In early January, General Motors announced enhancements to the vehicle structure and battery coolant system in the Chevrolet Volt would further protect the battery from the possibility of an electrical fire occurring days or weeks after a severe crash.
In early January, General Motors announced enhancements to the vehicle structure and battery coolant system in the Chevrolet Volt would further protect the battery from the possibility of an electrical fire occurring days or weeks after a severe crash.
The enhancements come in response to a National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) preliminary evaluation to examine post-severe crash battery performance.
NHTSA opened its Preliminary Evaluation on Nov. 25 following a severe-impact lab test on a battery pack that resulted in an electrical fire six days later.
The test was conducted to reproduce a coolant leak that occurred in a full-scale vehicle crash test last May that resulted in an electrical fire three weeks later.
The Volt is a Top Safety Pick by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety and has earned other safety awards from key third-party organizations.
 Through the first 11 months of 2011, Volt owners accumulated nearly 20 million miles without an incident similar to the results in the NHTSA tests.
Through the first 11 months of 2011, Volt owners accumulated nearly 20 million miles without an incident similar to the results in the NHTSA tests.
“The Volt has always been safe to drive. Now, we will go the extra mile to ensure our customers’ peace of mind in the days and weeks following a severe crash,” said Mary Barra, GM senior vice president of Global Product Development.
GM will conduct a Customer Satisfaction Program to further protect the Volt battery from the possibility of an electrical fire occurring days or weeks after a severe side crash.
Modifications will:
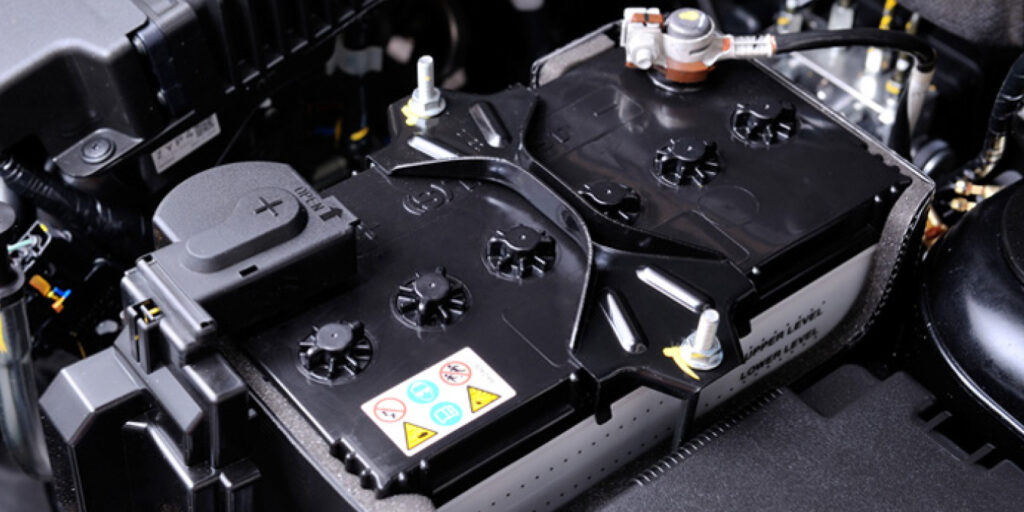
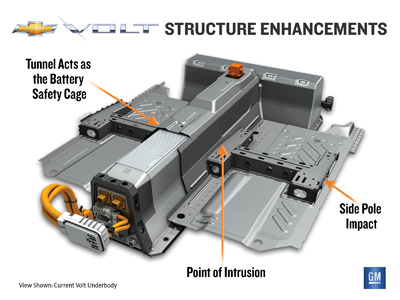
• Strengthen an existing portion of the Volt’s vehicle safety structure to further protect the battery pack in a severe side collision (see Figure 1);
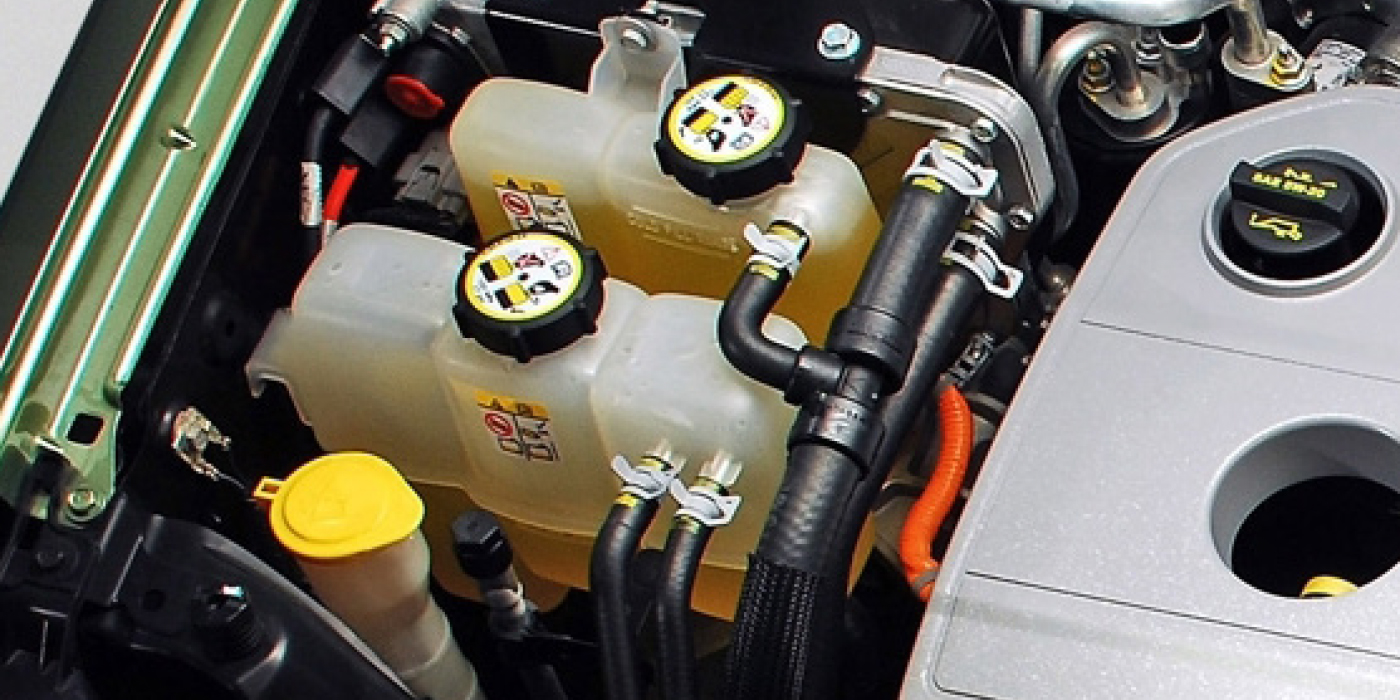
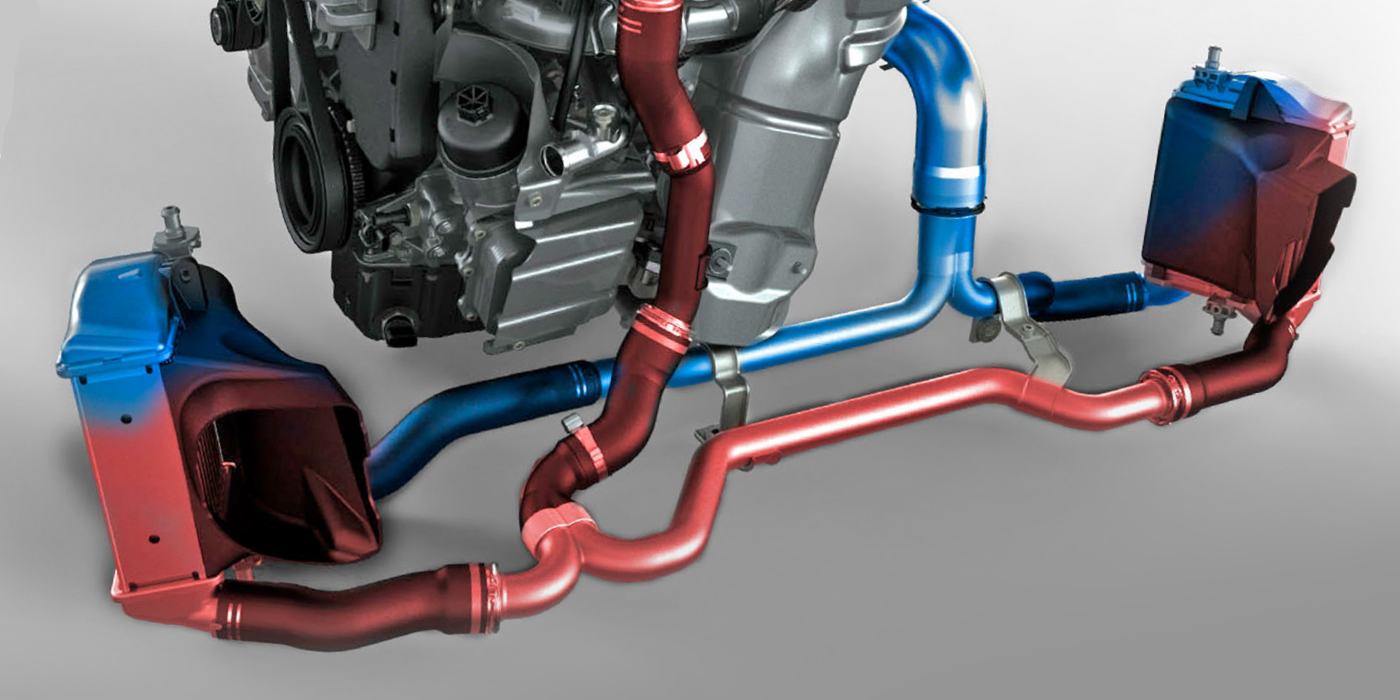
 • Add a sensor in the reservoir of the battery coolant
• Add a sensor in the reservoir of the battery coolant
system to monitor coolant levels (see Figure 2); and
• Add a tamper-resistant bracket to the top of the battery coolant reservoir to help prevent potential coolant overfill (see Figure 3).
GM conducted four successful crash tests between Dec. 9 and 21 of Volts with the structural enhancement. The enhancement performed as intended. There was no intrusion into the battery pack and no coolant leakage in any of the tests.
“These enhancements and modifications will address the concerns raised by the severe crash tests,” Barra said.
“There are no changes to the Volt battery pack or cell chemistry as a result of these actions. We have tested the Volt’s battery system for more than 285,000 hours, or 25 years, of operation. We’re as confident as ever that the cell design is among the safest on the market.”
Volt customers will be individually notified when the modifications are available for their vehicles. The enhancements are being incorporated into the Volt manufacturing process as production resumed in January.
Vehicle electrification technologies are important to future of the automotive industry, which is why GM will continue its leadership role in helping the Society of Automotive Engineers develop standards that will help tow truck operators, salvage yards and vehicle recyclers in the proper handling of electric vehicle components.
GM will help develop educational materials that can be used by these stakeholders in the future.
On Jan. 23, the government closed its investigation of Volt battery fires, concluding that there is no defect trend and that electric cars do not pose a greater risk of fire than gasoline-powered vehicles.
The NHTSA also said that it was satisfied with the plan by General Motors to address problems that triggered fires in Volts after crash tests.
“Generally all vehicles have some risk of fire in the event of a serious crash,” NHTSA said in closing the two-month investigation.
While no real-world fires were reported by regulators or the automaker, the investigation has cast a shadow over GM’s heavily promoted bid to lead on fuel efficiency and green technology with the Volt.