diesel averages 25% better mileage than a gasoline engine because there is more energy in diesel fuel than gasoline. And, thanks to technology, the day of the temperamental, noisy, vibrating and black-smoke-belching-from-the-exhaust diesel vehicle has all but disappeared.
Another advantage will come when the diesel engine is coupled to the hybrid transmission. This pair could give a large vehicle the same fuel economy as a medium-sized passenger car.
Technological Advancements
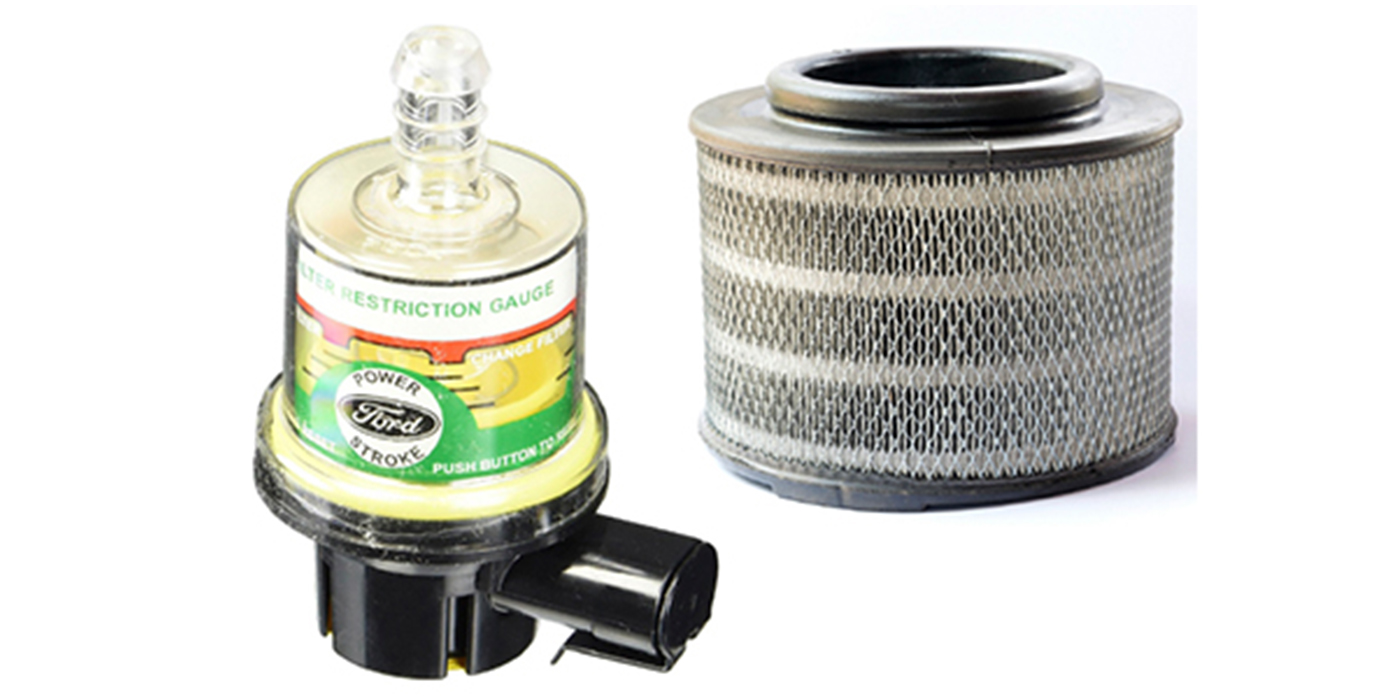
Improvements in materials, fluids and controls have reduced maintenance significantly. Electronic controls and diagnostics also have dramatically changed how these engines are maintained and repaired.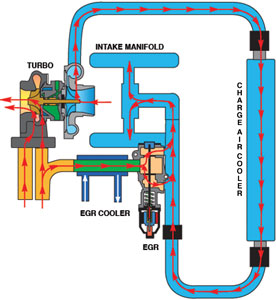
The Dodge 600 Cummins, Ford Power Stroke 7.3 and the GM 6.6 Duramax were introduced to meet the 2004 diesel emissions regulations. To meet the emissions requirements, these engines are equipped with a common rail electronic fuel injection system, variable geometry turbo with charge air cooler and EGR valve with cooler.
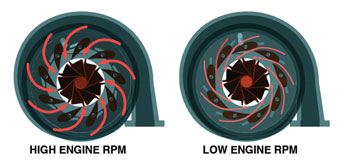
The common rail fuel system reduces emissions and engine noise and has been in use on some engines since 2001. This system uses an ultra high-pressure pump and common fuel rail that supplies solenoid-operated injector nozzles. The variable geometry turbo uses vanes to direct the exhaust flow on the turbine. At low engine rpm the vanes are partially closed to direct more exhaust at a right angle to increase turbine speed (see last illustration).
