oling for the coolant that circulates through it. Most newer radiators are aluminum and have a “crossflow” design in which the coolant flows from one end to the other. Older radiators are usually copper or brass and have a “downflow” design in which coolant flows from the top to the bottom. Most radiators also contain a loop(s) of pipe in the bottom tank or end tanks for cooling automatic transmission or power steering fluids. For the G1, they will ask questions about mixing fluids in the radiator like: Coolant was found in the transmission, what is the most likely cause?
Radiator Cap
A spring-loaded pressurized cap on the radiator prevents coolant loss and increases the temperature at which the coolant boils. Pressure ratings vary from 5 to 15 psi. Weak radiator caps can lead to overheating or coolant loss. Replace the cap if it does not seal properly or does not hold the rated pressure. For the G1, make sure you understand the relationship between temperature, pressure and boiling points.
Pressure Test
Pressure testing the cooling system is a quick and easy way to find an external leak. Perform the test on a cold engine using a hand pump with a gauge:
1. Remove the pressure cap and attach the pressure tester to the filler neck.
2. Pump the tester until the gauge reading matches the specified system pressure.
3. Observe the gauge; the reading should remain steady.
4. If the gauge shows a pressure loss, pump the tester to maintain pressure and check for leaks.
For the G1, understand how a leaking headgasket can cause changes in pressure and exhaust gases in the coolant. These gases can be detected with a combustion gas leak detector or a five-gas analyzer.
Coolant
While there will not be any specific questions on coolant chemistry, you need to know why coolant needs to be replaced. Coolant needs to be changed periodically to renew the chemical additives that protect the cooling system against corrosion.
Coolant Testing
A refractometer or cooling system hydrometer will test coolant concentration and effectiveness. For accurate test results, the coolant should be hot. Before testing, draw a coolant sample into the hydrometer and return it to the radiator several times to stabilize the internal thermometer of the hydrometer.
Coolant Fan
For the G1, you need to know how to inspect fans and how they activate. Concentrate on inspecting the fan for damage like missing blades, bearing noises and situations like weak motor mounts that can cause an engine-driven fan to make contact with the shroud.
For electrical fans, you need to have a basic understanding of the components and operation below.
• A temperature sensor is a switch that typically energizes an electrical relay to turn on a fan.
• A temperature switch closes a set of contacts inside the switch using a thermistor to either complete the power or ground side of the circuit for the fan. This sensor/switch can be mounted either in the engine or radiator.
• An air conditioning or high discharge pressure switch to energize an electrical relay to turn on the fan.
• Computer-controlled relays to energize the fans. This system uses the engine coolant temperature sensor (thermocouple) to gauge engine temperature. The coolant fan turns on when engine coolant temperature reaches about 230°F (110°C).
Further ASE Test Prep training
For additional in-depth instruction needed to achieve ASE Certification head to AVItestprep.com.
There you will find a wide-range of ASE Certification Test Prep quizzes and instructional videos covering sections L1, C1, A2, A4, A5, A6, A8 and more.
Toyota FJ Cruiser Water Pump Replacement
Toyota’s original Land Cruiser was the company’s version of a Jeep that could go anywhere. In its time it was highly rated and collected, which led the Japanese juggernaut to bring back an updated SUV in 2007 called the FJ Cruiser. The retro-styled vehicle was again a go anywhere machine powered by a 4.0L V6 (1GR-FE) used in the Tacoma. The engines are durable and considered relatively robust for the time.
Toyota’s original Land Cruiser was the company’s version of a Jeep that could go anywhere. In its time it was highly rated and collected, which led the Japanese juggernaut to bring back an updated SUV in 2007 called the FJ Cruiser. The retro-styled vehicle was again a go anywhere machine powered by a 4.0L V6 (1GR-FE) used in the Tacoma. The engines are durable and considered relatively robust for the time.
Long-Life Coolants Explained
Different types of coolants cover a range of applications from diesel to domestic, Asian and European vehicles. Each one is formulated to a specific manufacturer’s specifications to keep their engines at an optimal temperature. But, changes to the old one-size-fits-all formula has led to confusion for consumers and even some technicians.

VIDEO: Engine Efficiency Brings More Hoses
Andrew Markel discusses hoses and the necessity for several of them to route fluids to all parts of the vehicle due to the growing efficiency of engines. Sponsored by Dayco.

Diagnosing Intelligent Cooling Systems
The majority of cooling systems on the roads react to what is happening inside the combustion chamber. After the engine is stressed, the heat causes the thermostat to open. Increases in temperatures will also cause the cooling fans to come on. The heat carried by the coolant is the trigger for operation of the fans and thermostat.

Modern Cooling System Design: It’s Not About Temperature; It’s About Powertrain
Given the advanced state of internal combustion engine technology, some recent cooling system innovations will actually increase engine torque and fuel economy while reducing exhaust emissions. Let me simplify that idea: new cooling system technology will make engines run better and cleaner. So, let’s get on the same page by reviewing some basics.

