OBDII Codes and Catalytic Converter/Oxygen Sensor Problems
OBDII Codes and Catalytic Converter/Oxygen Sensor Problems
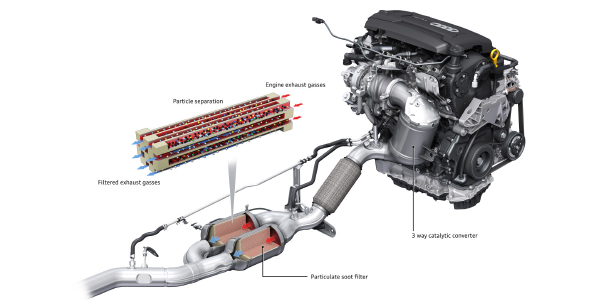
OBD II monitors include the catalyst heater, catalytic converter efficiency, secondary AIR, O2 sensor heaters, EGR system, PCV system, thermostat and A/C system (where used). These are all “non-continuous” monitors and are not set until certain driving conditions have been met. The converter efficiency monitor, in particular, is a hard one to set and may require driving the vehicle at various speeds and loads so the OBD II system can get a good look at what’s going on. More
 Diagnostic Solutions: Catalytic Converters
Diagnostic Solutions: Catalytic Converters
Converter problems typically fall into one of five categories:… More
 Mischievous Cats (Catalytic Converters)
Mischievous Cats (Catalytic Converters)