Engine oil can be one of the most confusing and controversial products to select for a domestic vehicle. Engines with turbochargers, direct fuel injection and advanced internal components are forcing OEMs to rewrite oil specification.
These specifications are typically listed on the back of the bottle, on a product data sheet or the oil manufacturer’s website. In the case of some 5W30 oils, the bottle might not be able to hold all of the OEM specification the oil meets.
If you are looking for the correct oil specifications, some OEMs have included the information on their service information websites, or can be accessed through the “Owner’s” website that contains the owner’s manual.
GM Dexos Motor Oil Specifications
GM Dexos1-approved oils are recommended for all 2011 and newer GM vehicles with gasoline engines. Dexos1-approved oils are designed to work with the oil life system in GM vehicles. These oils are designed to reduce carbon deposits in the combustion chamber that can occur in some Ecotec engines.
GM revised Dexos1 specifications in 2015. Oils that meet this standard are often labeled Dexos1 Gen2, but many oils do not include the Gen2 on the label due to confusion with Dexos2 oils for diesel engines. Dexos1 Gen2 oils are formulated to reduce incidents of low-speed pre-ignition (LSPI).
Chrysler
Chrysler has three proprietary oil specifications for gasoline engines. They call these standards Chrysler Material Standards or MS specifications.
The first specification is MS-6395 that covers 5W-20, 5W-30, 5W-20 and 10W-30 oils. This standard follows the API SM GF-5 standards with a few extra tests for Chrysler engines. Most GF-5 approved oils meet these standards. The MS-10850 specification is for SRT8, SRT10 and SRT6 engines that call for 5W-40 oil. MS-12633 approved oils are for SRT engines that specify 0W-40 oil.

Ford
Ford oil specification can get confusing because there are so many specifications or WSSs. In North America, Ford structures oil specifications around the weight of the oil. The WSS specifications for gasoline engine oils were last updated in 2012. WSS-M2C945-A and WSS-M2C946-A 5W-30 oils typically meet API SN GF-5 standards with a few extra tests performed on Ford engines like the EcoBoost. These standards cover 5W-20 and 5W-30 oils. WSS-M2C947-A approved oils are for 0W-30 oils and are typically synthetic.
Ford recommends that if Motorcraft oil is not available, to use motor oils of the recommended viscosity grade that meet API SN requirements and display the API Certification Mark for gasoline engines. Do not use oil labeled with API SN service category unless the label also displays the API certification mark.
ILSAC Rating
The International Lubricants Standardization and Approval Committee (ILSAC) is the gatekeeper of oil standards. ILSAC GF -1,-2,-3,-4 and -5 are specifications for multi-grade oils that were first rolled out in 1992. GF-5 certified oils are compatible with previous GF-1 to GF-4 oils of comparable weights.
The GF-5 requirements were rolled out in 2010 and will be replaced by GF-6 in the future. They were designed to provide improved high-temperature deposit protection for pistons and turbochargers; more stringent sludge control; improved fuel economy; enhanced emissions control system compatibility; seal compatibility and protection of engines operating on ethanol-containing fuels up to E85.
Higher viscosity oils cannot meet an ILSAC GF-5 rating. The GF-5 rating corresponds closely to the API SN rating.
The increasing impact of LSPI has prompted OEMs to request immediate implementation of a supplement to ILSAC GF-5 to protect turbo gasoline direct-injected engines from catastrophic damage. The API SN Plus supplement is not a new category and will be available alongside the current API SN and ILSAC GF-5 categories.
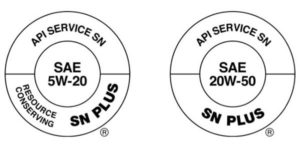 The SN Plus designation will appear in API donut symbols sometime in the second quarter of 2018 and will be a voluntary category alongside current API SN and ILSAC GF-5. Many OEMs like General Motors have tackled the issue by specifying its proprietary GM dexos1 Gen 2 specification. In the future, the GF-6 standard will also address the LSPI problem along with chain wear problems.
The SN Plus designation will appear in API donut symbols sometime in the second quarter of 2018 and will be a voluntary category alongside current API SN and ILSAC GF-5. Many OEMs like General Motors have tackled the issue by specifying its proprietary GM dexos1 Gen 2 specification. In the future, the GF-6 standard will also address the LSPI problem along with chain wear problems.
SIDEBAR
GF-6A AND GF-6B
The proposed ILSAC GF-6A specification would replace the current ILSAC GF-5 specification, represented by the Starburst/Certification Trademark, and would provide a new performance level of an engine oil for spark-ignited internal combustion engines.
GF-6 will be split into two categories: GF-6A and GF-6B. GF-6A will address traditional viscosities and will be backward compatible for GF-5 oils. For shops, this means that your oil options will be improving in the very near future.
GF-6A oils meet or exceed the GF-5 specifications in every category, so there won’t be a need to keep a supply of GF-5 oils for older vehicles.
The proposed ILSAC GF-6B oils would provide the same performance as GF-6A, but with the added aim of lower HTHS to deliver potential further fuel economy benefits. This offers the possibility of potential GF-6B oils operating at viscosity ranges of less than 0W-20 once these new viscosity grades are defined and accepted by SAE.
GF-6B will represent viscosity grades SAE 0W-16 and lower. These new lower viscosities will give OEMs another tool to improve fuel economy.
GF-6 oils also have lower concentrations of additives that can damage catalytic converters. The finalization of the GF-6 standards paves the way for OEMs to implement the use of these oils at the factory. Also, most OEMs will not specify a fluid if it is not available to consumers at the retail level.
