Other Posts
Why Does Engine Coolant Need Replacement?
Two specifications can be used to justify replacement — the condition of the additive package & the freezing point.
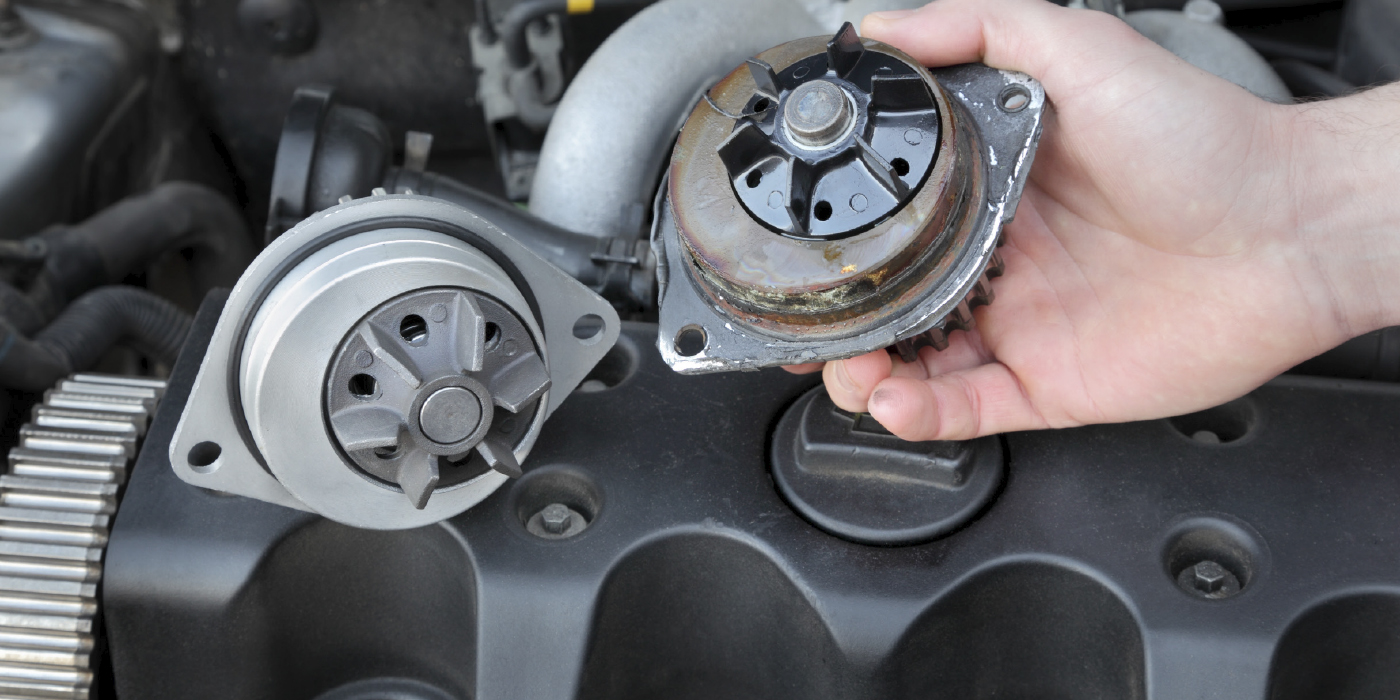