As engine speed increases, the vanes are opened to control turbine speed in the same manner as a pop-off valve. Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is not new to the diesel, but the cooler is. It improves the operation of the charge air cooler with lower intake air temperatures and density. (The EGR system requires a motor oil specified as CI-4 Plus by the American Petroleum Institute [API] for high-speed, four-stroke diesel engines.)
A Cleaner Diesel
The EPA has lowered diesel fuel sulfur content from 500 ppm (parts per million) to 15 ppm. This new ultra-low sulfur fuel has been available since October 2006. All 2007 and later diesel engines must comply with the new regulations that require the reduction of nitrogen oxide (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC) by 50% and particulate matter (PM) by more than 90% over the 2004 emission standards. Further reductions of NOx, HC and PM will be required by 2010.
 The 2007 emission requirements helped introduce a throttle valve for the reduction of NOx emissions at part throttle. A plus from the throttle is that it improves idle quality. A catalytic converter with a particulate filter (see photo to the right) is also installed as part of the emissions-reduction package. The throttle valve is installed on the intake manifold and is operated by an electric motor.
The 2007 emission requirements helped introduce a throttle valve for the reduction of NOx emissions at part throttle. A plus from the throttle is that it improves idle quality. A catalytic converter with a particulate filter (see photo to the right) is also installed as part of the emissions-reduction package. The throttle valve is installed on the intake manifold and is operated by an electric motor.
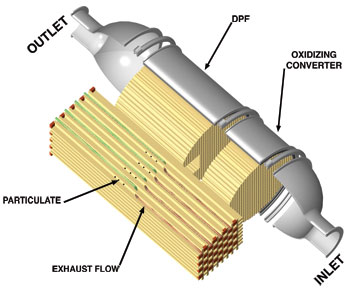
The diesel particulate filter (DPF) uses an oxidizing catalyst to control hydrocarbons. Soot and larger sulfate particles are captured in the ceramic honeycomb of the DPF. It is constructed by plugging alternate passages of the honeycomb to form channels that the gases will pass through and trap particulates on the channel walls. To keep the particulates from filling the channels, a regeneration process is used to oxidize the carbon into carbon dioxide gas that will pass through the honeycomb.
There are two types of regeneration: self-regeneration and forced regeneration. Self-regeneration takes place when the exhaust gases reach a temperature of approximately 1,000º F (538º C) oxidizing the carbon particulate.
Forced regeneration is a function of the engine operating system that will use temperature sensors, throttle valve, intake air heater and controller fuel delivery algorithms to cause regeneration.
The DPF has a life of approximately 100,000 miles for light trucks. The system will use pressure and temperature sensors to monitor the DPF. Service of the DPF will require the removal and disassembly of the converter and particulate filter. The ash that remains in the DPF can be cleaned by back flushing with air and then reinstalling.
Cleaning equipment for the DPF is available from several sources. A new motor oil with less than 1% ash content specified as CJ-4 by API will also be required for engines equipped with a DPF; It has to be used to extend the maintenance life of the DPF filter.
Service Intervals and Maintenance
The 3,000-mile oil change has been replaced by oil life sensing, with some oil change intervals starting at 15,000 miles. The automatic transmission fluid and filter are to be changed at 50,000 under regular service and every 25,000 under severe service. If the truck has a standard transmission and a wet clutch, the clutch fluid should be changed at 25,000 miles.
In 2008, a filter and oil change may be the only required service other than routine inspections. After resetting the oil change indicator light and topping off the fluids, are you done?
The 2007 emissions requirements affect all diesel engines produced after January 1, 2007, and their introduction has required additional accurate information and service procedures. The real key to properly maintaining light- and medium-duty trucks will be keeping the fuel in good condition by preventing water from collecting in the tank, which can cause the growth of microorganisms. Treatment of this condition uses a fuel additive called a biocide.
Number 2 diesel is a general-purpose fuel used for most highway and off-road applications in warm weather. Cold weather and temperatures below 32º F (0º C) can cause the fuel to produce wax or gel. Number 1 diesel is a special-purpose fuel with additives to prevent the fuel from creating wax or gelling, and is used in winter and cold climates.
Filter service is very important to the service life of the fuel and emissions system. Most light-duty trucks will have a single filter. Most of these fuel filters have a 10-micron rating, which means that it will not pass water. It will have a water drain at the bottom of the filter and a heating element to keep the fuel from gelling.
Some filters will have a manual-priming pump. After draining the water from the filter, you should use the priming pump to replace the drained water.
As fuel prices remain uncertain and vehicle owners look to keep their trucks and SUVs on the roads, diesel may become a choice to lower fuel bills. This can be a service opportunity for your shop, as your customers will need to be educated about servicing the diesel engine to prevent costly repairs.













