DENSO Corp. has developed a new and more efficient radiator that the company says is 40 percent smaller and lighter, compared to DENSO’s previous radiators. Also, the radiator’s tank is made with a plant-derived resin making it more environmentally friendly than conventional radiators.
“The radiator’s reduced size translates into greater design flexibility for installation in the engine compartment. This also helps make the vehicle safer in the event of a frontal collision because the reduced size allows for a larger impact or crash zone,” said Akio Shikamura, senior executive director of DENSO’s Thermal Systems Business Group. “In addition, the radiator’s tank is made of a plant-derived resin, which DENSO has been mass producing since 2009, making the radiator greener and environmentally cleaner than traditional radiators.”
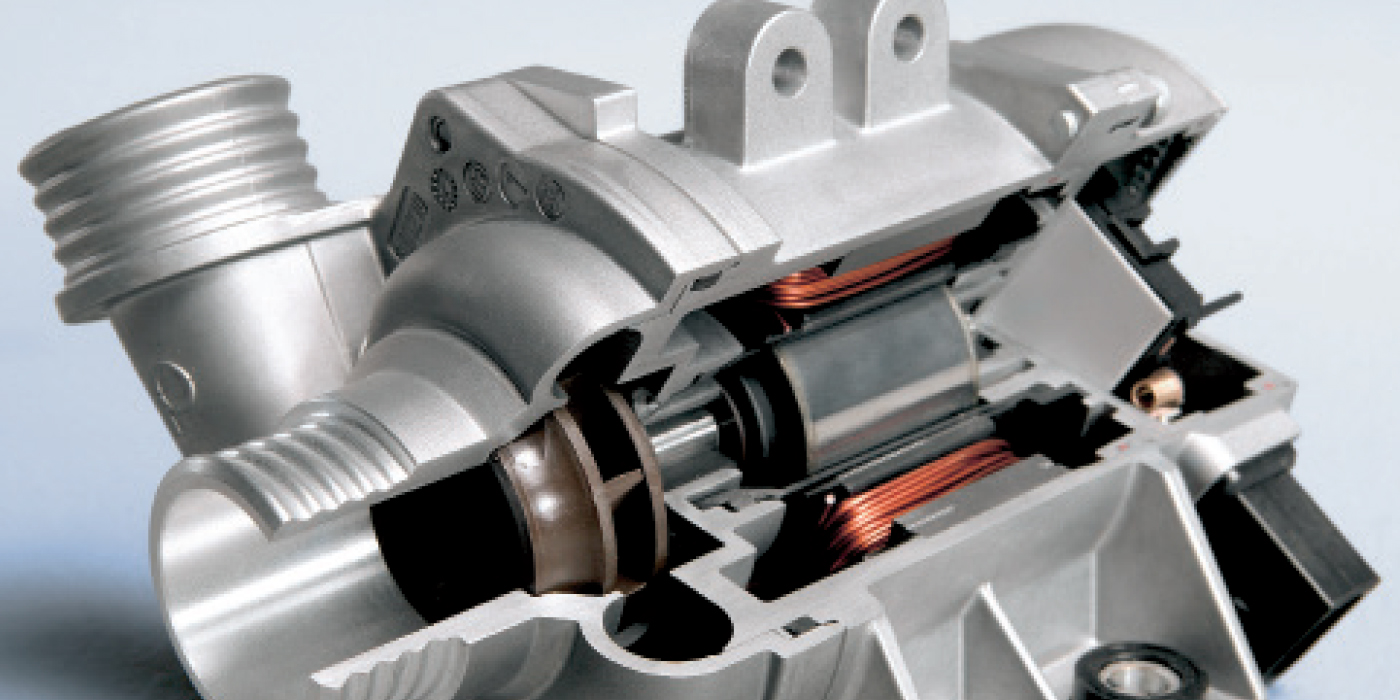
With higher heat radiation efficiency, the new radiator is only 16mm wide, but equal in performance to the conventional 27mm wide radiators, resulting in a substantial size and weight reduction, the company says. A radiator’s performance depends on its two major components — fins and tubes. The radiator’s more efficient heat radiation is achieved through improvements in the design of the fins. DENSO increased the amount of louvers, which are located on the surface of the fin, to 30 percent per unit area. This design change allowed the radiator to have 10 percent more efficient heat radiation than DENSO’s conventional radiators.
DENSO, along with a materials manufacturer, has jointly developed thinner and higher-strength materials that are used to make the fins and tubes. This new material allows for a global procurement of materials, which helps DENSO be cost-effective in all regions around the world. The fin, using DENSO’s manufacturing expertise, is the world’s thinnest of its kind, according to the company. DENSO says the radiator offers the same strength as its previous radiators while using thinner materials. All these advantages enabled the radiator to be 40 percent smaller and lighter than the previous models.
The newly developed 16mm wide radiator is installed in the Lexus GS. In addition to the 16mm wide radiator, DENSO will also commercialize a 27mm wide type, which is thinner than the conventional model of 36mm type, and 11.5mm wide type, which are thinner than the conventional model of 16mm, to offer a wider range of the new radiator series for a greater range of vehicle models.
DENSO says it will continue its research and development to expand its new radiator series into more environment-friendly and safer products to meet the increasingly diverse vehicle needs worldwide.