these engines are interference engines with tight valve-to-piston clearances, so accurate cam timing is absolutely essential. The cam phaser on the front of the exhaust cam can retard exhaust valve timing from 0 to 25 degrees.
At idle, it is in the fully advanced position, and must be installed in this position to prevent the exhaust valves from hitting the pistons.
Changing the timing chain requires using a J44221 Cam Holding Tool (or equivalent) to keep the cams from moving when the chain is taken off.
The basic procedure is to remove the intake and exhaust cam position sensors, remove the front cover, rotate the crankshaft so number one piston is at TDC (top dead center), install the cam holding tool, then release tension on the timing chain by moving the tensioner shoe in.
 Use a tee to lock the tensioner in place, remove the cam phaser from the exhaust cam, then the sprocket from the intake cam, and finally the crank sprocket (all three sprockets should be replaced along with the timing chain).
Use a tee to lock the tensioner in place, remove the cam phaser from the exhaust cam, then the sprocket from the intake cam, and finally the crank sprocket (all three sprockets should be replaced along with the timing chain).
Every seventh link on the timing chain is darkened to aid in aligning the timing marks. After installing a new sprocket on the crankshaft, align one of these marks on the chain with the mark on the sprocket (which should be at the 5 o’clock position).
Align another dark link on the chain with the timing mark on the intake cam sprocket (1 o’clock position). Then install the cam phaser on the exhaust cam. T
he word “Delphi” should be level and parallel to the seam on the head, and the cam phaser must be in the fully advanced position. Align another dark link on the chain with the mark on the exhaust sprocket (which should be at the 11 o’clock position).
Remove the tee from the chain tensioner and make sure all of the timing marks are correctly aligned.
 Sensors
Sensors
These engines use a single magnetic crank sensor mounted in the block near the back of the engine, and a pair of camshaft sensors mounted in the front of the cylinder head to monitor crankshaft position and cam phasing.
If the crank sensor, either cam sensor or the PCM (Powertrain Control Module) on one of these applications has to be replaced for any reason, you must perform a CKP System Variation Learn Procedure using a Tech 1 or similar scan tool.
It’s the same procedure that’s required on many other GM engines so the PCM can learn the relative positions of the crank and cam sensors. If the procedure is not performed, the engine may not run properly or may not start.
The 2004 version of the 3500 came with two knock sensors. Knock protection was deemed critical on these engines because of their high compression ratio (10:1) and use of regular 87 octane fuel.
But improved PCM programming allowed GM to discontinue the second knock sensor in 2005. The remaining knock sensor is located on the left side of the engine between cylinders number 3 and 4.
 Inputs for fuel management are provided by a mass airflow (MAF) sensor mounted ahead of the electronic throttle body, a manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor on the intake manifold and a throttle position (TPS) sensor on the throttle.
Inputs for fuel management are provided by a mass airflow (MAF) sensor mounted ahead of the electronic throttle body, a manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor on the intake manifold and a throttle position (TPS) sensor on the throttle.
A buildup of dirt or fuel varnish on the MAF sensor may cause lean codes to set. Cleaning the MAF sensor with aerosol electronics cleaner can often correct this kind of problem. Idle problems caused by dirt or fuel varnish in the throttle body can be removed with throttle cleaner.
Maintenance
Starting in 2004, the recommended oil for the 2800, 3500 and 4200 engines is 5W-30 that meets GF-4 specifications. The crankcase oil capacity is six quarts.
GM uses its Oil Life Monitor System on these applications to indicate when it’s time to change the oil.
Based on vehicle usage, temperature, run time, vehicle speed, load and so on, the estimated oil change interval may vary from as little as 3,000 miles to as much as 15,000 miles.
We think pushing the oil change interval much beyond 7,500 miles with any oil other than a top quality full synthetic is asking for trouble.
The Chevy Colorado and GMC Canyon both have conventional fuel filters located outside the fuel tank that can be replaced on an “as needed” basis. GM offers no recommended service interval for the filter.
