Toyota’s original Land Cruiser was the company’s version of a Jeep that could go anywhere. In its time it was highly rated and collected, which led the Japanese juggernaut to bring back an updated SUV in 2007 called the FJ Cruiser. The retro-styled vehicle was again a go anywhere machine powered by a 4.0L V6 (1GR-FE) used in the Tacoma. The engines are durable and considered relatively robust for the time.
Toyota’s original Land Cruiser was the company’s version of a Jeep that could go anywhere. In its time it was highly rated and collected, which led the Japanese juggernaut to bring back an updated SUV in 2007 called the FJ Cruiser. The retro-styled vehicle was again a go anywhere machine powered by a 4.0L V6 (1GR-FE) used in the Tacoma. The engines are durable and considered relatively robust for the time.
Different types of coolants cover a range of applications from diesel to domestic, Asian and European vehicles. Each one is formulated to a specific manufacturer’s specifications to keep their engines at an optimal temperature. But, changes to the old one-size-fits-all formula has led to confusion for consumers and even some technicians.

Andrew Markel discusses hoses and the necessity for several of them to route fluids to all parts of the vehicle due to the growing efficiency of engines. Sponsored by Dayco.

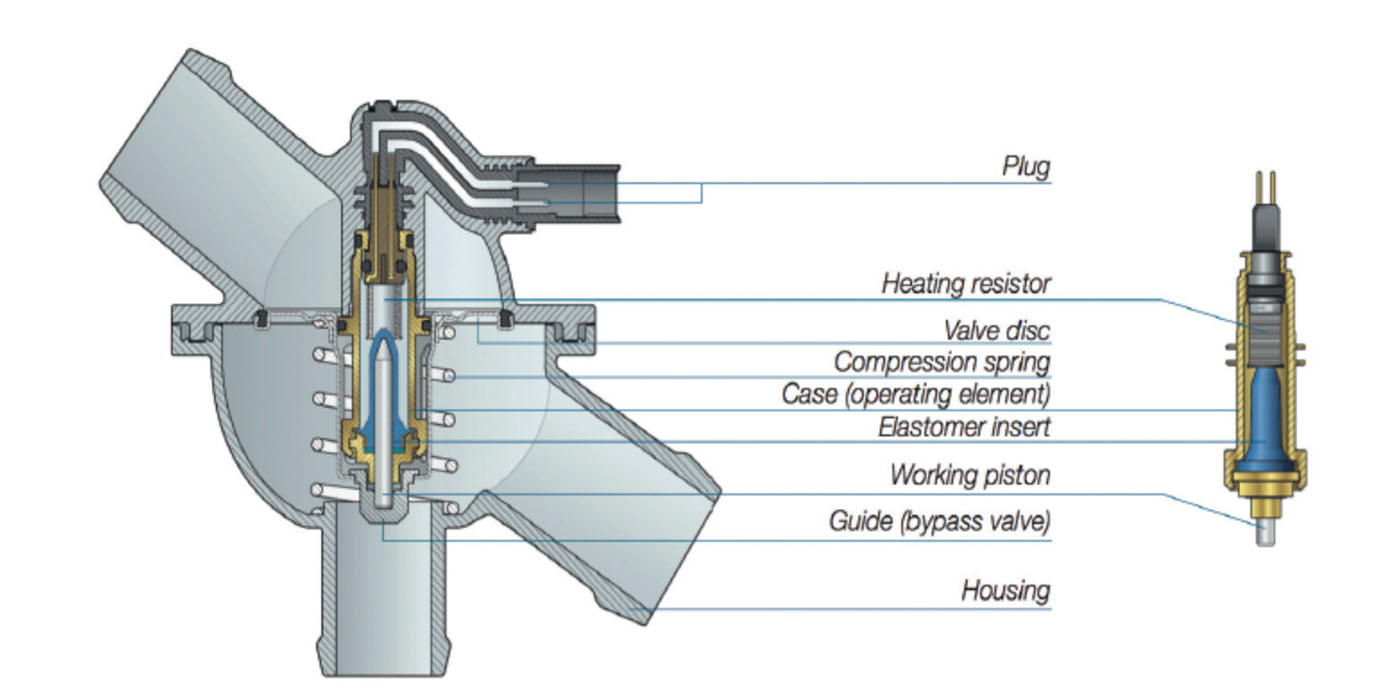
The majority of cooling systems on the roads react to what is happening inside the combustion chamber. After the engine is stressed, the heat causes the thermostat to open. Increases in temperatures will also cause the cooling fans to come on. The heat carried by the coolant is the trigger for operation of the fans and thermostat.

