The fuel pump may be one of the most misdiagnosed components on a vehicle. It is often replaced without finding the root cause of why there is no fuel pressure at the rail.
When a fuel pump does truly fail, it is typically a case where the brushes on the motor and the bearings that hold the armature in place wear out. When this happens, the pump stops turning. In some cases, the endplay in the motor can cause the turbine, rotors or vanes to come in contact with the housing and be damaged.
But, wear and damage to the pumping elements and electric motor are often faults of the environment inside the tanks and at the fuel rail. The key to making sure the new pump will not suffer the same fate, is to reset the environment to a like-new condition in the fuel tanks, lines and related electrical systems.
Clean The Tank

Even the smallest piece of debris can damage the pumping elements inside the fuel pump. Most in-tank filters and socks will catch large pieces, but even small pieces of grit can damage the pump.
Removing all contaminants from the tank is critical before replacing a fuel pump. Your goal should be to restore the inside of the tank to the same state it was when they put fuel in before it drove off the assembly line.
There are cleaning options out there ranging from replacement tanks to kits that have the correct solvents that can flush all of the contaminants out of the fuel tank.
If you think the new sock or filter on the full pump will catch all of the bad stuff, you are wrong. The typical sock or filter is designed to trap particles that are between 50-100 microns in diameter. Forty microns is the size of a human hair. A conventional inline fuel filter can catch particles as small as 10 microns. The sock also has a limited capacity due to its small surface area.
While plastic fuel tanks do not have the same issues with internal corrosion, it is still possible for dirt and debris to make it into the tank through the filler and neck. Often the leading cause of fuel tank contaminates is a missing fuel cap.
EVAP Issues

When the fuel pump removes fuel from the tank, a vacuum is produced. Under normal operation, the evaporative emissions system will allow outside air to enter the tank. If the vent valve is not working, it can cause the tank to have the sides and bottom sucked in. For some fuel pumps and in-tank modules, it can cause the bottom of the tank to come in contact with the bottom of the pump and restrict fuel pickup.
