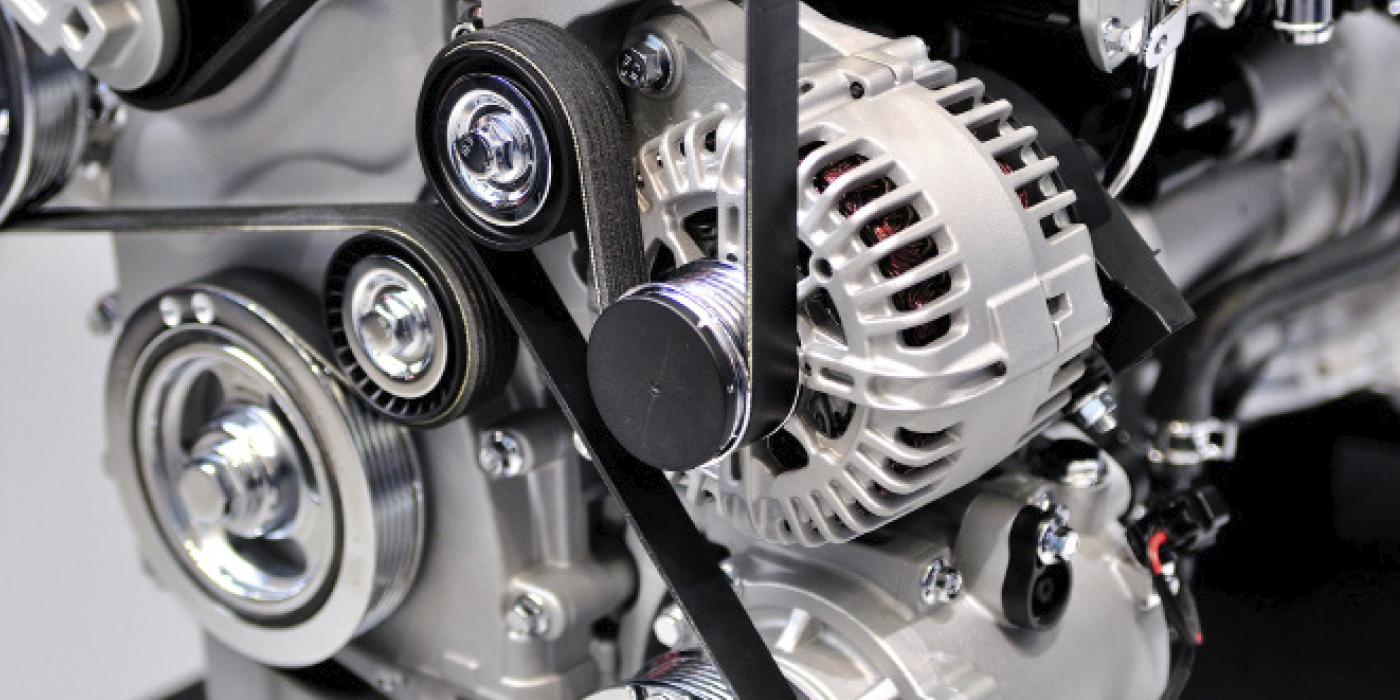
Factory-fresh serpentine belts can last more than 100,000 miles, depending on the application. Unfortunately, replacement belts might not last as long. Understanding why this is the case will allow your shop to help your customers get the most out of their next belt.
When a customer purchases a new vehicle or one with low miles on it, they become accustomed to having certain parts on the car last a long time. The average serpentine drive belt, for example, can last 60,000-100,000 miles after it was installed at the factory during the vehicle’s assembly.
While it isn’t unreasonable for a customer to expect the same service life on a replacement belt, in many cases, they see significantly less miles of service from the replacement belt. Let’s explore a few reasons why and how you put yourself in a position to see longer service intervals on the subsequent belts.
In short, you’re not dealing with a component, you’re dealing with a system. The serpentine drive belt system is actually made up of a set of sub-systems, designed to work in concert with one another. The belt will see different loads depending on the accessory being driven during the operation of the vehicle.
The initial replacement belt
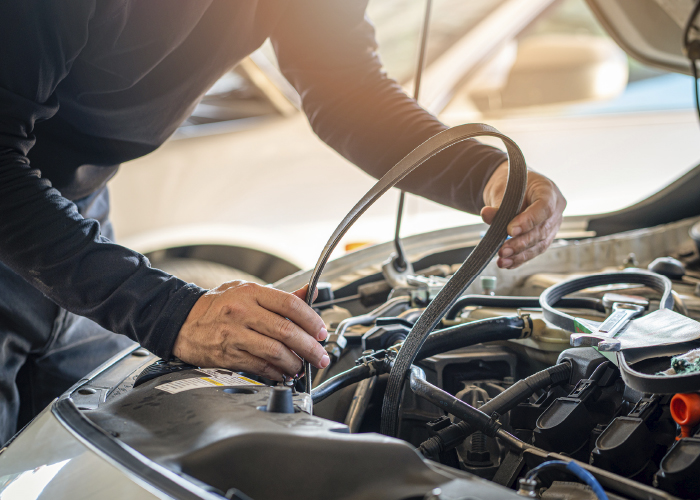
In most instances, the customer will have related underhood work or a preventive maintenance inspection during which the technician has suggested belt replacement for a variety of reasons. Most common are normal wear, usually revealed using a belt wear gauge, hearing belt squeak or visually due to contamination from petroleum products.
