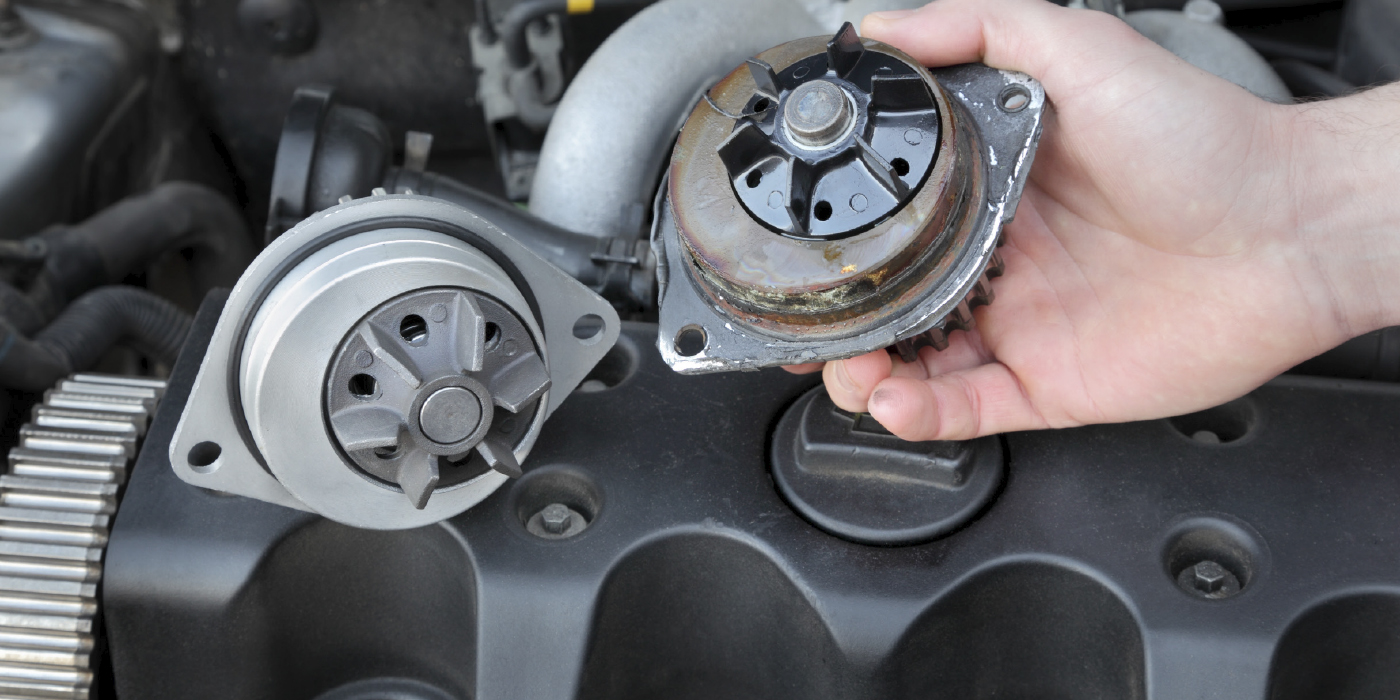
p can restore gear-to-gear clearances but not gear-to-housing clearances. The end plate that covers the pump often develops a heavy wear pattern that is most noticeable on the outlet gear side. Regrinding the face of the plate smooth can restore end play tolerances between the plate and gears but it can’t compensate for wear inside the housing. Deep scratches or grooves worn into the sides of the housing will leak oil and reduce the pump’s ability to move oil. In the case of front cover oil pumps on overhead cam engines, the pump turns at engine rpm and generates more flow at idle than crankcase-mounted pumps.
Consequently, when the pump becomes worn it isn’t always necessary to replace the entire cover assembly ‹ provided the pump housing inside the cover isn’t worn or damaged. A new drive gear can be mounted on the crankshaft and a new rotor installed in the cover to restore normal oil pressure. This approach eliminates the need to replace the entire cover assembly.
In cases where an engine has experienced a bearing failure or any other kind of internal failure that puts debris into the crankcase, the oil pump should always be replaced.
You should also replace the pump’s pickup tube and screen. Pickups are difficult to clean and can hide debris that may damage a new pump or the engine.
 Pump Modifications
Pump Modifications
If you want to rework a stock oil pump to maximize flow, use a die grinder to smooth and blend the sharp edges of the pump inlet and outlet ports. This will reduce turbulence and enhance flow through the pump. The clearance between the end of the gears and the pump housing cover also should be minimized to reduce pumping losses around the ends of the gears. If you’re working on a small block Chevy V8, another trick that can boost oil flow is to install a big block Chevy oil pump instead of a small block oil pump. A stock big block Chevy oil pump has 12 teeth per gear versus seven for the small block version, and flows about 10% more oil at the same rpm.