Given the advanced state of internal combustion engine technology, some recent cooling system innovations will actually increase engine torque and fuel economy while reducing exhaust emissions. Let me simplify that idea: new cooling system technology will make engines run better and cleaner. So, let’s get on the same page by reviewing some basics.

Two specifications can be used to justify replacement — the condition of the additive package & the freezing point.
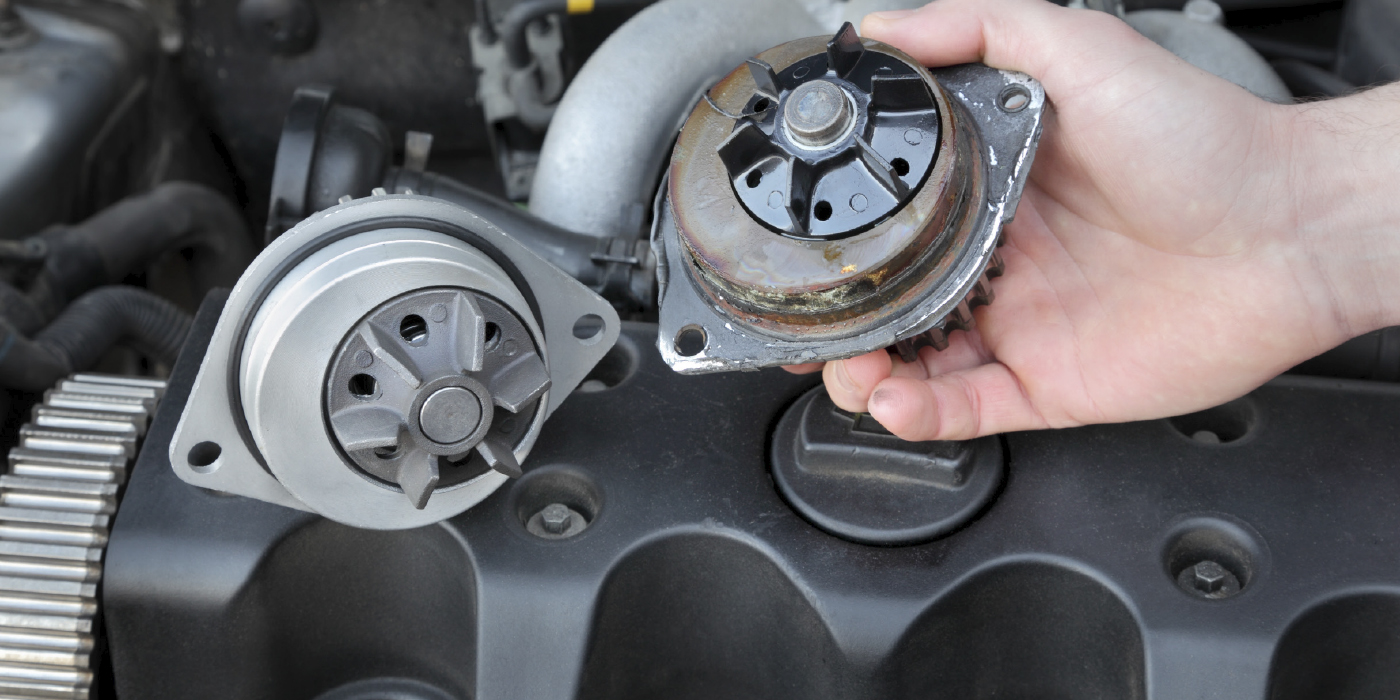