However, it’s more than just the serpentine belt.
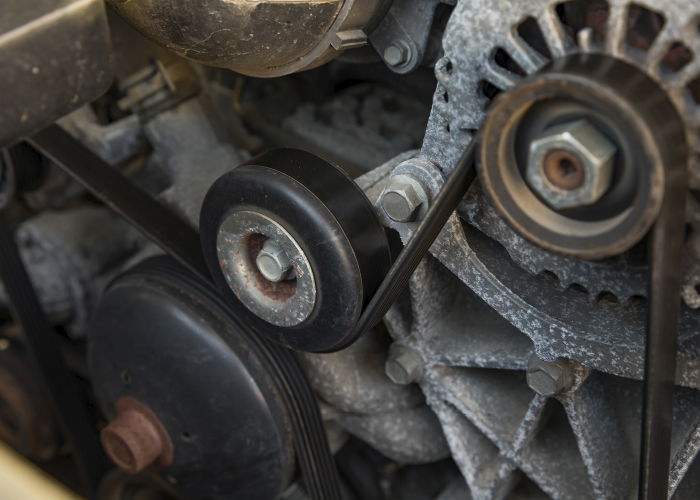
Tensioners wear at the same rate as the belt. The belt tensioner is spring-loaded, and the constant movement of the tensioner will wear down the spring’s ability to apply the correct amount of force to the belt. A belt without the appropriate force applied will not effectively drive the accessory pulleys, which creates an inefficient transfer of power, underperforming accessories and accelerated wear of the newly installed belt.
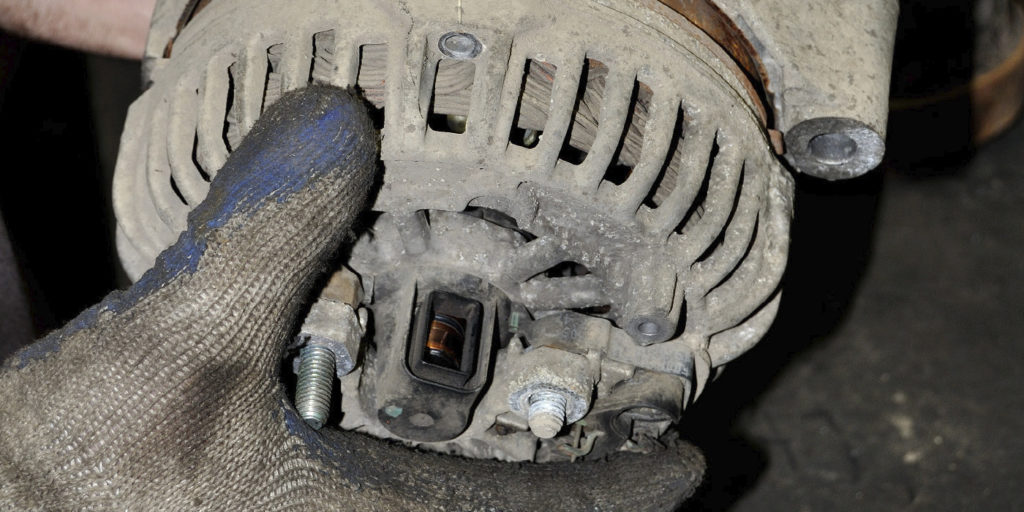
Idler pulleys and tensioner pulleys have sealed ball bearings and are designed with the same service life as a typical serpentine belt. A worn-out bearing can cause the pulley to operate at an abnormal angle, creating excessive wear on one side of the belt.
Another issue could be a seized pulley, resulting in the pulley breaking off the pulley mount. This, in turn, causes the belt to ride off the pulleys.
Pulley alignment
According to a leading belt manufacturer, pulley misalignment is the number one cause of belt chirp on serpentine belt systems. In addition to an annoying belt chirp, misaligned pulleys will actually accelerate belt wear.
To most accurately inspect the pulley system, use a laser alignment tool. By doing so, you can uncover if you have one or more belt-eating culprits such as parallel or angular misalignment. Pulley run-out is misalignment from a bent component shaft or worn bearings. During your inspection, keep an eye out for bent or broken accessory brackets, and look for loose, missing or broken bolts – these items will contribute to belt alignment issues.
Contributors to belt failure
Be sure fluid leaks are addressed at the time of belt replacement. Petroleum-based fluids will soften belt material, causing the belt to weaken, wear faster and, in some cases, cause belt delamination. Along with oil-based leaks, a coolant leak might not cause physical belt damage but will cause the belt to slip on the pulleys. The slippage will cause the belt to wear and add heat to the belt which can result in premature belt failure.
When the technician suggests a belt replacement, our default is to order just the belt and install it to correct the deficiency. Consider though, that the most efficient solution may be a belt kit that includes a new belt, belt tensioner and idler pulley for the application. Installation of the kit can reduce comebacks, save time by performing the complete belt service at one time and increase sold hours.
In a nutshell, belt replacement is one of the simplest jobs in the shop and, in most cases, will be performed by a less-experienced technician. Create a best practice that includes a standardized inspection and installation process that each technician, regardless of their experience, should follow. This will ensure that each service visit is maximized from the customer and shop’s perspective. Time is the most valuable resource in the shop, whether you are a customer, manager or technician.
Following this process each and every service visit will go a long way toward increasing customer satisfaction and profitability.