This type of failure can be intermittent. It could occur when the vehicles run for a specific period of time. It can also happen when the fuel and vapors inside the tank cool.
Most fuel pumps are controlled by a module in the rear of the vehicle. Some modules can be on a class-two CAN network or a simple LIN network with the engine control module as master and the fuel pump module as the slave. If the network is not communicating or there are issues with other modules on the network. Often the best tool is a scan tool to make sure the modules are talking.
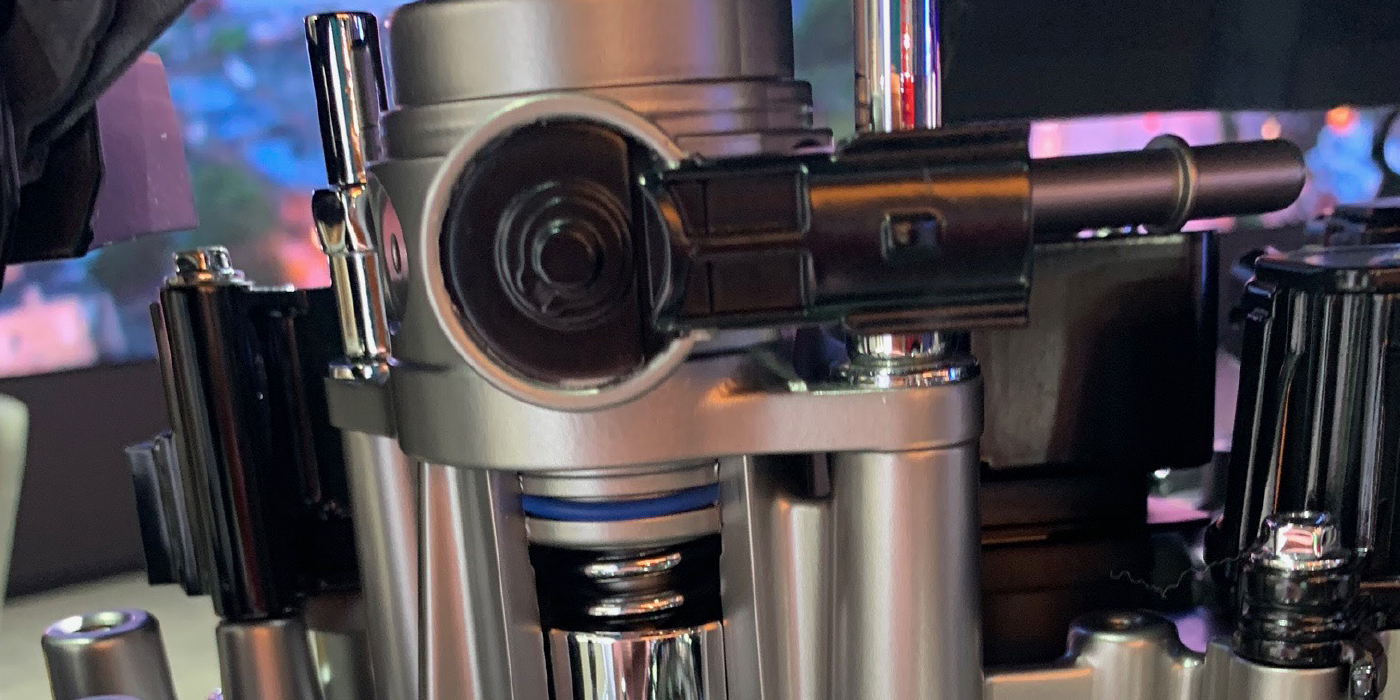
When the fuel pump is operating, it can draw a considerable amount of current. If the connection has a high amount of resistance, it can cause the pump to run slowly or not at all. The corrosion typically happens at the connector, where the pump meets the vehicle’s wiring harness. Performing a voltage drop test can reveal if there are any problems. Also, if there are any signs of melted plastic, the connector and the harness needs to be replaced. When some pumps fail, they will draw large amounts of current or short the circuit to ground. This can also cause thermal damage to the connectors and wiring to the pump.
Internal Leaks
Some fuel pumps can develop internal leaks but show the same symptoms of a weak fuel pump that can deliver enough fuel when loads and engine speed increases. The most likely causes of this are leaky hoses inside the tank.
Some fuel pump modules use clear corrugated flex hoses inside the tank. This hose is designed to stand up to fuel and can reduce noise from the fuel pump.
Some applications use SAE 30R10 fuel hose that is designed to be submerged in fuel. This type of hose has a special layer on the inside and outside to prevent the core layers from being saturated in fuel. If you use normal SAE rated fuel hose, it will degrade and start to leak inside the tank and cause an internal leak.
Any restriction in the fuel lines means the electric pump has to turn faster to deliver the same amount of pressure at the fuel rail. If a fuel filter or sock in the tank is restricted, the fuel pressure at idle might be within specifications. But during increased engine loads and speeds, the engine will be starved for fuel.
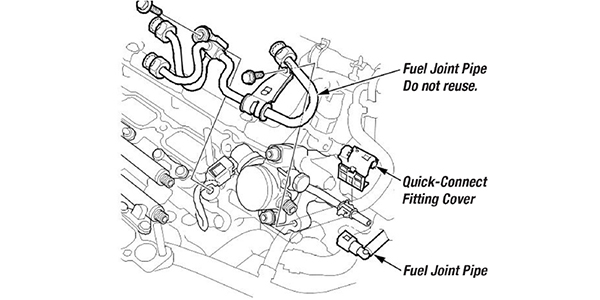
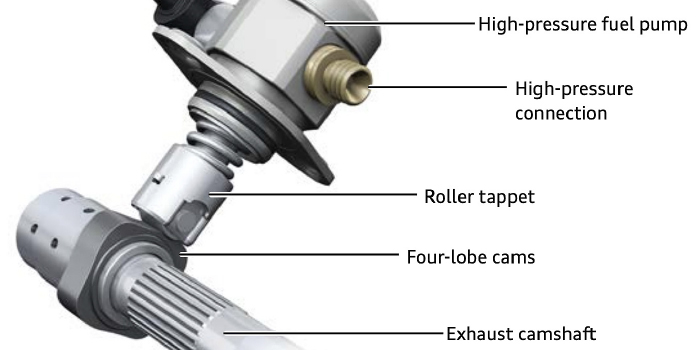
If the fuel pump is replaced, any filter or screen should be inspected and replaced if possible. Some direct-injection high-pressure pumps will have screens on the inlet. Often the bits and pieces of the old electric pump in the tank will be trapped on these screens.