If you encounter a vehicle that experiences coolant coming out of the coolant reservoir tank, it may be caused by the radiator cap pressure valve being stuck open by debris sucked up through the reservoir tank hose. As the cooling system cools down, it sucks coolant back into the radiator.
If there is debris that settles to the bottom of the reservoir tank, the hose is low enough to also suck debris back into radiator. This causes the radiator cap not to seal, allowing excessive amount of coolant to escape overflowing the reservoir tank. If this condition continues over time, there will not be enough coolant in the system to maintain proper engine temperature.
In order to correct the condition you need to clean (and test) or replace the radiator cap, clean out the reservoir tank, and slightly shorten the hose, following the below repair procedure.
 Affected Vehicles:
Affected Vehicles:
• 1999 and later Impreza and Forester;
• 2000 and later Legacy and Outback; and
• 2006 and later Tribeca.
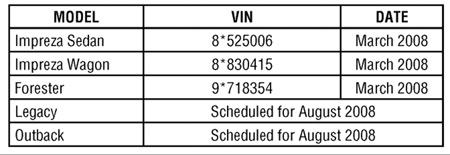
The shorter coolant reservoir tank hose was used in production as shown in Chart 1.
Repair Procedure/Information:
1. Radiator Cap Cleaning: Many caps can be successfully cleaned. The important part is the thorough cleaning of the negative pressure valve. If this is not done completely, remaining debris may result in a repeat issue. If there is an excessive amount of debris or the sealing rubber on the cap appears to be pitted or damaged, replace the cap.
 Note: If replacing the cap, skip to Step 2.
Note: If replacing the cap, skip to Step 2.
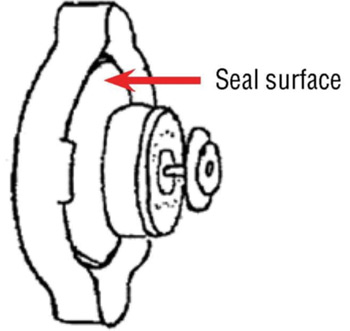
• Using clean water and a brush, thoroughly clean the cap seal surface. See Fig. 1.
Note: A used toothbrush that has been cleaned works great.
• Manually open the negative pressure valve. See Fig. 2.
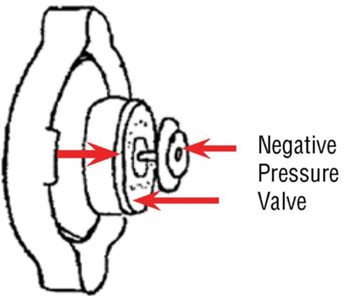 • Using clean water and a brush, thoroughly clean the valve (inner and outer surface) and the valve seal surface.
• Using clean water and a brush, thoroughly clean the valve (inner and outer surface) and the valve seal surface.
• Check the radiator cap valve opening pressure using a radiator cap tester to ensure the cap is within specification (refer to the applicable Subaru service manual).
Note: If the cap is out of specification, replace it.
2. Coolant Reservoir Tank Cleaning:
• Remove the reservoir tank (refer to the applicable Subaru service manual).
• Using clean water, thoroughly clean the inside of the reservoir tank.
• Reinstall the reservoir tank. Fill with coolant to the Full mark.
Note: Be sure to use Genuine Subaru Super Coolant or Subaru Long Life Coolant, depending upon what type of coolant is currently in the system.
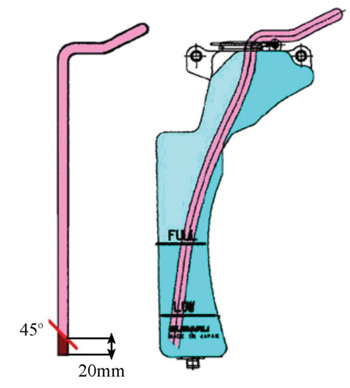 3. Coolant Reservoir Tank Hose Modification:
3. Coolant Reservoir Tank Hose Modification:
• Remove the hose from the reservoir tank. Cut 20 mm from the bottom of the hose at a 45° angle. Reinstall the hose in reservoir tank. See Fig. 3.
• Start the engine and allow it to fully warm up.
• Turn off the engine and allow it to fully cool down.
• Re-check coolant level in the reservoir and add coolant, if needed.
Note: Be sure to use Genuine Subaru Super Coolant or Subaru Long Life Coolant, depending upon what type of coolant is currently in the system.
Courtesy of ALLDATA.