Solving Intermittent Overheating
New cooling systems anticipate and influence changes in coolant temperature.
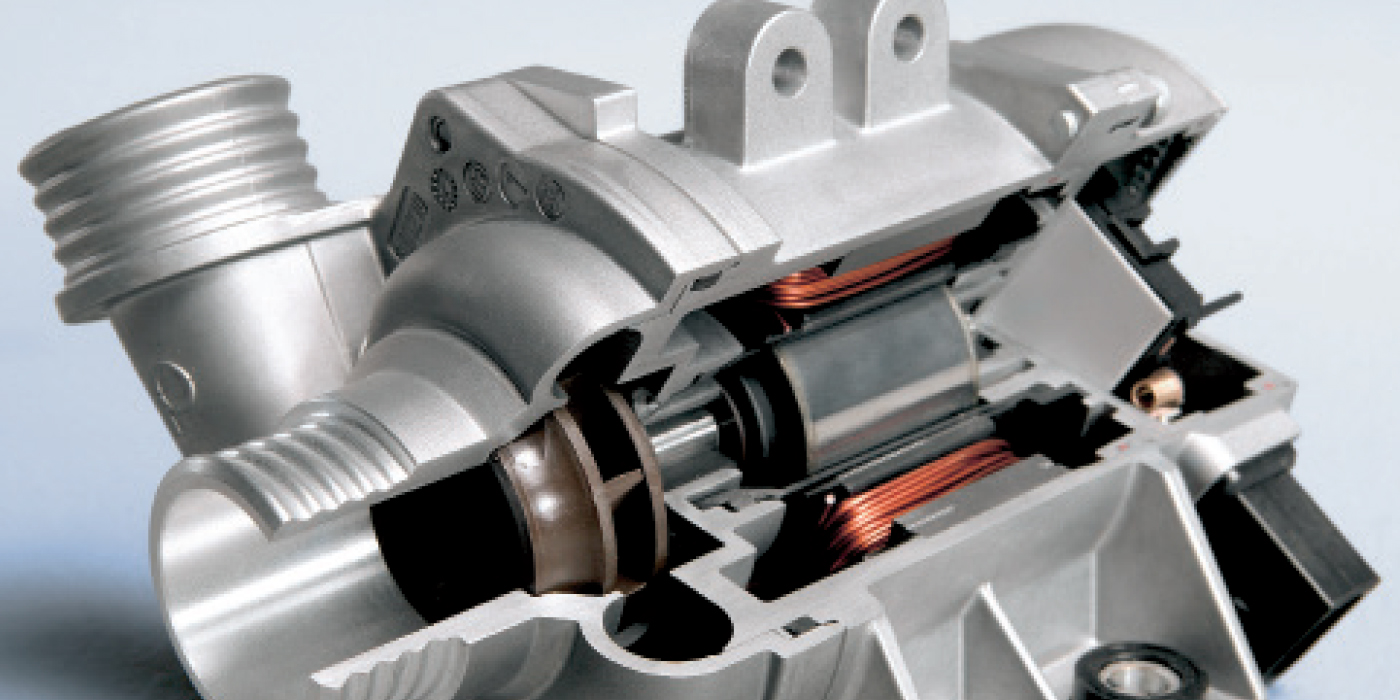
Auxiliary Coolant Pumps
Don’t be fooled into thinking that these pumps will go away with the surge in hybrid and electric vehicle production.
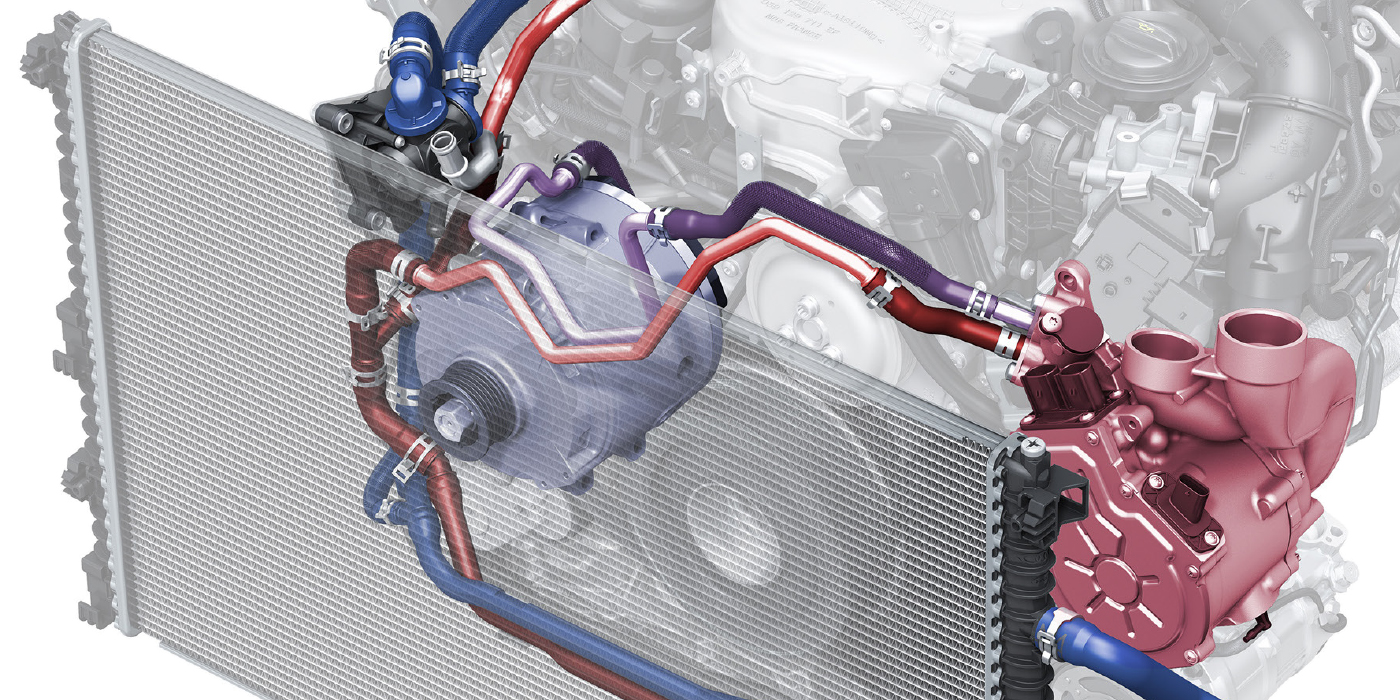
Solving No Heat Complaints
Here are 10 guidelines for making sure a customers heat functions.






