


All-season coolant used inorganic acid technology and worked great for almost 30 years.
In the 1960s, coolant was changed twice a year. In the fall, antifreeze with ethylene glycol-based coolant was put into the engine to prevent the coolant from freezing and cracking the block when a cold front hit. Often, if the engine got hot, the antifreeze would boil off. In the spring, the engine would be drained and filled with water and maybe a small can of an anti-corrosion treatment.
Why do ignition systems give technicians problems when diagnosing ignition-related misfires? The answer is that some technicians use tests that might give inconclusive results or do damage to the coil or drivers inside a module.

Servicing the serpentine belt on some vehicles is a tough task.

Here are six tips to use when diagnosing a vehicle with a dead battery.

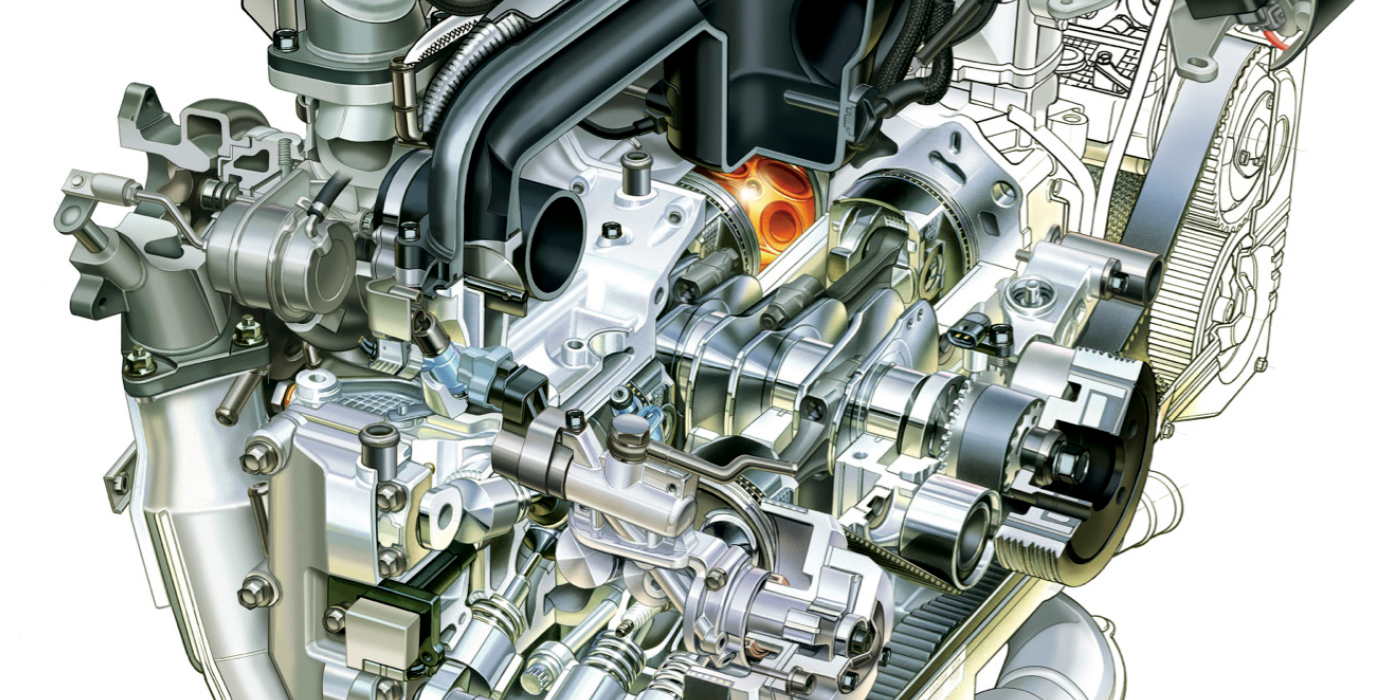
As the timing chain wears, it can change the timing of the camshaft and crankshaft.

The primary cause of these problems is that fuel and added detergents are not hitting the back of the intake valves.

It is important to check the operation of the solenoids that control vacuum to the actuators.

Most of the EJ head gasket failures occur around the 100,000-mile mark and start as a slow oil or coolant leak.
Many 0W16 oils have a new donut certification mark on the bottle called API SN-PLUS and SN-PLUS Resource Conserving.