It is estimated that by 2022, 50% or more of vehicles sold in the U.S. will have one or more turbochargers under the hood.
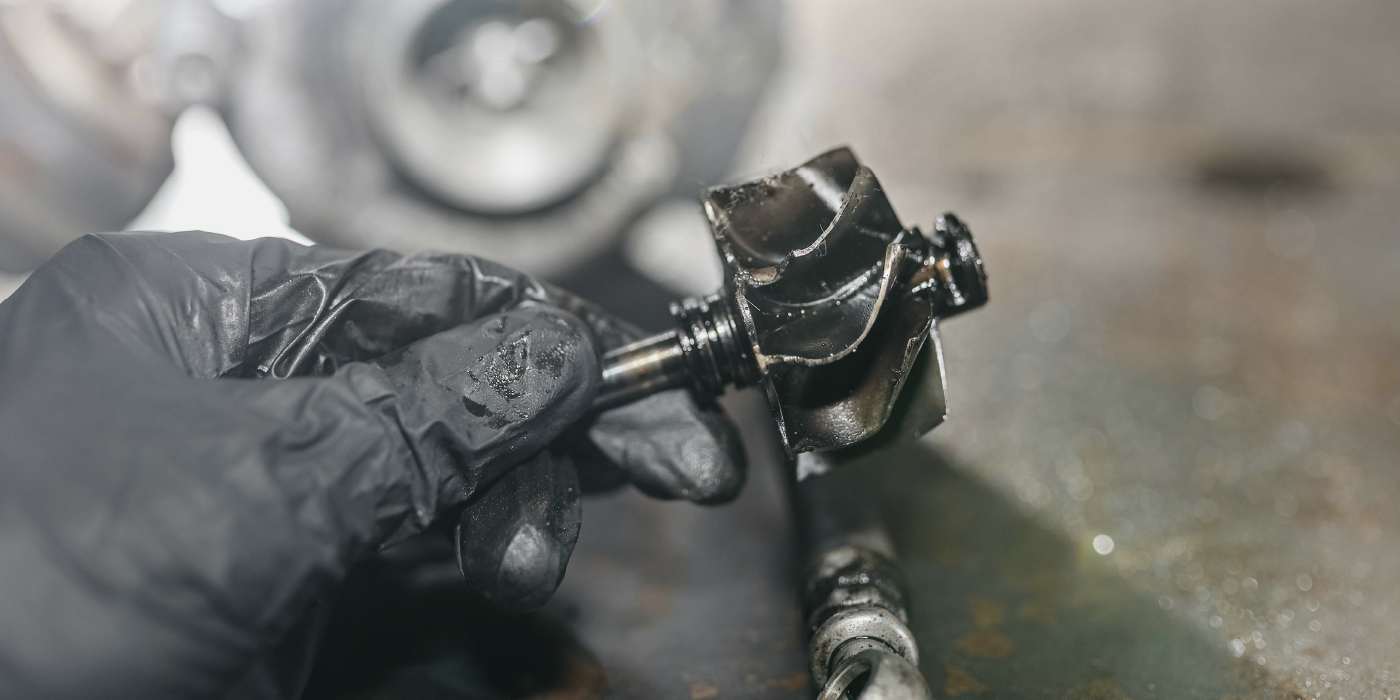

