CC:
Radiator hoses as well as heater and bypass hoses are a part of a very complex coolant distribution system that is designed to regulate engine temperatures within a very precise range. Internal combustion engines create heat in the process of generating power. The heat must be precisely controlled or the engine will fail. The radiator hose is a flexible connection between the engine and radiator, allowing coolant to circulate between the engine and radiator maintaining a prescribed engine temperature for maximum engine performance.
All hoses which are made of synthetic rubber are important to coolant flow. The hoses are a component of a sealed and pressurized cooling system, but the hoses can be considered the weakest link. If not properly maintained, hoses can rupture causing loss of coolant and a possible engine over heat condition. Hose failure can lead to a roadside breakdown or engine damage. It is recommended that radiator or other coolant hoses be periodically inspected and replaced as necessary. A visual inspection may reveal the condition of the hose and an indication of replacement. Coolant hoses will harden with age and heat. A simple test of squeezing the hose might reveal a hose problem and indicate the need for replacement.
A hose in good condition will maintain its shape, springing back into its original form. Symptoms of hose replacement include a hose which is brittle or hard, cracked, bulged or swollen or chafed. When squeezing the hose, any crack in the cover might lead to a blowout later. The hose should be soft and pliable, but without bulges or swelling which could be caused by oil exposure or internal failure of the two. A chafed area is an area where the textile reinforcement has been exposed due to constant wear from a hot or abrasive component.
Hoses that are brittle, cracked or chafed would be a strong indication of imminent hose failure. These symptoms are an indication of a hose cover or tube failure, which would lead to a loss of coolant pressure and coolant causing an overheat situation. Radiator hoses, along with any of the other coolant hose components, including the heater and bypass hoses should be periodically inspected and properly maintained to prevent loss of coolant and to ensure optimum performance of the cooling system.
A visual inspection may reveal the condition of the hose and an indication of replacement. In some cases, a failure of a related component in the cooling system would suggest the hose be replaced. Some of the visual inspections that we’re going to be looking for are cracks, abrasions, swelling, hose clamps, hose softness from exposure to oil or grease, or even coolant discoloration. It’s hard to detect the true condition of the hose from an outside appearance. Most radiator hoses will fail from the inside. The failure of the hose tube or pinhole leaks are not easily seen without a pressure check or some other means of detecting leaks, such as with a soap and water solution.
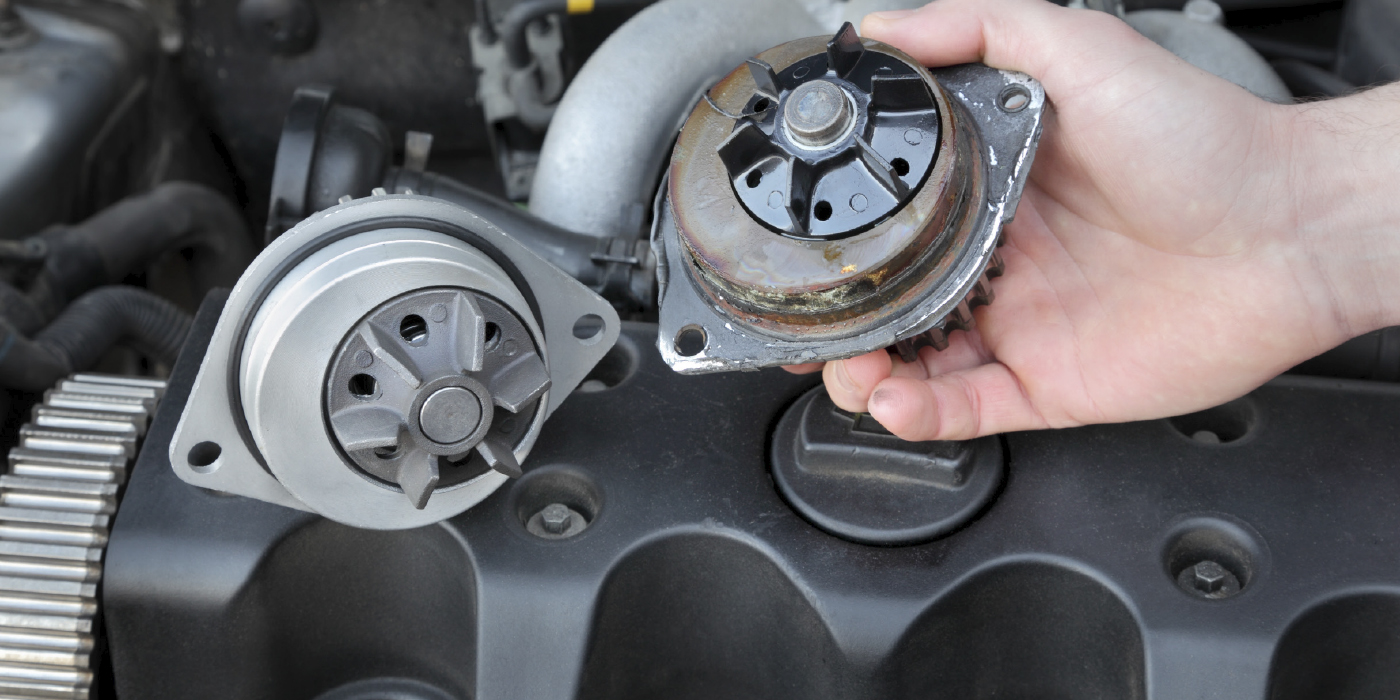
It is important to note that radiator hoses can fail from related component failure or improper maintenance. As part of the coolant distribution system, all components, including the cooling itself, the radiator, radiator cap, thermostat and water pump must all be functioning properly to ensure optimum performance of heat transfer or cooling of the engine. In general, a regular preventive maintenance inspection should include the following: the coolant level and condition and the concentration, replace the coolant and or flush if necessary. Inspect the hoses, replacing if showing signs of wear or damage. Include the replacement of hose clamps when replacing hoses. Worm type clamps are recommended for replacement as the OE spring type clamp may lose tension with age. Check the operation of the radiator, radiator cap, thermostat and water pump.
Other things to think about including in preventive maintenance are such things as heater hoses, bypass hoses, including where the coolant reservoir and electric pumps are located, coolant condition and concentration, heater cores. And don’t forget about the turbocharger coolant hoses, water pumps, radiator cap, thermostat, and the condition of the hose clamps. Hoses will typically last three to four years before a suggested replacement. Coolant hose should be periodically inspected at every opportunity the hood is open. Hose replacement and lights will depend on driving conditions and the exposure to higher temperatures.
Hoses should be replaced at any time they are found in less than perfect condition, regardless of age. Hoses should be replaced if a visual inspection reveals any hardness, leaks, cracks, swelling, chafing, or other damage. In addition, any other cooling system maintenance or repair that includes water pump replacement, thermostat replacement or coolant replacement should include hose replacement as well. If a hose is to be replaced it is recommended that a replacement hose be used with the same form and fit as the original equipment hose. Original equipment hoses were designed to fit into the powertrain compartment and were designed and routed for proper function and performance. Molded hoses have been designed to avoid kinks or tight bends, which could restrict coolant flow. A replacement hose should be the same length and ID as the original hose. Thanks for watching.
This video is sponsored by Continental.