The serpentine belt likewise has no recommended replacement interval. Most belts are good for 100,000 miles, but need to be inspected to check for wear and proper tension. Belt noise and/or accelerated wear can be caused by pulley misalignment. GM TSB 08-06-01-006A says to use a laser pulley alignment checker if you suspect belt noise or wear may be due to misalignment of the power steering pump pulley.
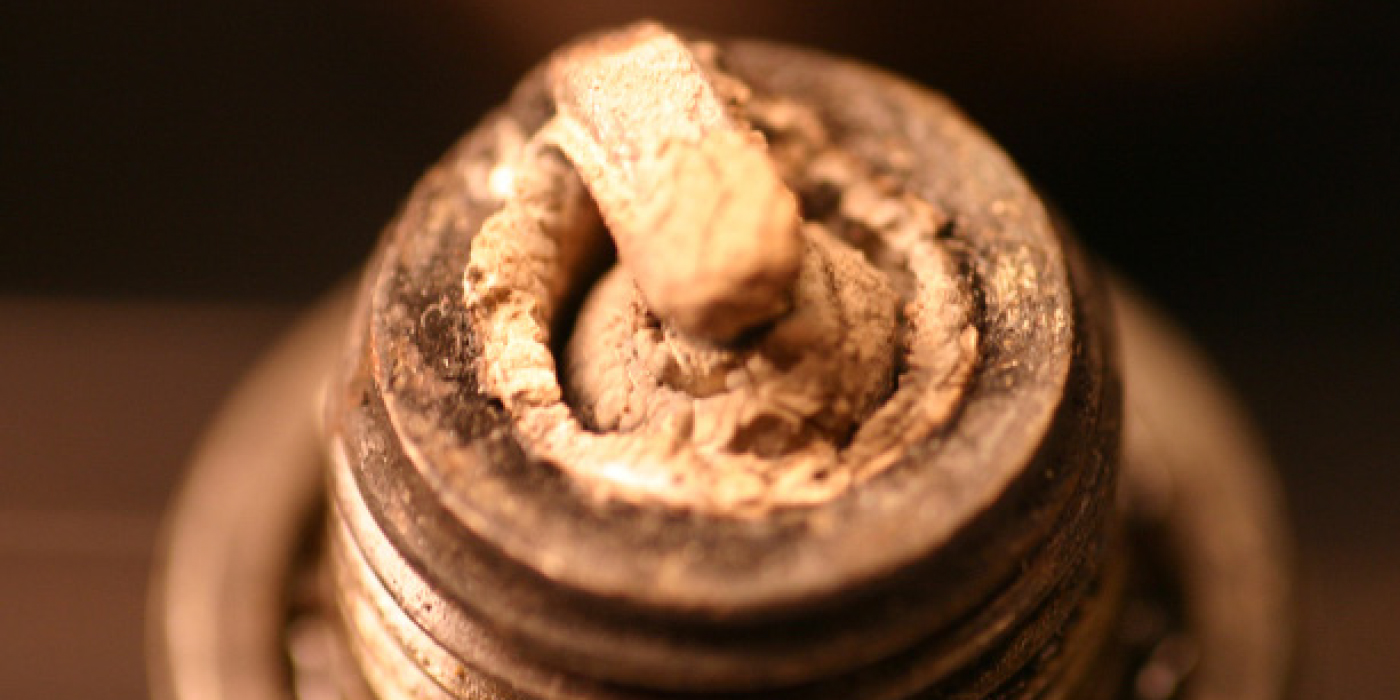
The original equipment spark plugs have a 100,000-mile replacement interval (gap is 0.042”).
Inspect the engine air filter every 15,000 miles and replace as needed. The Chevy Colorado and GMC Canyon are not equipped with a cabin air filter.
The Dex-Cool coolant is a five-year/150,000-mile coolant. Most trucks will reach five years before the odometer hits 150,000 miles, so recommend changing the coolant after five years of service. Waiting longer increases the risk of damaging coolant corrosion and expensive cooling system repairs.