One bad hose can cause an engine malfunction. This video is sponsored by Continental.
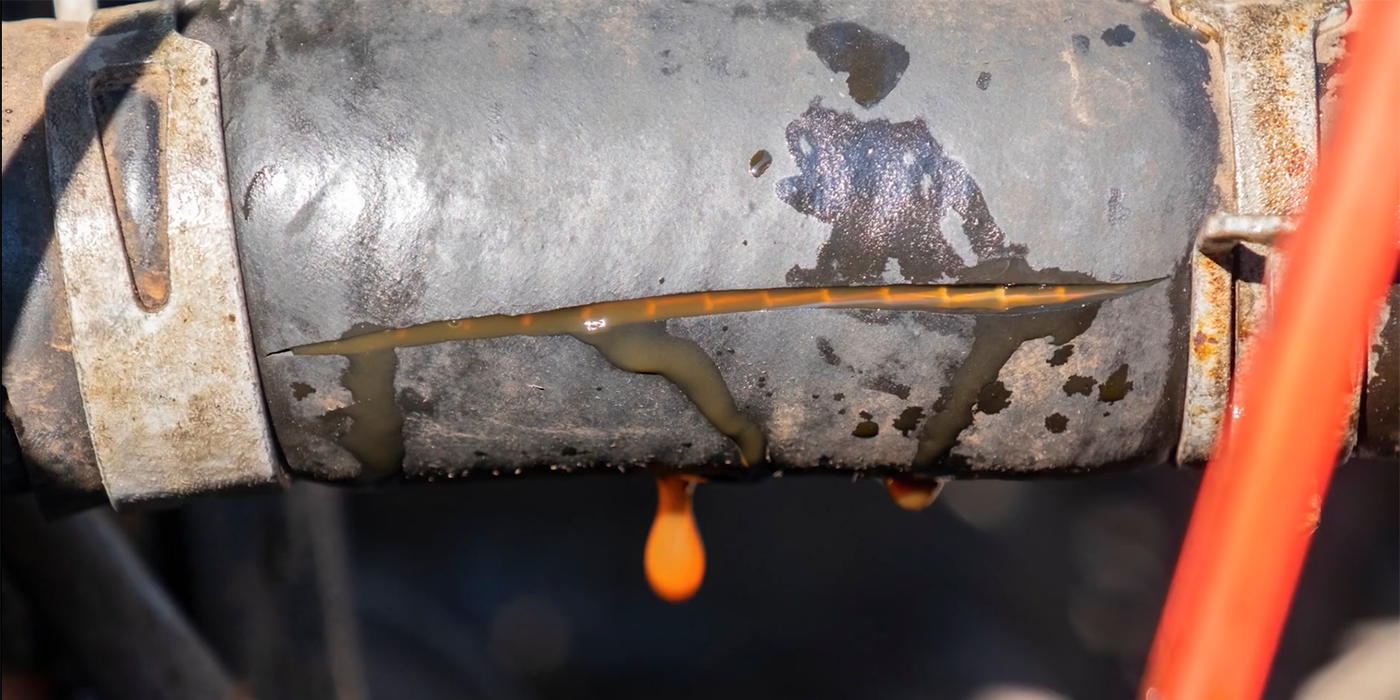

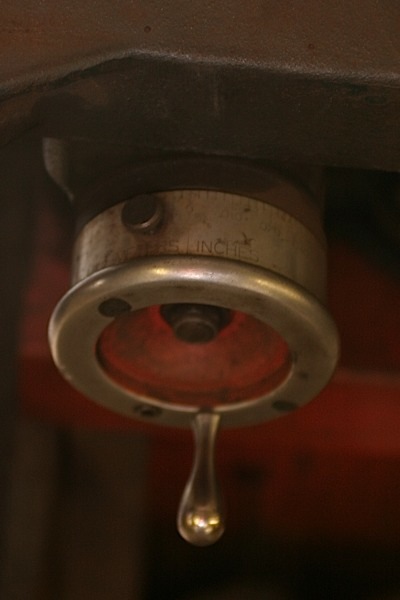
When the heater circuit fails, most of the time it will create an open circuit.