Something else to watch out for when installing a high-volume oil pump in a small block Chevy V8 is the nylon retainer on the pump shaft. A better choice is a pinned steel retainer to provide extra support between the intermediate shaft and pump shaft.
Care must also be used when tightening down the pump mounting bolts on small block and big block Chevy V8s because the pumps do not use a mounting gasket. The bolts should be torqued to 60 to 70 ft.-lbs. so there are no leaks or sloppiness that would eventually cause the shaft to break.
 Preventing Oiling Problems
Preventing Oiling Problems
The greatest oil pump in the world won’t keep an engine properly lubed if it is dry when the engine is first started, or if it sucks air because the oil level in the crankcase is low or the pickup screen is mounted too far above the floor of the oil pan.
The pickup tube should be installed so it is located no less than 3/8″ above the floor of the oil pan (to allow good intake flow), and no more than 1/2″ above the floor so it doesn’t run out of oil in a sharp turn. The pump should also be filled with oil when it is mounted on the block to prime it and reduce the risk of a dry start. Do not use grease or assembly lube here. In the case of front-mounted oil pumps inside the timing cover, the pump rotors can be coated with heavy oil such as 50W or even gear oil to keep the pump primed.
Before starting the engine, prime the oil system with a pressurized oiler.
Oil tends to drain off bearing surfaces when an engine sits for more than a week or so without running.
On older engines with distributor-driven oil pumps, the engine can be primed by using a drill to spin the oil pump shaft through the distributor hole.
But on engines with no distributor or those with oil pumps inside the front cover, this isn’t possible. Feeding pressurized oil into the main oil gallery through the oil pressure sending unit fitting will route oil to all the critical areas inside the engine and eliminate the risk of scuffing the bearings when it is first started.
Another option to consider is installing “coated” main and rod bearings if you’re replacing crankshaft bearings. Several major bearing suppliers have recently introduced performance engine bearings coated with a low-friction, moly-based anti-scuff surface treatment. The special coating increases the price of the bearings but provides added protection in the event of oil starvation.
|
Causes of Low Oil Pressure
|
Possible causes include:
Excessive main and rod bearing clearances (someone may have installed the wrong-sized bearings or standard-sized bearings on a reground crankshaft). Only 0.001″ of extra clearance in the main bearings can reduce oil pressure by up to 20%!
Excessive camshaft bearing clearances (a bearing may have slipped out of place when the cam was installed).
Excessive clearances inside the oil pump.
Leaks between the oil pump and engine.
Oil pump relief valve stuck open or installed backward.
A loose or mispositioned oil pickup tube (too high in the oil pan).
A defective oil pressure sending unit or oil pressure gauge.
Low oil level in the oil pan.
Cracks or leaks in the oil galleries or gallery plugs.
Cracked oil pump housing (improper installation).
Oil viscosity too thin for hot weather.
Oil viscosity too thick for cold weather.
| Presentation Available on Engine Lubricant Quality |
As vehicle maintenance professionals, you all are well aware of the importance of basic auto maintenance, especially the need to change lube oil and filters regularly. Over the past few years, we have seen not only major changes in automotive technology, but some say there also have been changes in the quality of engine lubricants. The net effect of these changes is that some engine oils that remain available in the marketplace are obsolete for modern engines, according to the Association of International Automobile Manufacturers (AIAM).
To receive a PDF version of a Powerpoint presentation developed by the AIAM that describes some of the excessive engine wear and sludge buildup problems that can occur when improper motor oils are used in modern engines, email us at [email protected]. Please include your name, shop, location and e-mail address.
| Oil Change Association Holds Convention |
The Automotive Oil Change Association (AOCA) will be holding its “AOCA & All That Jazz Annual Convention & Fast Lube Expo” April 23-26 at the Ernest N.
Morial Convention Center in New Orleans.
The sixth-annual AOCA Boot Camp will be held on Saturday, April 23rd. This full-day program is designed to help new lube owners improve their operations and their bottom line.
Seminars include Getting and Keeping Customers; Add-On Services: Tire Rotation, Power Steering and A/C Service; Dude, Where’s My Car?; Warranty Claims Self Defense and Customer Satisfaction; Working With the Media; and To Go of Grow.
On the exhibit floor, AOCA will host a new “demo theater” during which featured exhibitors will share their insights and techniques on cabin air filter service, water and deposit removal, training, car wash management, on-board diagnostics and the effects of thermal expansion on lube equipment.
For more information on AOCA and the convention, visit www.aoca.org or call 800-331-0329.