 Fuel System
Fuel System
Fuel problems on these engines are no different than those on any other engine. The injectors can get gummed up from burning gasoline that contains low levels of detergents. GM recommends using “top tier” gasoline that contains higher levels of detergent to keep the injectors clean. This is especially important for engines that are used for short-trip driving and frequent stop/starts, or prolonged idling.
If you have a no-start condition because there’s no fuel, the first check would be fuel pressure. On a Series II 3800 engine, fuel pressure should be 48 to 55 psi with the key on and engine off. GM does not provide a fuel volume test spec but, as a rule, a good pump should deliver about a quart of fuel in 30 seconds.
On a Series III 3800 engine in a Buick Lucerne, the returnless EFI system has the fuel pressure regulator mounted in the fuel tank with the pump instead of on the fuel rail. There is no fuel return line from the engine back to the tank. The fuel pressure on these engines should be 56 to 62 psi with the key on and engine off.
If you have a cylinder misfire, but have a good spark and compression, the fuel injector is probably clogged or dead. The 3800 engine uses high-impedance 12 ohm injectors, and the test spec is 11.80 to 12.60 ohms, so check the resistance across the injector terminals if you suspect a bad injector. If an injector reads outside this range, even a few tenths of an ohm, it may be enough of a difference to cause a problem.
If an injector reads good, use a noid light to check for an injector pulse from the PCM injector driver circuit. No pulse? The problem could be a bad injector driver circuit in the PCM, or no input from the camshaft position sensor (CMP), which the PCM uses to fire the injectors. The CMP sensor is mounted on the front timing cover.
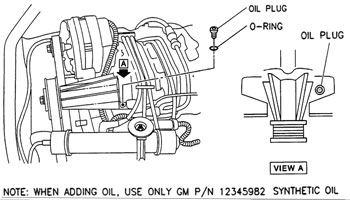
On the supercharged 3800 engines, one item that is often overlooked is the oil reservoir for the supercharger. The oil reservoir provides oil for the rotor gears and bearings. If the oil runs low, the supercharger may seize. The oil level can be checked by removing the small drain plug located near the supercharger input shaft.
Caution: Do not open the drain plug when the engine is hot. Let it cool at least two hours so hot oil does not spray out of the reservoir. The oil level should be at the bottom of the inspection threads in the drain plug hole. If the reservoir is low, top it off with GM Supercharger oil P/N 12345982 (a special 5W-30 synthetic oil).
Supercharger boost is controlled by the PCM via a boost solenoid, and a vacuum-operated bypass valve, which regulates the amount of boost pressure according to intake vacuum (engine load). At idle and low engine loads, the bypass valve is open allowing air to bypass the supercharger. When the driver steps on it and intake vacuum drops, the bypass valve closes allowing the supercharger to deliver boost pressure. The PCM usually commands the boost solenoid at 100% duty cycle (on all the time), unless the vehicle is shifted into reverse, in which case it kills the boost pressure. If there is a problem with the boost solenoid, the engine may not receive normal boost when accelerating, causing a noticeable loss of power.













